The Kedi Trojan is a newly discovered malware that is being distributed worldwide that uses Gmail to communicate with the hacker-controlled servers. The code analysis reveals that it is a complex computer virus that can be used in many infiltration scenarios. Our article provides an overview of the Trojan operations and it also may be helpful in attempting to remove the Trojan.

Threat Summary
| Name | Kedi Trojan |
| Type | Trojan |
| Short Description | The Kedi Trojan is a utility malware that is designed to silently infiltrate computer systems, active infections will spy on the victim users. |
| Symptoms | The victims may not experience any apparent symptoms of infection. |
| Distribution Method | Freeware Installations, Bundled Packages, Scripts and others. |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
| User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss Kedi Trojan. |

Kedi Trojan – Distribution Methods
The Kedi Trojan is a new weapon used by computer criminals to infect users all around the world. At the moment the primary method of distribution is the use of phishing email messages. The captured samples indicate that the malicious users behind it attempt to confuse the recipients into believing that they have received a legitimate message from a well-known company. The goal is to deliver an infected payload to the users. They can be either attached directly or linked in the body contents.
In addition the payload files can also be uploaded to hacker-created sites. They are made by taking the web design elements of well-known portals or vendors and uploading the files to it.
There are two main types of malicious payloads that are being used to the Kedi Trojan:
- Infected Software Installers — The hackers can take the legitimate setup files of famous applications and modify them to include the Kedi Trojan code. In this particular case the attacks target a popular system utility.
- Malicious Documents — The criminals can take advantage of macro-infected files. They are usually documents of different types (rich text files, documents, spreadsheets and presentations). Once they are opened by the victims a notification prompt will appear asking them to enable the built-in macros. Once this is done the infection will follow.
The infected files can also be spread on file sharing networks such as BitTorrent trackers where pirate content is usually spread. During the coordination of the attacks the criminals can also opt to utilize malicious scripts.They can be spread onto ad networks with the intent of redirecting more users to the malicious sites where the Kedi Trojan is hosted. Such behavior warrants the use of a lot of techniques and produced code — banners, pop-ups, redirects and in-line hyperlinks.
Advanced infections can be done via browser hijackers as well. They are dangerous plugins made for the most popular web browsers — Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge and Opera. The various strains are then uploaded to the associated repositories. The posted descriptions aspire to coerce the victim users into downloading the malicious samples to their computers, often they are accompanied by fake developer credentials or user reviews. Once they are installed on the infected machines the built-in behavior pattern will be triggered. Similar threats like this one are programmed to redirect the victim users to a hacker-controlled page by changing the default settings — home page, search engine and new tabs page. Once this is done the malicious engine will proceed with the Kedi Trojan execution.

Kedi Trojan – Detailed Description
One of the distinct characteristics of the Kedi Trojan is the way it has been created. The hackers behind it have modeled it to pose as a legitimate utility. This is done by including counterfeit signatures in the executable files (reading “Citrix NetScaler Unified Gateway”) and having a hijacked a legitimate looking splash screen. When starting up the file it will show a loading status which raises no suspicion when run.
During its initialization the analysts have detected that it contains a stealth protection functionality. This is executed by a component that scans for the presence of applications that can interfere with the virus execution. The list includes anti-virus solutions, sandbox environments or virtual machine hosts. If configured so the engine can block the real-time engines or delete the software altogether. In certain cases the virus samples can delete themselves if they are unable to perform this step. This behaviour is programmed in order to hide the infection from being noticed by the system administrators.
Following the successful infection of the host computers the Kedi Trojan will install itself in the application data folder belonging to Adobe. This shows that criminals have implemented a masquarade feature that implants the threat in a predefined location. The main module will be accompanied by a lock file (with the .lck extension) which is as marker that shows processes and applications not to interact with it. The newly created folders can also be used for utility storage of log files, screenshots and other useful output.
The code analysis shows that the Kedi Trojan is also capable of modifying certain Windows Registry entries.
It can create entries belonging to itself or modify existing ones belonging to the user-installed applications or to the operating system itself. This can lead to the inability to start certain applications or services, in addition the victims will experience performance issues. The configuration file of the Trojan is stored in a protected form that is decrypted on-the-fly as the malware is run.
The configuration file can be fine tuned to deliver specific customized variants according to local conditions. This means that the malicious engine can also engage a thorough data harvesting module. Similar threats like this one can extract strings that can be grouped into two main types:
- Personal Information — This data set can directly expose the identity of the victims. The collected strings include the person’s name, address, phone number, interests, location and any stored account credentials.
- Campaign Metrics — The engine can be used to hijack data that can be useful to the hacker operators. The data harvesting module can generate a report of the hardware component and certain user-set settings.

Kedi Trojan – Trojan Operations
Once all prior components have finished execution the Trojan infection will be triggered. It contains many advanced features that are not found in other common threats. This gives the analysts the assumption that custom code has been implemented by the hacker operators.
The Kedi Trojan connects to a hacker-controlled server using a secure connection however instead of using a common channel (such as IRC, Telnet or something else) it uses a Gmail-based back end. The client machine connects to a Gmail account viathe basic HTML web interface using an automated behavior pattern. This is an interesting approach as it has two major advantages. The first one is that Gmail access should not raise suspicion during network analysis. The creation of Google accounts can also be automated to a certain degree which can supply a steady stream of different accounts.
The exact mechanism follows a predefined model that follows a step-based behaviour:
- The Trojan module establishes the connection to the Gmail account va the built-in credentials.
- Using the Gmail connection the host sends a report to the hackers signaling them about the newly made infection.
- Using an automated approach the Trojan module will refresh the inbox checking for new commands and instructions sent by the hackers.
The successful installation of this module can be used to deliver additional threats. This is especially dangerous if done with ransomware or banking Trojans. Triggering the Trojan’s capabilities can also allow the hackers to generate screenshots of the active user’s activities either manually or automatically. If custom code is used the attackers can generate malicious pop-ups that can be used in carrying out scams. Trojans like this one can lead to the initialization of keyloggers — automated software that can grab certain strings that falls into a specific category. They can sense when users enter account credentials into login prompts and other related fields.
Preparation before removing Kedi Trojan.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
Step 1: Scan for Kedi Trojan with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by Kedi Trojan on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by Kedi Trojan there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
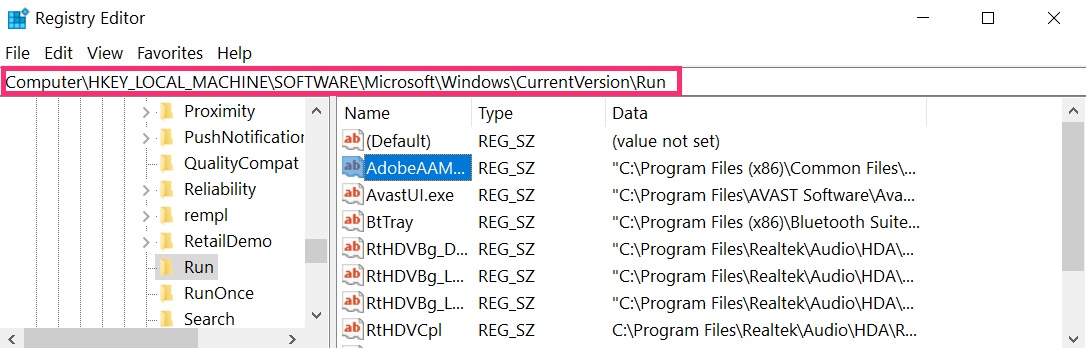
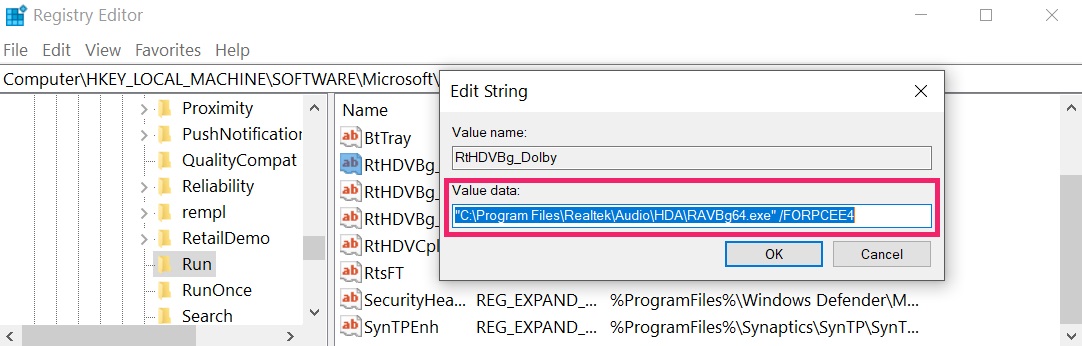 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by Kedi Trojan on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
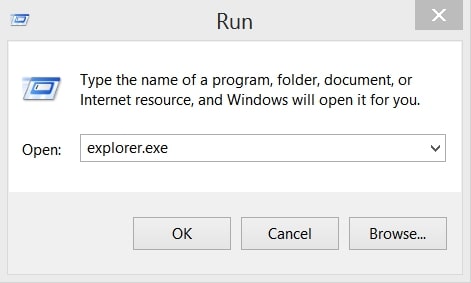
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
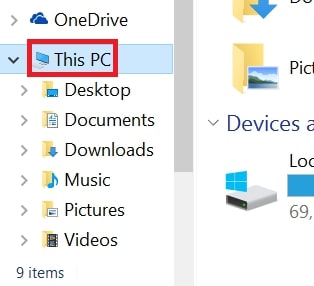
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
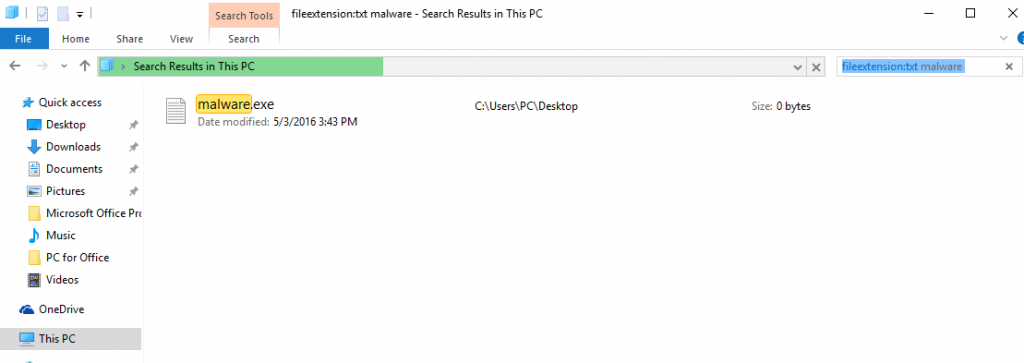
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
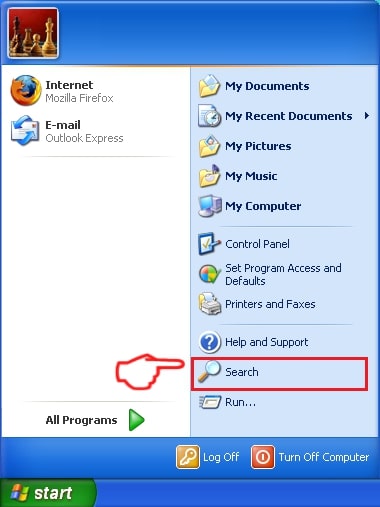
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
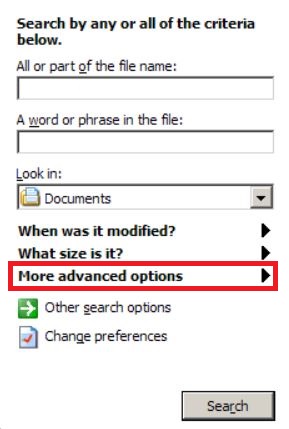
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
Kedi Trojan FAQ
What Does Kedi Trojan Trojan Do?
The Kedi Trojan Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like Kedi Trojan, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can Kedi Trojan Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can Kedi Trojan Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the Kedi Trojan Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this Kedi Trojan how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on Kedi Trojan?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the Kedi Trojan threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.



