FortiGuard Labs has detected a new variant of the Snake Keylogger (also known as 404 Keylogger) using the advanced features of FortiSandbox v5.0 (FSAv5).
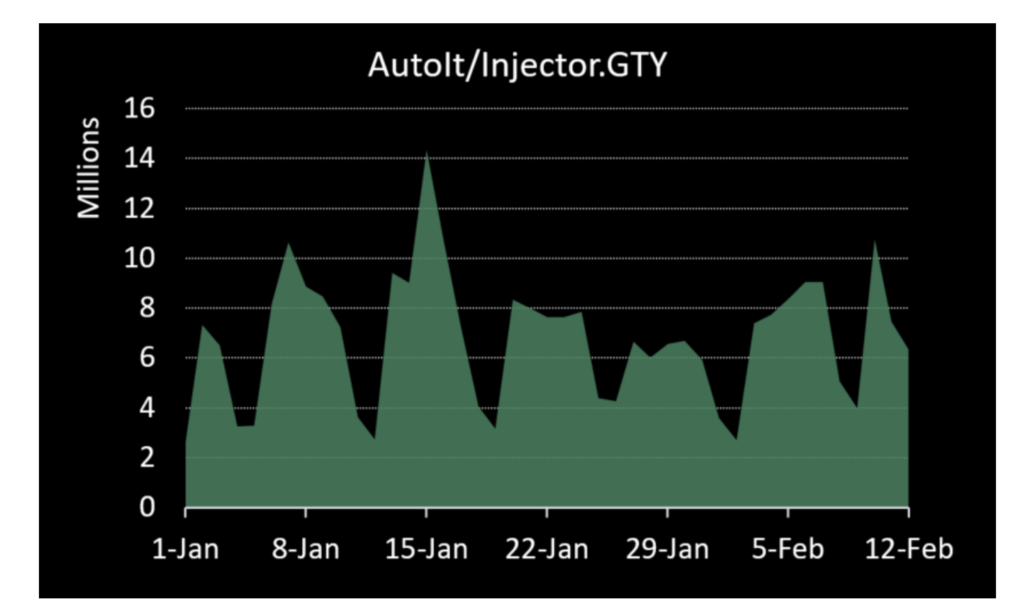
This new strain, identified as AutoIt/Injector.GTY!tr, has triggered over 280 million blocked infection attempts worldwide. The highest concentrations of attacks have been reported in China, Turkey, Indonesia, Taiwan, and Spain, indicating a significant global impact.
How Snake Keylogger Steals User Data
This malware is primarily delivered through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links. Once executed, it starts stealing sensitive information from popular web browsers such as Chrome, Edge, and Firefox. Some of the key capabilities include:
- Keylogging – Captures every keystroke, including passwords and financial data.
- Credential Theft – Extracts saved login credentials from browsers.
- Clipboard Monitoring – Records copied text, including sensitive information.
- Data Exfiltration – Sends stolen data to hackers via SMTP (email) and Telegram bots.
Advanced Evasion Techniques
The latest variant uses AutoIt scripting to deliver and execute its payload. By embedding the malware in an AutoIt-compiled binary, it evades traditional detection tools. This allows it to bypass static analysis and appear as legitimate automation software.
How the Malware Maintains Persistence
Snake Keylogger ensures continued access to infected systems by:
- Dropping a copy of itself as “ageless.exe” in the %Local_AppData%\supergroup folder.
- Placing “ageless.vbs” in the Windows Startup folder to launch automatically on reboot.
- Injecting its payload into a legitimate .NET process (regsvcs.exe) using process hollowing, making detection difficult.
Tracking Victims and Geolocation
Snake Keylogger also collects information on its victims by retrieving their IP address and geolocation using online services like checkip.dyndns.org. This helps attackers monitor their infected machines more effectively.
The new Snake Keylogger variant continues to pose a serious cybersecurity risk worldwide. Its ability to steal data and evade detection makes it a dangerous threat which calls for adequate protection mechanisms.


