The Astaroth Trojan is a dangerous weapon used against computer users worldwide. It infects mainly via infected software installers. Our article gives an overview of its behavior according to the collected samples and available reports, also it may be helpful in attempting to remove the virus.

Threat Summary
| Name | Astaroth Trojan |
| Type | Trojan |
| Short Description | The Astaroth Trojan is a computer virus that is designed to silently infiltrate computer systems. |
| Symptoms | The victims may not experience any apparent symptoms of infection. |
| Distribution Method | Software Vulnerabilities, Freeware Installations, Bundled Packages, Scripts and others. |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
| User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss Astaroth Trojan. |

Astaroth Trojan – Update May 2020
The newest strategy surrounding the distribution of Astaroth Trojan samples includes a twist in the hacker’s strategy. In May 2020 a new sample has been captured by security analysts documenting new features and a new infection strategy.
A much improved security bypass feature is implemented — it will actively scan the contaminated system for installed programs that can interfere with it and disable them. This also works against sandbox environments and virtual machine hosts.
The newest strategy used to spread Astaroth involves the creation of YouTube channels that contain a link to the command and control servers of the Trojan. This can be done either in an automated manner or by hacking already existing accounts. Phishing email messages continue to be sent to the target users. A link leading to the Trojan is placed in the contents, as soon as the users click on them the download command will be issued leading to the infection.
We remind our readers that the Astaroth Trojan is distributed in a several stages manner — the infection will not start immediately. A first stage installation involves the activation of a complex deployment sequence.
When the victims click on the malware URl this will activate an iFrame script leading to a ZIP file download hosted on a Google-owned folder. The hackers have created accounts in order to use the free cloud file hosting services such as Google Drive.
A LNK file inside it will retrieve a JavaScript file that will start the actual deployment sequence. A follow-up JavaScript will retrieve a Bitsadmin service that will download from hacker-controlled servers the 3rd stage Trojan DLL files — they are used to control the malicious processes. Using a function in the operating system these DLL files will be loaded into memory and the Astaroth Trojan will start to function.
Before issuing any further actions the security bypass feature will be run in order to disable the active security services. Only when this stage has completed the other malware actions will take place.
At the moment the active campaigns appear to target users in Brazil, like other contemporary infections the phishing messages are themed with COVID-19 related notifications.
Astaroth Trojan Further information
Some of the new samples associated with the Astaroth Trojan have been uncovered by security researchers. Their method of distribution is through the use of phishing tactics however instead of relying on the traditional mechanisms of orchestrating bulk email campaigns or websites, they choose to spread the threat via social network profiles. They are either stolen or automatically generated and utilize both Facebook and YouTube. They are chosen because these sites are one of the most active communities worldwide and the hackers can reach a wide audience.
The captured attacks appear to be localized to Brazilian users and the contacted configuration pattern appears to be very complex. The initial payload dropper will interact with the Windows Management Instrumentation Console (WMIC) service of the Microsoft Windows operating system in order to retrieve its components.
The phishing tactics also make use of email messages that are sent as a supportive measure:
- Faux Invoice
- Faux Show Ticket
- Fake Civil Lawsuit Notification
When the users interact with the emails or the social network they will lead to a download of a .ZIP archive containing a .LNK file. When opened it will execute a JavaScript code leading to the Astaroth Trojan infection.

Astaroth Trojan – Distribution Methods
The Astaroth Trojan is being spread in an ongoing campaign, the reports indicate that the majority of affected victims are from Brazil and Europe. This is a very dangerous threat as it uses the method of exploiting vulnerabilities in the machines, specifically a weakness in a popular anti-virus product (Avast!). The mechanism is unusual — the hackers abuse the legitimate Windows Service called BITSAdmin which is used to download, upload and manage jobs, part of the “Background Intelligent Transfer Service” feature available for Windows developers. Instead of programming it for the usual tasks it is programmed to download malware threats, in this case the Astaroth Trojan.
Email Phishing messages that are sent in a SPAM-like manner are sent to the targets by impersonating Microsoft or other trusted vendors. They have archive attachments in the .7zip format. When opened inside there will be a .lnk file which when executed will spawn the relevant wmic.exe process. This will lead to an attack that is known as a “XSL Script Processing Attack”.
In practice the hackers abuse a trusted binary which will run the script, thus hijacking the Avast anti-virus process. According to the security reports this is not an injection or a privilege escalation. Instead the avast binaries are programmed to run the malware files. The avast engine itself contains a self-protection mechanism which does not permit any abuse of the application itself. The vendor is currently patching the software.
The identity of the criminals is not known at the moment, an investigation is ongoing into the possible origins of the threat. We anticipate that this payload-based infection mechanism can be used with other similar methods:
- Infected Documents — The criminals the virus installation script in documents across all popular variants: text documents, spreadsheets, databases and presentations. When they are opened a macros execution prompt will appear asking the victim users to enable the scripts, the quoted reason is that this is required in order to correctly view the files.
- Infected Application Installers — The criminals can take the installers of popular applications and modify them to include the Astaroth Trojan. This is done by acquiring the legitimate setup files from their official sources and inserting the appropriate virus installation code. Usually applications that are frequently downloaded by end users: system utilities, creativity suites, productivity apps and etc.
- File-Sharing Networks — The files can be spread via peer-to-peer networks like BitTorrent which are popular for distributing both legitimate and pirate content.

Astaroth Trojan – Detailed Description
As soon as the Astaroth Trojan infection is triggered a series of dangerous actions will occur. The relevant BITSAdmin utility will be programmed to download a malicious payload from a predefined hacker-controlled server. The code analysis reveals that the the malware is obfuscated as image files or data without a specific extension. This is done in order to evade regular anti-virus scans.
We anticipate that future versions may include a standalone security bypass which can locate security software that can potentially block the virus execution: anti-virus products, firewalls, intrusion detection systems and virtual machine hosts.
A dangerous component that is part of the Trojan’s code base is the information gathering module:
- Personal Information — The Trojan engine is capable of acquiring data that can be used to directly expose the identity of the victims by looking for strings such as a person’s real name, nicknames, interests, phone number, address and any stored account credentials. The collected information can be used for various crimes including financial abuse, identity theft and blackmail.
- Machine Information — The Trojan engine can create an identifier that is assigned to each compromised machine. It is done using an algoirthm that takes its input parameters from values such as the installed hardware parts list, user settings and certain operating system environment values.
The gathered information will then be sent to the criminal controllers via a network connection to their C&C servers. This allows them to take over control of the victim machines, files theft and to spy on the users. What’s more dangerous is that the Trojan can be programmed to interact with the Windows Volume Manager, thus giving it the ability to access removable storage devices and network shares.
Other malicious actions that can follow include the following:
- Persistent Installation — The Astaroth Trojan code will be launched every time the computer is powered on. This step in most of the cases will also disable access to the boot menu options thereby making most of the manual user removal guides useless.
- Windows Registry Changes — Modification to the Windows Registry values is a common action undertaken by many malware of this category. Changes to strings that are used by the operating system can cause overall performance degradation and stability issues. If any third-party applications or services values are changed then the accompanying programs may quit unexpectedly with errors.
- Additional Payload Delivery — The Trojan client can be programmed to download other threats to the infected computers.
- Data Removal — Important files can be deleted automatically as soon as the Astaroth Trojan infection is triggered. Common data that is to be removed includes System Restore Points, Shadow Volume Copies and Backups. Effective restore of the compromised computers is done by using a combination of an effective anti-spyware utility and a data recovery program.
Depending on the forthcoming versions and future attack campaign we might see a radically different Astaroth Trojan release in the near future.

Remove Astaroth Trojan Completely
To remove Astaroth Trojan manually from your computer, follow the step-by-step removal tutorial written down below. In case this manual removal does not get rid of the miner malware completely, you should search for and remove any leftover items with an advanced anti-malware tool. Such software can keep your computer secure in the future.
Preparation before removing Astaroth Trojan.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
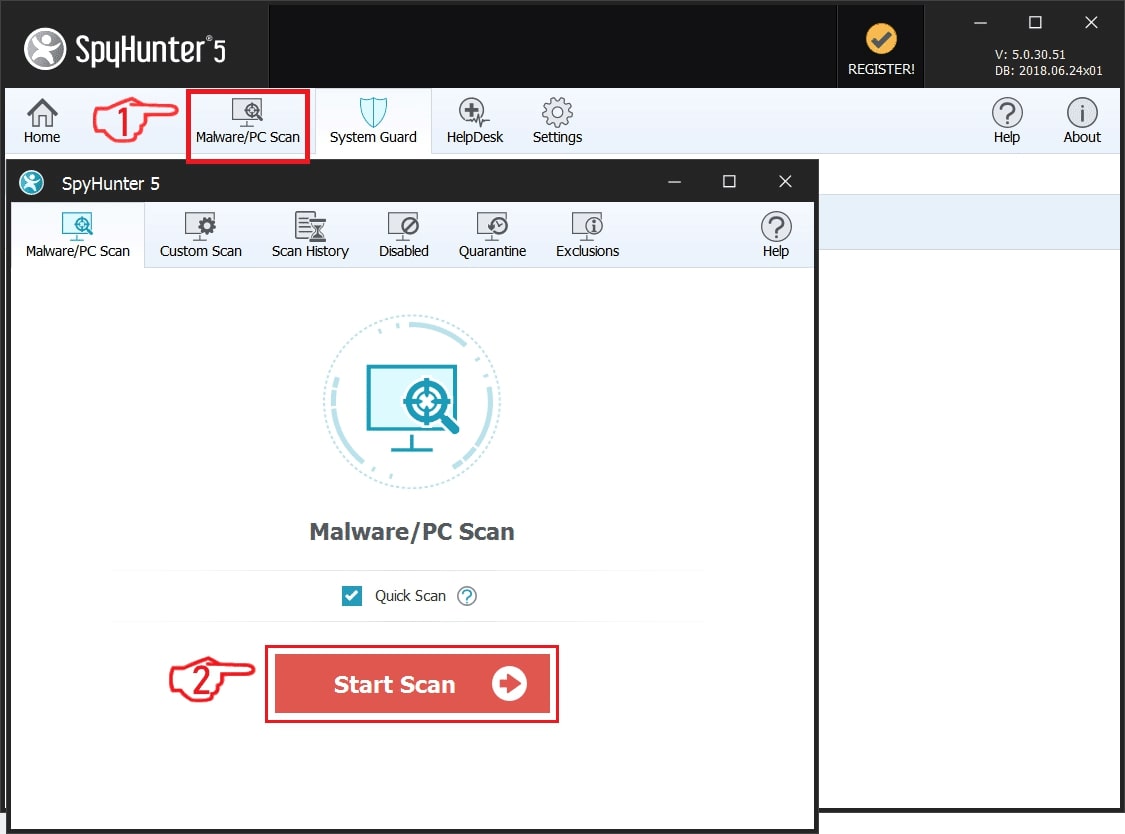
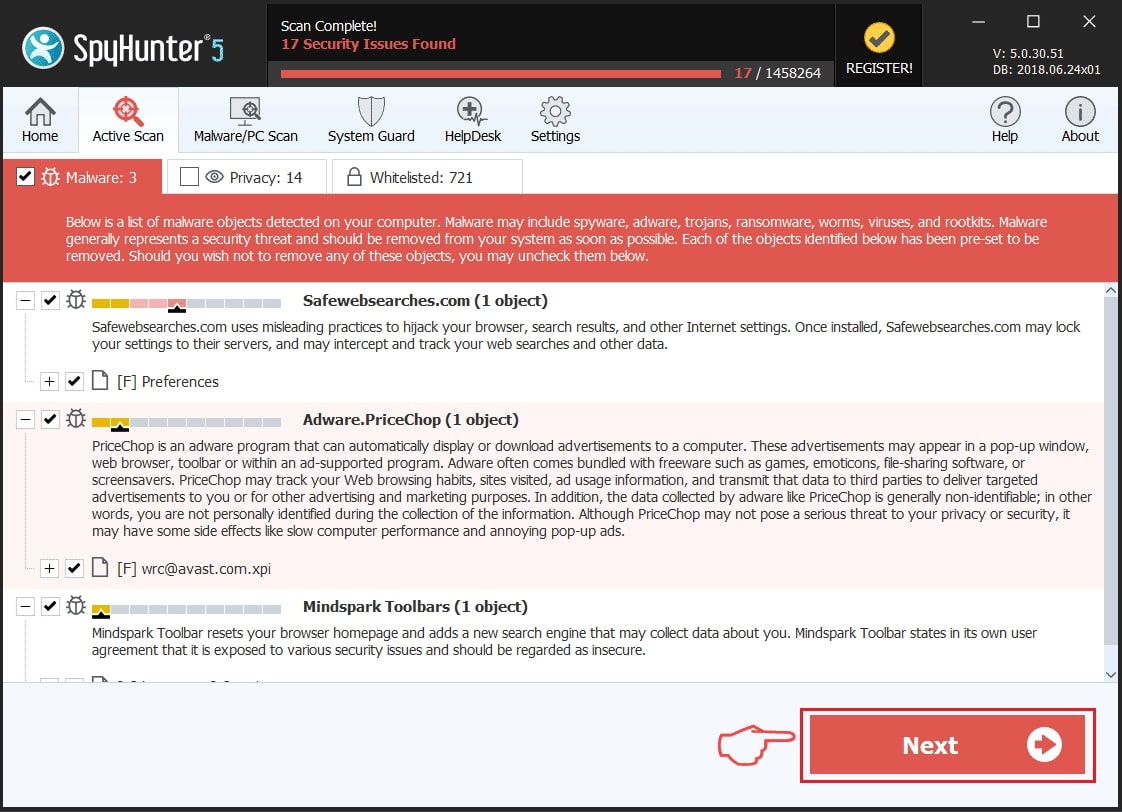
Step 1: Scan for Astaroth Trojan with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by Astaroth Trojan on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by Astaroth Trojan there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
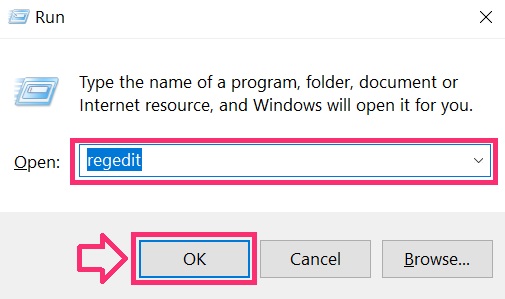
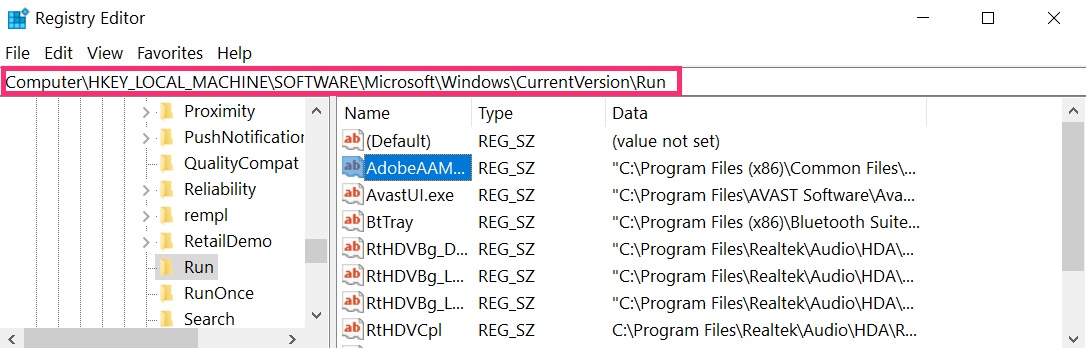
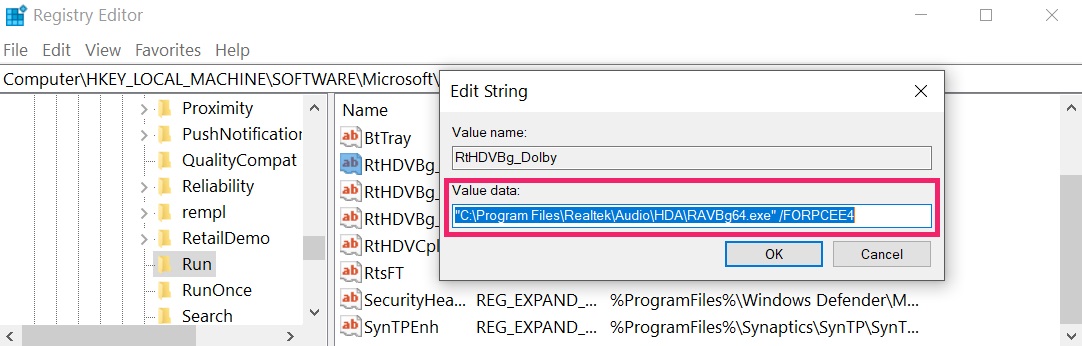 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by Astaroth Trojan on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
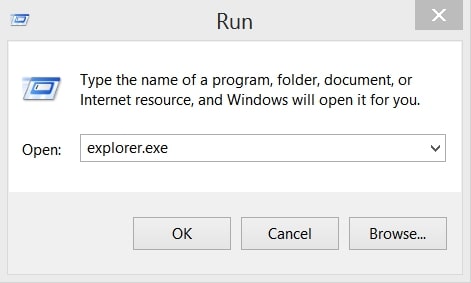
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
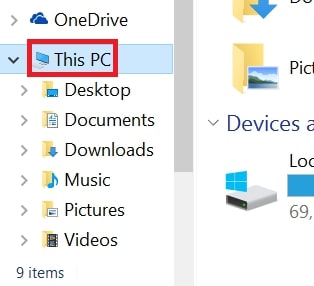
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
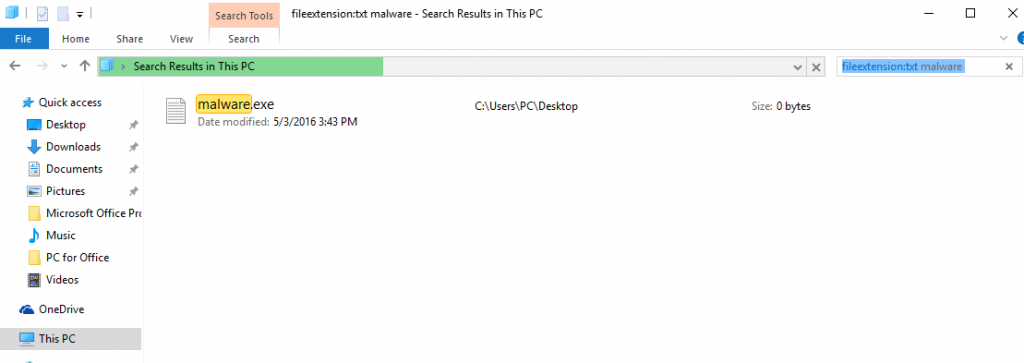
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
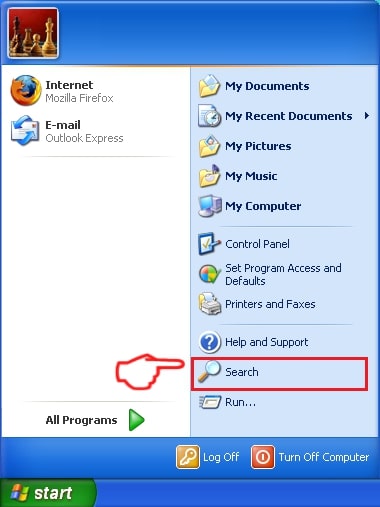
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
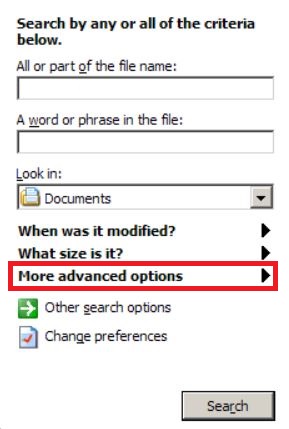
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
Astaroth Trojan FAQ
What Does Astaroth Trojan Trojan Do?
The Astaroth Trojan Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like Astaroth Trojan, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can Astaroth Trojan Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can Astaroth Trojan Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the Astaroth Trojan Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this Astaroth Trojan how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on Astaroth Trojan?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the Astaroth Trojan threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.



