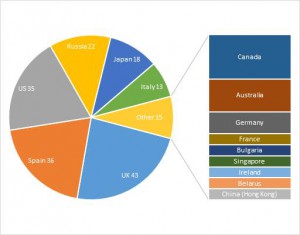
 Security experts with Kaspersky Lab report that a brand new strain of the infamous ZeuS Trojan is hitting banking systems over the world. The new threat Trojan-Banker.Win32.Chthonic, or just Chthonic, has already affected a hundred and fifty banks and twenty payment systems in fifteen countries. Financial institutions in Spain, Russia, Italy, Japan and the UK seem to be the primary targets of the Chthonic attack.
Security experts with Kaspersky Lab report that a brand new strain of the infamous ZeuS Trojan is hitting banking systems over the world. The new threat Trojan-Banker.Win32.Chthonic, or just Chthonic, has already affected a hundred and fifty banks and twenty payment systems in fifteen countries. Financial institutions in Spain, Russia, Italy, Japan and the UK seem to be the primary targets of the Chthonic attack.
The Way of Chthonic
The authors of Chthonic have designed it to exploit PC functions along with the keyboard and web camera in order to steal online banking credentials, like passwords. The crooks can also connect to the compromised machine from a remote location and command it complete various transactions.
Chthonic’s weapon of choice – web injectors, which can enable the threat to insert its malicious code and images into the code of the bank’s web page loaded directly from the affected computer. This allows the crooks to get their hands on the victim’s PINs, phone number and one-time passwords, along with any login details (username and password) that the user has entered.
Chthonic’s Distribution and Infection
Experts report that the main infection method used to distribute Trojan-Banker.Win32.Chthonic to the targeted machine is through malicious emails containing exploits. In this case, the email contains an attached document with a .DOC extension, which purpose is to establish a backdoor for malicious code. In the attachment, there is a specially designed RTF document that exploits the CVE-2014-1761 vulnerability in Microsoft Office products.
As the threat is downloaded, malicious code containing an encrypted configuration file is inserted in the msiexec.exe process, which results in numerous malicious modules being installed on the compromised computer.
These modules can perform the following tasks:
- Collect system information
- Enable remote access
- Steal passwords that have been saved
- Log keystrokes
- Record sound and video using the microphone and the web camera
Another technique employed by the attackers to deliver Chthonic is by downloading the threat to the victim’s machine via the Andromeda bot (aka Backdoor.Win32.Androm).
Chthonic’s Victims
Experts report that in the case of a Japanese bank that has been hit by Trojan-Banker.Win32.Chthonic, the malware managed to hide the warnings of the bank and inject script that lets the crooks complete a number of transactions through the victim’s account instead.
Another fresh example is a Russian financial institution, whose clients were presented with fake banking pages the moment they were logged on. For this purpose, the Trojan has created an iframe with a phishing copy of the web page having the exact same size as the original window.
Trojan-Banker.Win32.Chthonic is similar to other Trojans in the wild, for example:
- Chthonic uses the same downloader and encryptor as Andromeda bots
- Uses a virtual machine that reminds of the one used in KINS malware
- Has the same encryption technique as Zeus V2 and Zeus AES Trojans
Luckily, a large part of the code fragments employed by Chthonic for web injections cannot be used anymore, because of the fast reaction of the banks. In some cases, they have changed their pages’ structure and in other – the domains, too.
The Senior Malware Analyst at Kaspersky Lab, Yury Namestnikov says that the discovery of Chthonic is a clear sign that the ZeuS Trojan is still evolving. Malware writers are employing the latest techniques, which were helped by the leak of source code of ZeuS. According to the expert, Chthonic is the next level in ZeuS’evolution.
Spy Hunter FREE scanner will only detect the threat. If you want the threat to be automatically removed, you need to purchase the full version of the anti-malware tool. Find Out More About SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool


