In this Article you will find out how to remove Zeus Trojan virus and get rid of infected files. Zeus Trojan horse virus is spread on a large scale via the RIG Exploit Kit. That new version is dubbed “Chthonic” and it first emerged a couple of years ago, when it hit 150 banks all over the world. That activity is still ongoing, although the Trojan is also used for the distribution of ransomware. The malware has had many names over the years, and a very notable one is Zbot.

Threat Summary
| Name | ZeuS also known as Trojan.Zeus.C |
| Type | Trojan horse, Virus |
| Short Description | The Zeus Trojan horse virus is used in a variety of ways, which involve stealing of information, dispersing other malware online or as a payload dropper for ransomware and other malware. |
| Symptoms | An infection with the Zeus Virus might be silent, if it’s used as an infostealer or a loud one, if used to infect you with more malware. Your PC is quite likely to slow down either way, if it gets infected. |
| Distribution Method | Fake Tech Support, Spam Emails, Email Attachments, Executable Files |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss ZeuS. |
| Data Recovery Tool | Windows Data Recovery by Stellar Phoenix Notice! This product scans your drive sectors to recover lost files and it may not recover 100% of the encrypted files, but only few of them, depending on the situation and whether or not you have reformatted your drive. |

What Is a Zeus Trojan Virus?
Before revealing what the ZeuS Trojan virus is, you should first get familiar with what is a Trojan Virus. That is a combination of terms that are used to describe malware that is both a Trojan horse and a virus.
A Trojan horse is a piece of malware that injects itself into a computer device, under false pretenses, for instance presenting itself as the famous program Skype. You won’t be surprised to find out that the term Trojan horse in computing comes from the ancient Greek story of how Greek soldiers stealthily invaded Troy, by using a giant wooden horse, presented as a gift. A virus is a malicious program that once executed, will blatantly start replicating itself and infecting other programs by modifying them without the user’s permission.
Thus, a combination of the two types of malware described above, will be a malicious program that could do some or all of the following:
- pretends to be a known or a useful program, so you give it initial access
- uses other stealth tactics to sneak into your computer
- modifies/infects other programs and processes on your PC
- copies itself in different locations on your PC

Zeus Trojan Virus – Chronological Background
The Zeus Trojan Virus has spread over the whole world, and probably mostly known for delivering the infamous CryptoLocker encrypting virus. Below you will find a brief history of the malware in all its forms, since its first appearance to early 2017.
2007 – ZeuS and Its First Appearance
The year 2007 marked the beginning of the ZeuS malware that later became known as the Zeus Trojan horse. Back then it was used to steal information from the United States Department of Transportation. After that it began gathering momentum.
2009 – ZeuS Becomes Widespread
In 2009, Zeus became widespread for the first time, and it was seen as a major threat. It had compromised over 74.000 FTP accounts, on websites of big companies, such as the Bank of America, NASA, Monster.com, ABC, Oracle, Play.com, Cisco, Amazon, and BusinessWeek.
2010 – ZeuS The Worldwide Threat
2010 was the year in which the FBI announced that the Zeus virus was used to infect computers across the whole globe. In this form, Zeus was mainly used as a banking Trojan, to steal information by registering keystrokes made when using a browser or by form grabbing. Also, e-mails were used to reach individuals at municipalities and firms, so it can grab any data related to online banking accounts.
2013 – ZeuS The CryptoLocker Helper
Late 2011 set new heights for ZeuS as it led its code to be used for the creation of the Gameover ZeuS botnet. The botnet was less vulnerable to law enforcement operations, since it used an encrypted peer-to-peer system to communicate with its C2 (Command&Control) servers. Banking fraud was once again a primary aim for the Zeus malware family. In 2013, everything escalated when Gameover ZeuS was responsible for the mass distribution of [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/remove-cryptolocker-ransomware-virus/”] CryptoLocker Ransomware Virus around the World.
2015 – ZeuS Evolves Into Chthonic
2015 was also an emblematic year for Zeus as it evolved even further into Chthonic – a new variant discovered by malware researchers from Kaspersky. The same encryption technique is used by this variant as the “Zeus V2” and “Zeus AES” Trojans. [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/chthonic-a-new-version-of-the-zeus-banking-trojan-hits-150-banks-in-15-countries/”] Chthonic is known to have hit over 150 banks in 15 countries, back in 2015.
2016 – ZeuS and the Sphinx
In August 2015, the code of ZeuS was used to create a custom variant for it, called the [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/rio-2016-malware-sphinx-banking-trojan-targets-brazilian-banks/”] “Sphinx Banking Trojan”, sold on the black market for $500. The TOR network was used by it, to the fullest. To the last quarter of 2016, there were detections of the Trojan, proving that is still active. Mainly Brazilian banks were hit, including Boleto payment methods used in Brazil.
2017 – ZeuS Trojan
Zeus Virus – Technical Insight Update 2017 : ZeuS is still one of the biggest computer infections with many of its variants still spreading in 2017. Read below to find out more.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Ways of Distribution
The ZeuS malware had many forms of distribution over the years for the original and for later variants. One of the first ways for it to get onto your computer system, was with the help of redirects. Lots of redirects could be triggered by clicking something online as a link or a button. One of the redirects contains a script which downloads the malware. Another way to download is by clicking an advertisement that poses a question, and whether you click “Yes” or “No” will both result in getting the ZeuS Trojan Virus on your PC.
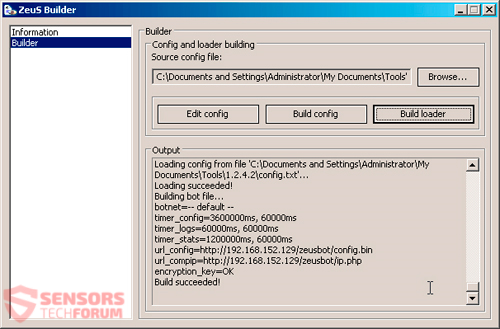
As the source code for Zeus was leaked in 2011, a toolkit builder was offered for free that looked like the following:
Tweaked versions of the toolkit and the malware in the form of either a Trojan horse or a Botnet soon followed. The abovementioned versions, featuring specific functions, are still sold to this day, with prices typically ranging from $700 to $15.000.
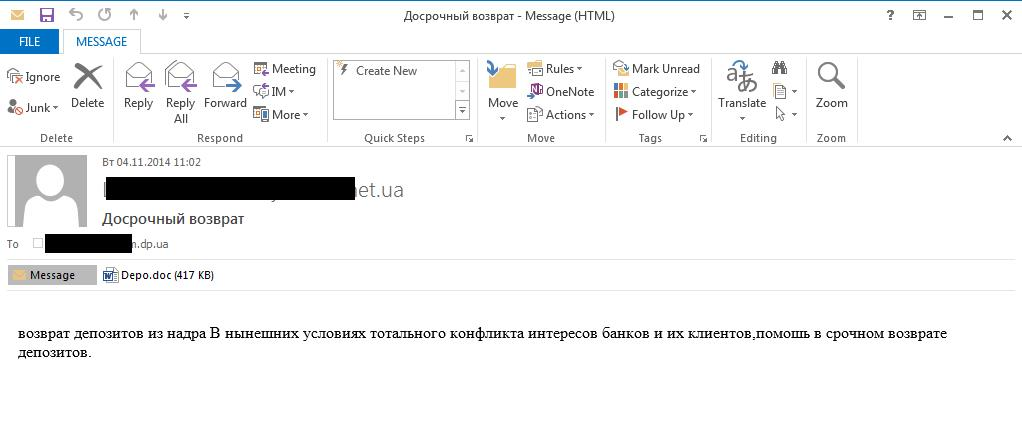
Spam e-mails with attachments were and still are a prominent way of distribution for ZeuS. Inside the attachment there is an executable file that is obfuscated and hidden as some sort of a document file, with an extension like .pdf or .doc as seen in the screenshot below:
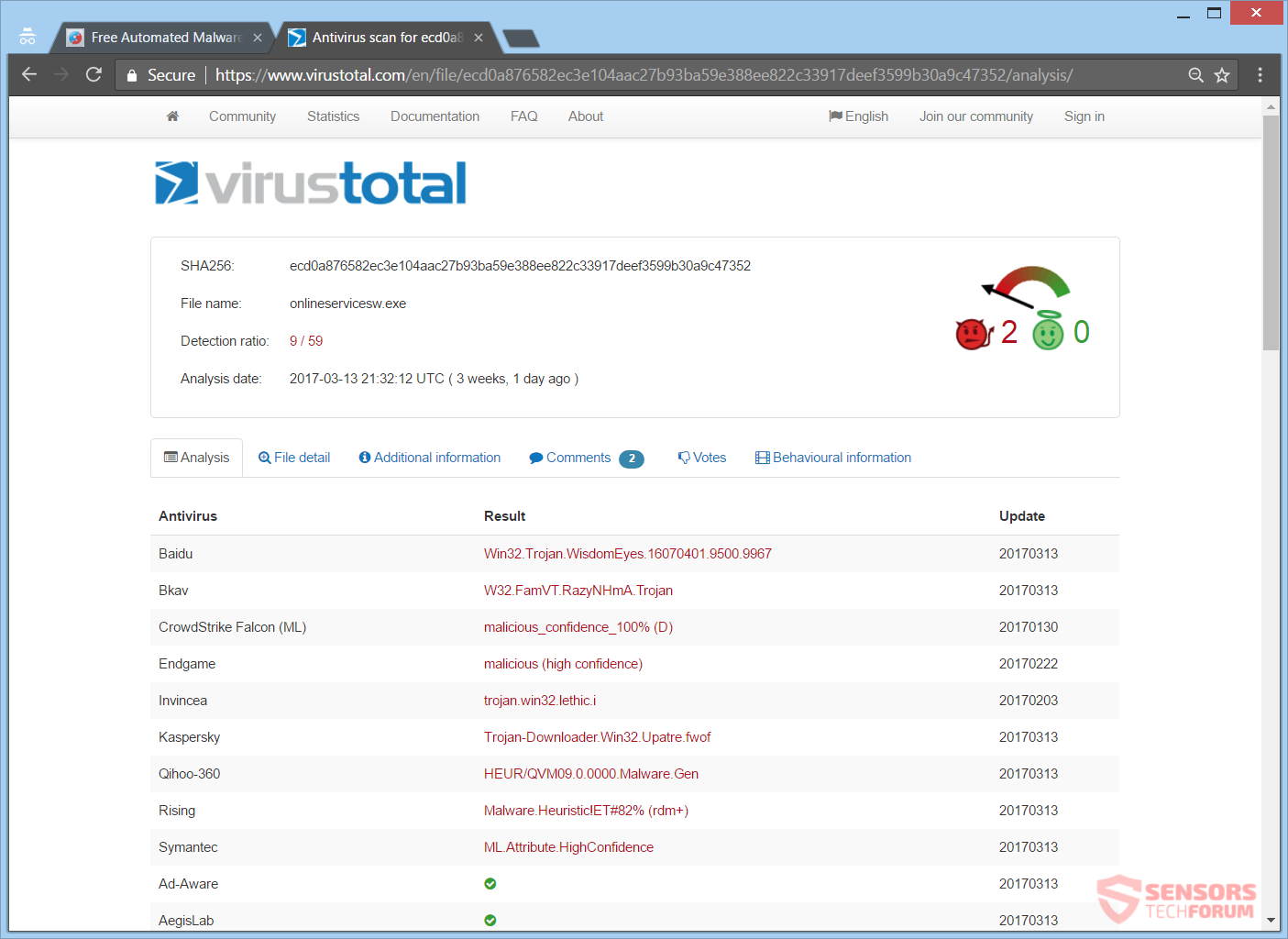
Another distribution way is with the ZeuS being sent worldwide with a malvertising chain. You can see the last reported such attack (April 2017) and the detections of security vendors for it on the VirusTotal service right here:
The last attack consisted of over 300 redirects, which results into loading a compromised site with the [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/new-version-rig-exploit-kit-developed/”] RIG Exploit Kit on it. Once you find yourself on the landing page, vulnerabilities based on Adobe’s “Flash” will be exploited when finally the payload will be dropped. The payload shown in the image above, is originally named “73mendjd.exe”.
As you can see the ways of distribution for Zeus can vary, and even other ones could be utilized as the malware continues to evolve.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Update November 2018
Zeus keeps being sold on Dark Net forums in some shape or form even in late 2018. Some Banking Trojans stem from the code of the original Zeus as you already may know. Some of the most common names given to the virus by various anti-malware companies are the following:
- Trojan-Spy:W32/Zbot
- PWS-Zbot
- Trojan-Spy.Win32.Zbot
- Trojan.Wsnpoem
- Troj/Zbot-LG
- Troj/Agent-MDL
- Troj/Zbot-LM
- Troj/TDSS-BY
- Troj/Zbot-LO
- Troj/Buzus-CE
- Sinowal.WUR Troj/QakBot-D
- Troj/Agent-MIR
- Troj/Qakbot-E
- Troj/QakBot-G
If you see any of the above listed names to pop up as a notification from your security software, make sure that it can remove it. Otherwise, change your tool immediately.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Update November 2017
In November the [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/panda-zeus-trojan-black-hat-seo/”] Panda ZeuS Trojan horse returns with the help of black-hat SEO and malvertising techniques instead of phishing and spam campaigns. These techniques are new for the distribution of malware overall. The attackers hacked websites and used a network of spam botnets to boost their SEO rating of other sites in a black-hat way.
When a user visits one of these sites, now appearing at the top search results, he is redirected and a document containing the payload of the ZeuS Panda virus is sent to his computer system. The user had to enable macros for the virus to take effect, but that doesn’t take much effort. The ZeuS Trojan virus was quite successful with its attacks and continues to spread over the Internet. Beware and check the URL, before trusting a website.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Update September 2017
The Zeus variant Chthonic has been detected recently by malware researchers as one that is still active. The following domain was spreading it:
- dako.gov(.)ua/files/text/load.exe
That domain has been known to be “The State Archive of the Kiev region” and after the payload dropper has downloaded the malware, the virus drops a copy of itself inside the %appdata%\roaming directory of the Windows operating system. The Panda Banker Trojan still remains active as another counterpart of the notorious Zeus Trojan. As the source code of the virus has been sold for quite some time now, more variants are very likely to be active as well.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Update August 2017
Update August 2017 Now, in August 2017 the Zeus trojan is spreading in its newest form – the [wplinkpreview url=”https://sensorstechforum.com/zeus-panda-banker-trojan-suchka-exe-remove-it-completely/”] ZeuS Panda Banker Trojan. That variant has been seen in multiple languages, most notable of which is in Italian. It is currently trying to infect systems of banks worldwide. It is spread with spam e-mail campaigns. The ZeuS Panda Trojan is also known as suchka.exe because of that same name used for the payload obfuscated inside the spam e-mails. The interesting thing is that the virus poses to be a ticket from your local Police Departament. The attached file in the emails is inside a .ZIP file to try and hide it from security software.

Zeus Trojan – Technical Insight Update June 2017
The module files unifying all the malicious activity behind the latest variants of ZeuS Trojan malware are with a similar behavior and even similar names for some of the variants of the virus, as you will see in this update. The executables and the malicious functions behind them which are of interest for the latest Zeus variants are believed to be the same as the original v2 variant as reported by Sysforensics. They are reported to be the following:
- Kernell32.dll
- Advapi32.dll
- User32.dll
These so-called support modules of Zeus Torjan’s main executable all have multiple functions that aim to modify different aspects of the infected computer and we will thoroughly review them.
Kernell32.dll
In this file, the first function of interest is called GetModuleHandleA. Researchers believed that it is utilized tin order to modify code of the OS so that an injection of malicious code while undetected is possible. Another similar function is GetModuleFileName. It aims to roll back the name of modules which are active as system processes. It can be used to insert processes in Windows Task Manager as if they were legitimate ones. There is also the OpenMutexA function in this file, primariy responsible for handling mutex objects. It can be used so that a second infection with Zeus Trojan is impossible and there is only one infection present. Commonly met function for most malware.
Advapi32.dll
This module has two functions that aim to act as a unique identifier of the infection, most likely serving as an easier way for the hacker to manage many infections, by having their unique names. The two functions are GetUserNameA and GetAuditedPermissionsFromAclW. The two most interesting functions for us, however are CreateServiceA as well as CreateProcessAsUserW. They are used primarily to create processes and for monitoring.
User32.dll
This module uses the function GetDesktopWindow and GetKeyboardState. They point out to the monitoring part of the malware, which may be:
- Logging keystrokes (keylogger feature).
- Screen capture or screenshot ability.
This is definitely a serious virus that continues to evolve. If new information is found the article will be duly updated.

Zeus Trojan Virus – Further Information
The Zeus Trojan virus has taken many forms over the years and has infected as many as 3.6 million computers in the United States alone, not to mention the ones worldwide. Now, in April 2017, the malware is still actively infecting computer systems. The Chthonic variant is back and this time is delivered by the RIG Exploit Kit. The distribution is with a malvertising chain and described above.
Below you can see a list with IPs involved in that attack:
- 5.200.52.240
- 45.56.117.118
- 144.76.133.38
- 89.18.27.34
And here are some of the URLs that serve as the last redirect to the landing page with RIG:
- dfg.twitttwoo.co.uk
- https://dfg.twitttwoo.co.uk/
- pationare.bit
- https://pationare.bit/
- avaneredge.bit
- https://avaneredge.bit/
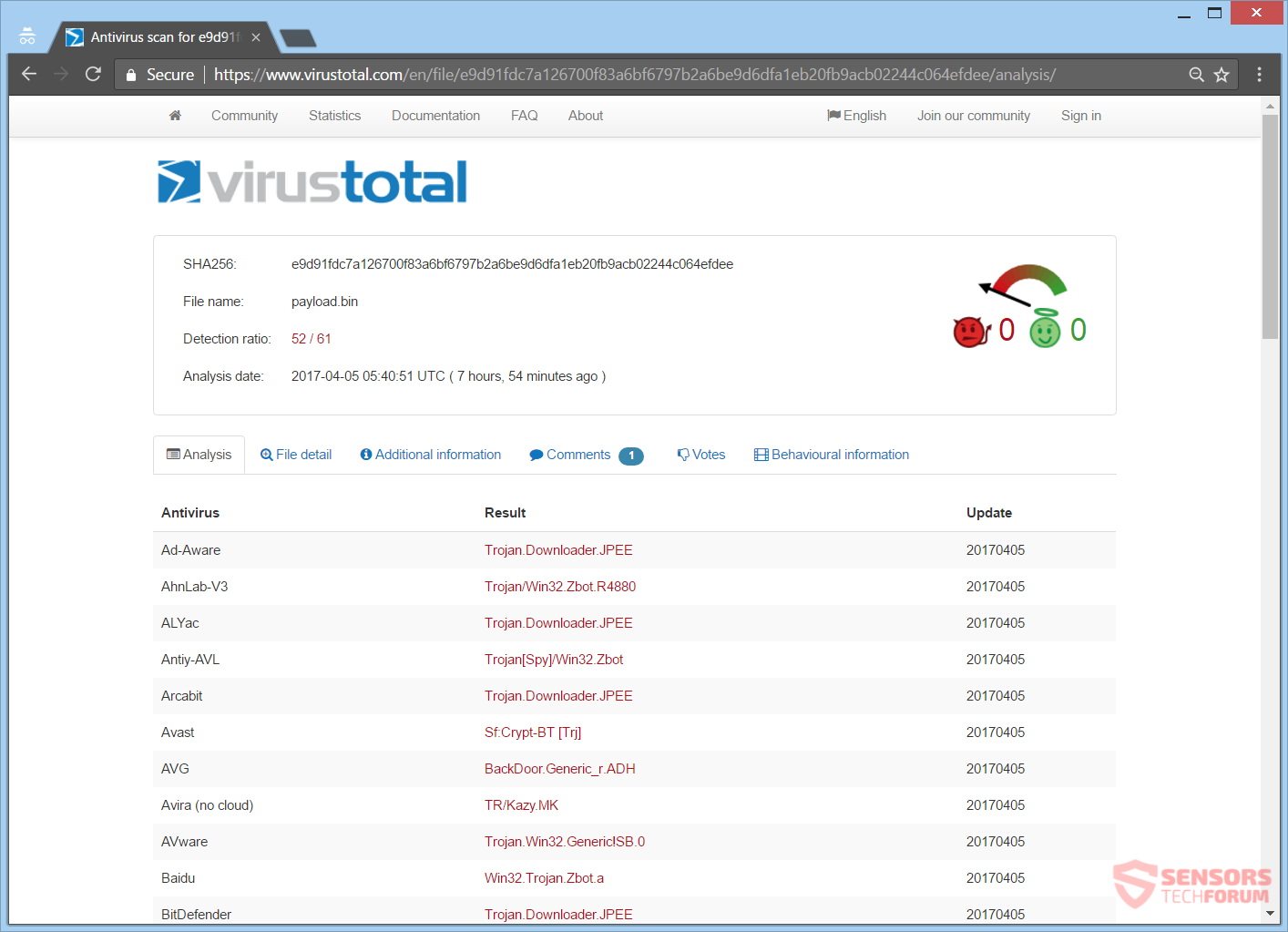
Since the leak of the ZeuS source code back in 2011, new variants have kept infecting computer machines. The common use of the Trojan involved, injecting code in browsers, which would show phishing web pages, in order to steal passwords, credentials and similar data related to banking. The Trojan is utilized under other purposes, like being the payload dropper for ransomware viruses. A sample analyzed on the VirusTotal service:
For that ransomware, the following rule is added to the Windows Firewall:
→netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”explore” dir=in action=allow program=”%APPDATA%\Wiezycr\itetiwe.exe”
The command makes the Windows Firewall to unlock the particular executable that is written there, which will give it Internet access for sending and receiving traffic online. Thus, data can be stolen from the infected system and commands could be sent from a hacker through that newly-created backdoor.
In January 2017, another variant of Zeus was detected, namely Terdot Zloader/Zbot. Here, the Sundown Exploit Kit is used for the distribution. The Trojan has also integrated legitimate applications inside its package to further avoid detection and to use those apps for malicious reasons. Interestingly enough, people who have the Russian language on their computer will not get infected.

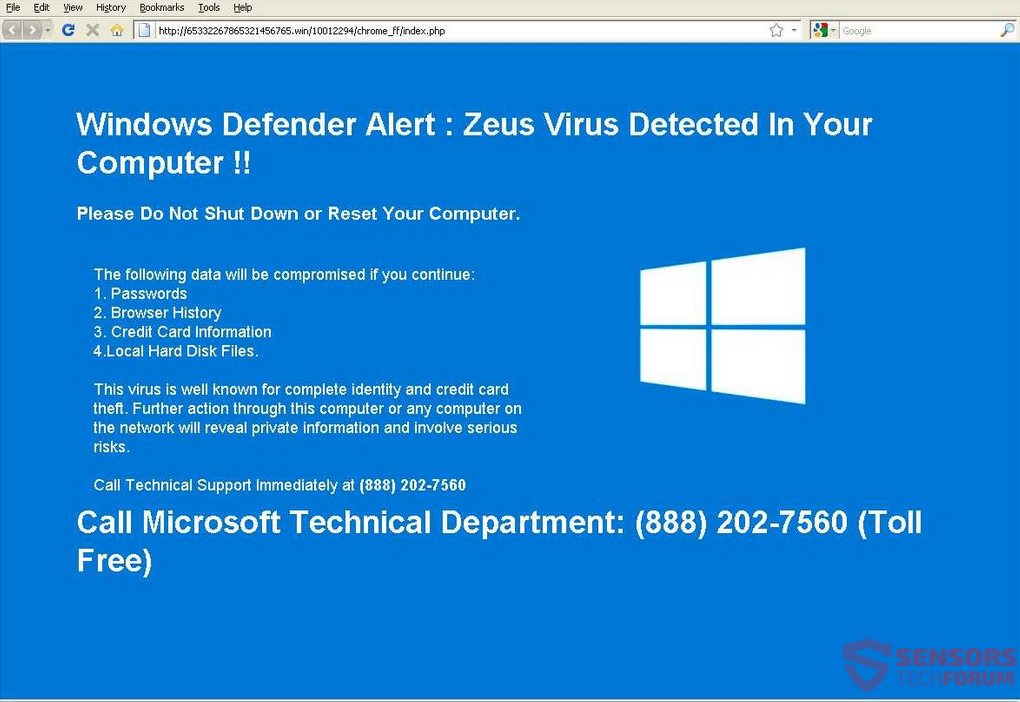
What Is ZeuS Virus Alert?
From 2016 to this day, lots of technical support scams have been using an alert message that claims that you have been infected with the ZeuS Virus, such as the example provided in the screenshot down here:
The following tech support scams and one ransomware have also written that your PC is infected with ZeuS as a scare tactic:
- Porn Virus Detected Scam – Remove It
- Remove 1-844-324-6233 Tech Support Scam (WinCpu.exe)
- Remove Vindows Locker Virus and Restore .vindows Files
In the above three cases however, you should not worry as much, because the real ZeuS Trojan virus will probably not have infected your computer and the ZeuS virus alert message is fake.
Besides those fraudulent detections which were exhibited, there are also several other detections which were reported to be associated with browser hijacking software otherwise known as Potentially Unwanted Applications. Such software is usually slithered onto your computer via what many refer to as bundling, which is modifying the setup of a free program to add an installation step to the unwanted software. Usually, bundling began as a marketing tool, but now it is also used in suspicious websites as a tool, which aims to slither such applications in computers:
Since the apps are essentially classified as low-level type of threats, they remain active on the computer, and may begin to modify the settings on it’s web browsers, for example Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer and others. As soon as these settings are modified, the web browsers may have different suspicious browser extensions added to them that may cause:
- Online pop-ups.
- Browser redirects.
- Highlighted text.
- Taken over banners.
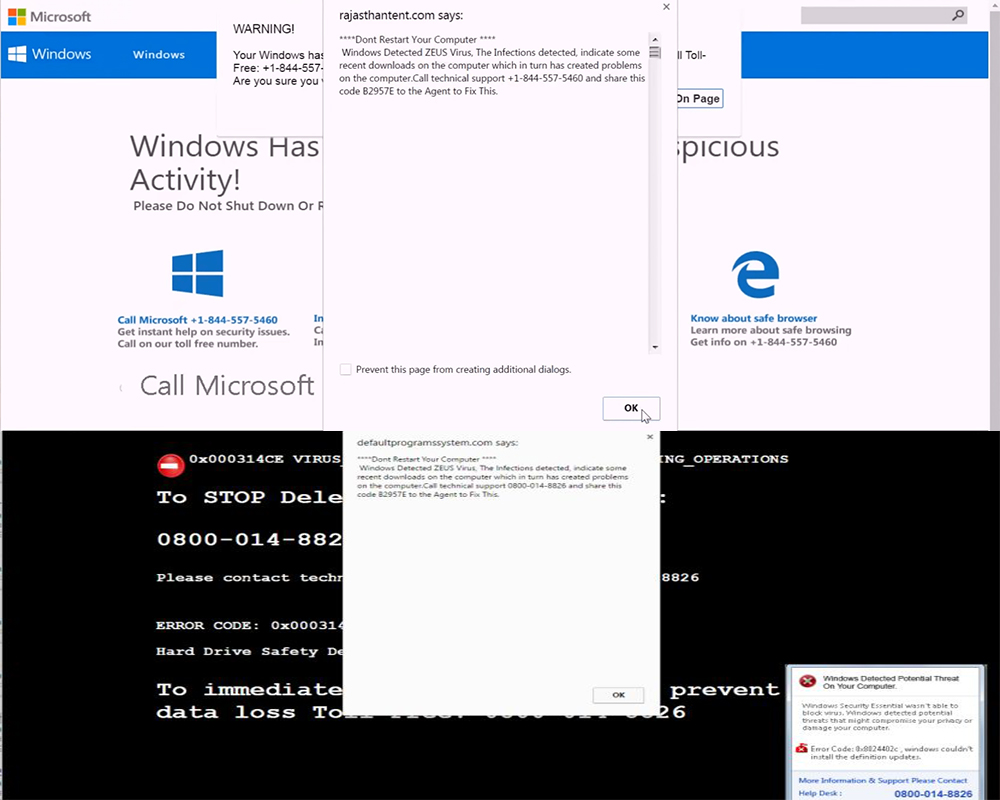
Once those have been performed, one of the redirections may lead to third-party web links that simply lock the user out of his browser and display a pop-up with a message claiming the computer has been infected with the Zeus virus. But this is actually a fake tech support scam, aiming to get users to call the numbers provided in the fake messages. The messages are very convincing and may even be accompanied by a robotic sound notification:
Here are some examples of such notifications:
“Windows Detected ZEUS Virus. The infections detected indicate some recent downloads on the computer which in turn has created problems on the computer. Call technical support 0800-014-8826, 1-844-557-5460 and share this code B2957E to the Agent to Fix This.”
When such tech support scams are encountered, we strongly advise you to check out our removal video to help you get rid of the tech support scam and any potentially untanted programs related to it.

What Is a Zbot Virus?
In case you were wondering what the ZeuS malware is, or otherwise also known as Zbot Virus, here is the right place to find out. Below, you will see the files of the virus and what they might be, how you can detect it if it’s put on your computer silently and waiting to receive a command to steal your data. Here is how to find it, step by step:
With Administrator rights, look for these directories and files:
- %systemroot%\system32\sdra64.exe (malware)
- %systemroot%\system32\lowsec
- %systemroot%\system32\lowsec\user.ds (stolen data file – encrypted)
- %systemroot%\system32\lowsec\user.ds.lll (file for stolen data – temporary)
- %systemroot%\system32\lowsec\local.ds (configuration file – encrypted)
Without Administrator rights, look for these directories and files:
- %appdata%\sdra64.exe
- %appdata%\lowsec
- %appdata%\lowsec\user.ds
- %appdata%\lowsec\user.ds.lll
- %appdata%\lowsec\local.ds
The ZeuS virus will also tamper with the Windows Registry, changing the following two registry entries to ensure that it loads with Administrator privileges:
→HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon
The default is:
“Userinit” = “C:\WINDOWS\system32\userinit.exe”
and it is changed to:
“Userinit” = “C:\WINDOWS\system32\userinit.exe,C:\WINDOWS\system32\sdra64.exe”
If you do not have Administrator rights, look for this string here:
→HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
The ZeuS Trojan horse virus adds the following:
“Userinit” = “C:\Documents and Settings\<user>\Application Data\sdra64.exe”
Note! As there are many variants of ZeuS the executable file may vary. Except the one described above (sdra64.exe), the following ones are recorded to be used in the past, as well:
- ntos.exe
- oembios.exe
- twext.exe
- pdfupd.exe
- 73mendjd.exe (used in 2017)
- onlineservicesw.exe (used in 2017)
Afterward, the Zeus Trojan horse will use one of the above mentioned executables to inject code into one of the following two processes (depending on what privileges it succeeded to acquire): winlogon.exe or explorer.exe. That code-injection is made with the aim to hide Zeus among other processes, so you as the user to not suspect a thing. Code is then injected into other processes as well, in order to steal data. If you notice a spike of activity in a general process from the Task Manager, check it out, as you might have been infected and unaware of the fact.

How Do I Remove Trojan ZeuS?
If your computer got infected with the Zeus Trojan horse virus, you should have a bit of experience in removing malware. You should get rid of this Trojan horse as quickly as possible before it can have the chance to spread further and infect other computer systems. You should remove the virus and follow the step-by-step instructions guide provided down below.
Preparation before removing ZeuS.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
Step 1: Scan for ZeuS with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
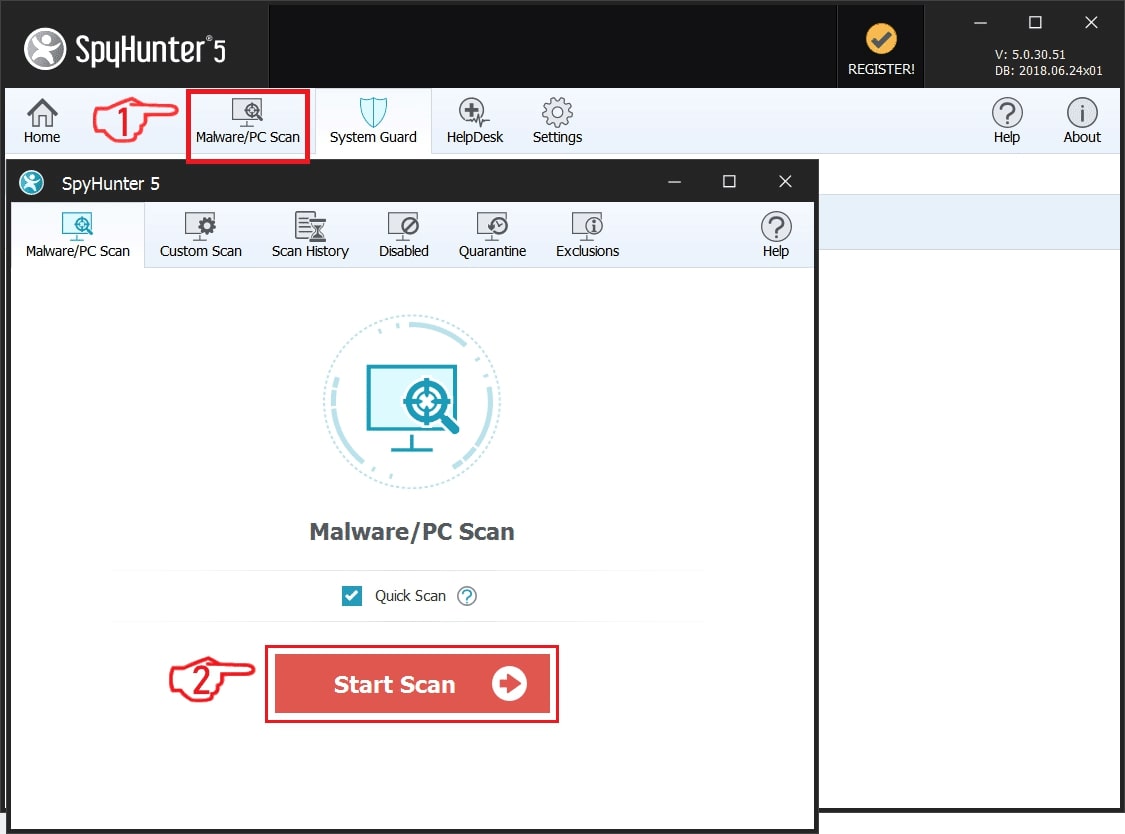
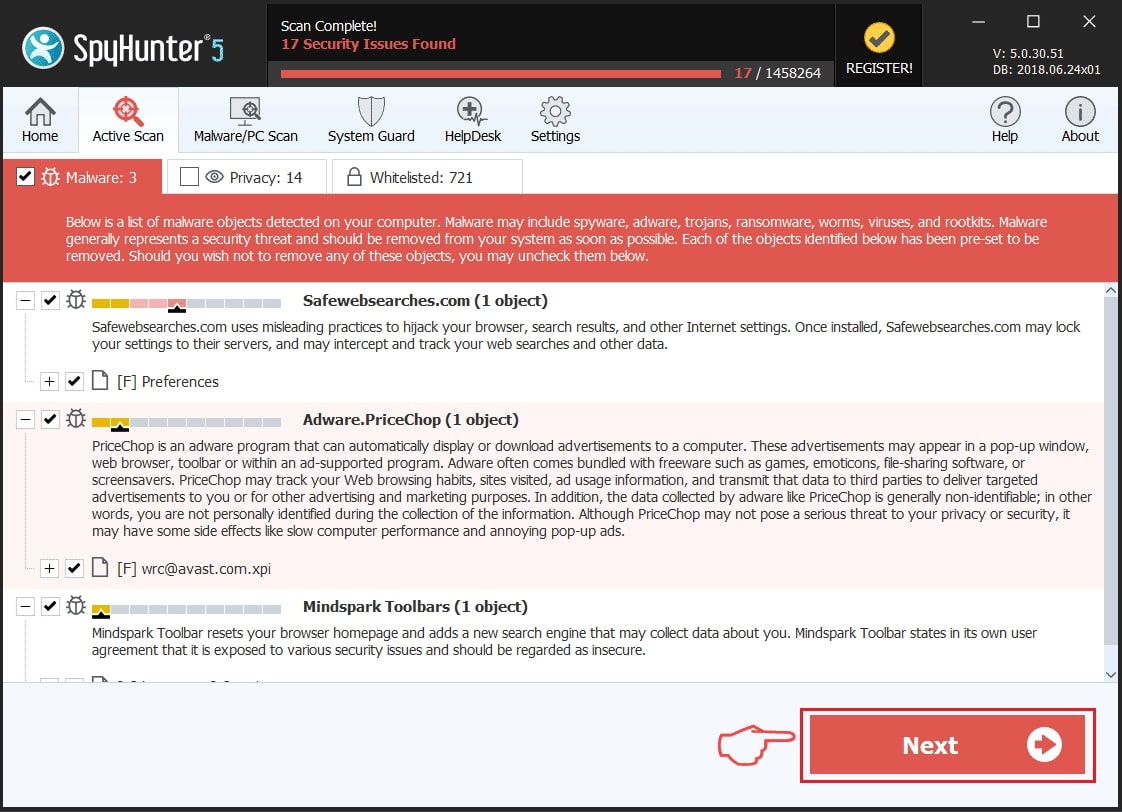
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by ZeuS on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by ZeuS there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
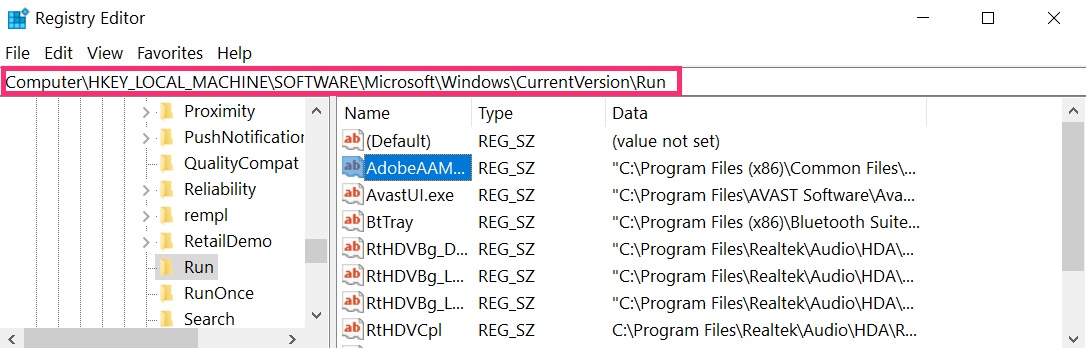
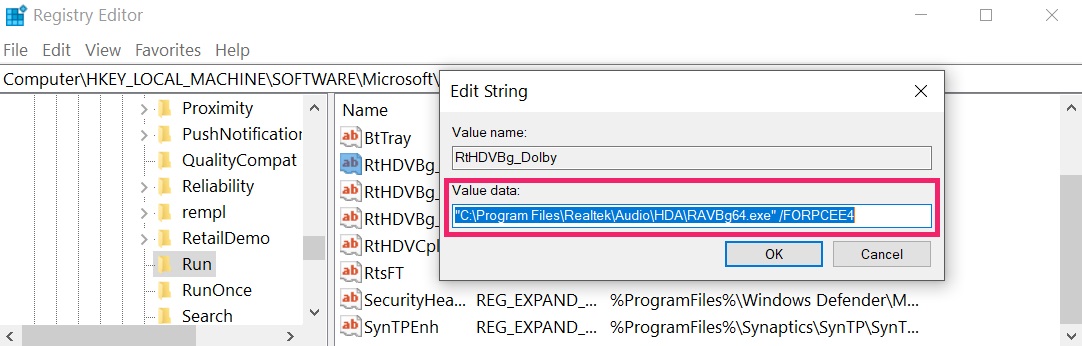 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by ZeuS on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
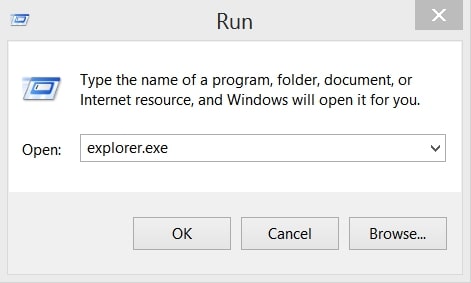
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
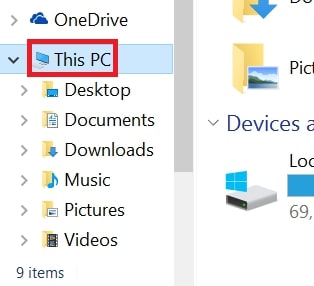
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
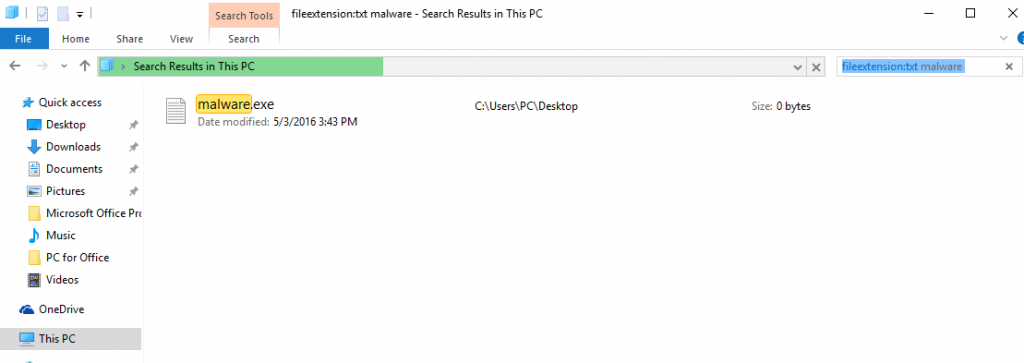
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
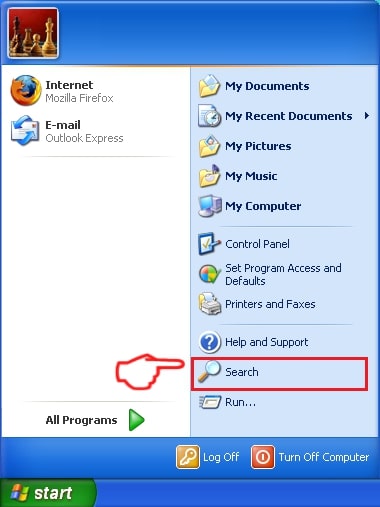
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
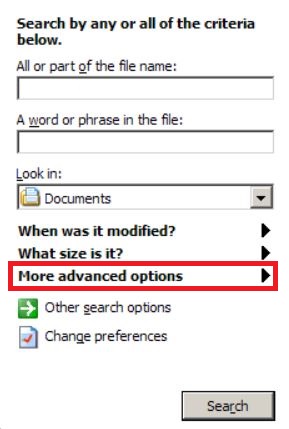
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
ZeuS FAQ
What Does ZeuS Trojan Do?
The ZeuS Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like ZeuS, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can ZeuS Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can ZeuS Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the ZeuS Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this ZeuS how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on ZeuS?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the ZeuS threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.