Andrei Costin (Eurecom), Apostolis Zarras (Ruhr-University Bochum), Aurelien Francillon (Eurecom) performed a research tht unveils the vulnerability of many COTS.
Andrei Costin (Eurecom), Apostolis Zarras (Ruhr-University Bochum), Aurelien Francillon (Eurecom) performed a research tht unveils the vulnerability of many COTS.
A prevalent number of the future hacks that await us involve the Internet of Things.
One of the studies, carried out by a group of European researchers that focused on IoT, has verified that the web interfaces for user administration of commercial, mass-produced embedded devices such as routers, VoIP phones, and IP/CCTV cameras, are quite vulnerable to attacks.
The experts tested embedded firmware images and web interfaces for existing vulnerabilities.
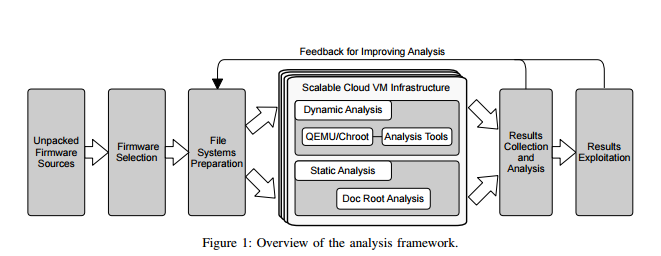
In their paper, titled ‘Automated Dynamic Firmware Analysis at Scale: A Case Study on Embedded Web Interfaces’, the three researchers – Andrei Costin, Apostolis Zarras and Aurelien Francillon – present the first fully automated framework via dynamic firmware analysis to achieve automated bug disclosure within embedded firmware images. The scientists have also applied framework to research the security of embedded web interfaces present in Commercial Off-The-Shelf devices (COTS) like routers, DSL/cable modems, VoIP phones, IP/CCTV cameras.
Unique Framework Not Dependable on Vendor, Device or Architecture
A new methodology has been introduced by the expert team that doesn’t depend on the vendor, device or architecture. Their framework consists of full system emulation to accomplish the execution of firmware images in a software-only environment (without having to involve physical embedded devices).
The researchers didn’t want to use physical devices owned by users because this practice would be considered ethically wrong and even illegal. The researchers also analyzed the web interfaces within the firmware via static and dynamic tools. What is crucial about their study and its methodology is it is quite unique in its nature.
Some statistics
During the case study, 1925 firmware images from 54 vendors were tested and 9271 vulnerabilities were disclosed in 185 of them. Approximately 8 percent of the embedded firmware images contained PHP code in their server-side, and had at least one flaw. The firmware images represented a total of 9046 security-related problems such as:
- Cross-site scripting;
- File manipulation;
- Command injection flaws.
Dynamic Security Testing Done on 246 Web Interfaces
Here are the results:
- 21 firmware packages were claimed vulnerable to command injection.
- 32 were deemed by XSS flaws.
- 37 were vulnerable to CSRF (cross- site request forgery) attacks.
Unfortunately, as pointed out by the research team, a prevalent number of the manufacturers are not interested in investing time and means in improving their devices’ security. Nonetheless, at some point, vendors must focus on all security-related issues in their products. With the growth in popularity of Internet of Things, malicious coders will surely target vulnerable systems and devices.
The good news is the researchers don’t plan to give up their vulnerability-unveiling activities:
‘We plan to continue collecting new data and extend our analysis to all the firmware images we can access in the future. Further we want to extend our system with more sophisticated dynamic analysis techniques that allow a more in-depth study of vulnerabilities within each firmware image.’