The Rakhni Trojan is among the most devastating computer viruses in the last few years combining both a miner and a ransomware engine. It is fairy complex and can evaluate each infected system by running a custom attack sequence. The fact that it can spread through the local network using a worm function has made it a critical threat that must be removed instantly after the infections have been reported. Read our complete analysis and removal guide to learn how to restore infected hosts.

Threat Summary
| Name | Rakhni Trojan |
| Type | Trojan, Ransomware, Cryptocurrency Miner |
| Short Description | The Rakhni Trojan is capable of spying on the users and their machines and the installation of cryptocurrency miners or ransomware code. It is one of the most dangerous and persistent threats in the last few years because of it’s very advanced malicious engine. |
| Symptoms | Depending on the case the users may find that their files have been encrypted by ransomware or feel unusual performance issues. |
| Distribution Method | Spam Emails, Email Attachments |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss Rakhni Trojan. |
| Data Recovery Tool | Windows Data Recovery by Stellar Phoenix Notice! This product scans your drive sectors to recover lost files and it may not recover 100% of the encrypted files, but only few of them, depending on the situation and whether or not you have reformatted your drive. |

Rakhni Trojan – Distribution Methods
The Rakhni Trojan has been in distribution since 2013 using various attack campaigns. Throughout the years it’s code has shifted in several generations of different strains each using different mechanics to intrude into the target machines.
At the moment the security reports indicate that the top 5 countries where the infections have been found are the following: The Russian Federation, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Germany and India. The ongoing attack campaigns have been found to rely on email phishing messages. The hackers have created multiple language versions of the emails that pose as being sent by a well-known company. They coerce the victim files into opening up an infected payload document. When it is accessed by the users a notification prompt appears which asks them to enable the built-in macros (scripts). If this is done an automatic trigger will execute the built-in download sequence that will ultimately lead to the Rakhni Trojan infection.
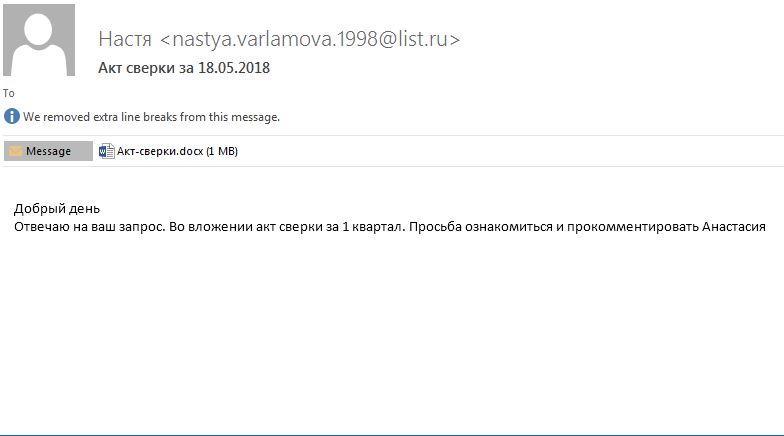
Other files that can be used to deploy the infection also include the following:
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Databases
- Application Installers
An interesting characteristic is that the infection engine will also produce an error message explaining that a download has failed. This is done in order to take away the victim’s attention from the script.

Rakhni Trojan – In-Depth Analysis
The security analysis reveals that the Rakhni Trojan follows a carefully planned preconstructed behavior pattern. The malicious engine responsible for the correct execution of the Trojan initiates several installation checks before proceeding further. They are responsible for deploying the Trojan instance in several system location posing as the Adobe Reader application. This is done in order to make it more diffract for the users and system administrators to spot the infection as it is one of the most commonly installed applications. The engine also creates the relevant Windows Registry values so that everything matches up.
The next step in the infection process looks for the signatures of programs that may interfere with its correct execution: anti-virus programs, virtual machine hosts and debug/sandbox environments.
The main infection engine installs two certificates that pose as being signed by Adobe and Microsoft. This step is accompanied by the download of additional files to the Windows Temporary files folder.
The unique characteristic of this Trojan is that it can enforce either an ransomware engine or a cryptocurrency miner depending on several environmental checks. The implemented mechanism looks for signs of Bitcoin software installation – if such are found the virus code deems that the victim users might have digital assets that can be stolen. This will activate the miner download and execution command. In another case the ransomware engine will be started.
The ransomware engine will be downloaded in case no Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency software is found on the target machines or if their hardware resources are deemed ineffective for mining. Before this component is started the Trojan once again checks if certain applications and services are running and terminates them to facilitate the correct execution. It has also been found to delete all identifed Shadow Volume Copies and possibly the System Restore data. This means that file recoery will be possible only via a professional-grade solution. Refer to our instructions for more information on this.
The produced ransomware analysis reveals that the following file type extensions are targeted:
“.ebd”, “.jbc”, “.pst”, “.ost”, “.tib”, “.tbk”, “.bak”, “.bac”, “.abk”, “.as4”, “.asd”, “.ashbak”, “.backup”, “.bck”, “.bdb”, “.bk1”, “.bkc”,
“.bkf”, “.bkp”, “.boe”, “.bpa”, “.bpd”, “.bup”, “.cmb”, “.fbf”, “.fbw”, “.fh”, “.ful”, “.gho”, “.ipd”, “.nb7”, “.nba”, “.nbd”, “.nbf”, “.nbi”,
“.nbu”, “.nco”, “.oeb”, “.old”, “.qic”, “.sn1”, “.sn2”, “.sna”, “.spi”, “.stg”, “.uci”, “.win”, “.xbk”, “.iso”, “.htm”, “.html”, “.mht”, “.p7”,
“.p7c”, “.pem”, “.sgn”, “.sec”, “.cer”, “.csr”, “.djvu”, “.der”, “.stl”, “.crt”, “.p7b”, “.pfx”, “.fb”, “.fb2”, “.tif”, “.tiff”, “.pdf”, “.doc”,
“.docx”, “.docm”, “.rtf”, “.xls”, “.xlsx”, “.xlsm”, “.ppt”, “.pptx”, “.ppsx”, “.txt”, “.cdr”, “.jpe”, “.jpg”, “.jpeg”, “.png”, “.bmp”, “.jiff”,
“.jpf”, “.ply”, “.pov”, “.raw”, “.cf”, “.cfn”, “.tbn”, “.xcf”, “.xof”, “.key”, “.eml”, “.tbb”, “.dwf”, “.egg”, “.fc2”, “.fcz”, “.fg”, “.fp3”,
“.pab”, “.oab”, “.psd”, “.psb”, “.pcx”, “.dwg”, “.dws”, “.dxe”, “.zip”, “.zipx”, “.7z”, “.rar”, “.rev”, “.afp”, “.bfa”, “.bpk”, “.bsk”, “.enc”,
“.rzk”, “.rzx”, “.sef”, “.shy”, “.snk”, “.accdb”, “.ldf”, “.accdc”, “.adp”, “.dbc”, “.dbx”, “.dbf”, “.dbt”, “.dxl”, “.edb”, “.eql”, “.mdb”, “.mxl”,
“.mdf”, “.sql”, “.sqlite”, “.sqlite3”, “.sqlitedb”, “.kdb”, “.kdbx”, “.1cd”, “.dt”, “.erf”, “.lgp”, “.md”, “.epf”, “.efb”, “.eis”, “.efn”, “.emd”, “.emr”,
“.end”, “.eog”, “.erb”, “.ebn”, “.ebb”, “.prefab”, “.jif”, “.wor”, “.csv”, “.msg”, “.msf”, “.kwm”, “.pwm”, “.ai”, “.eps”, “.abd”, “.repx”, “.oxps”, “.dot”.
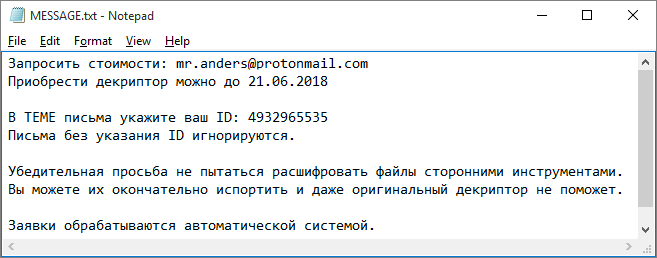
The associated Rakhni Trojan institutes the miner instance as a randomly-named executable in the %AppData folder. It generates a script that installs it as persistent threat — this means that this component will be automatically started once the computer is booted. The analysis shows that the downloaded miner is configured to mine the Monero (XMR) currency.

Rakhni Trojan – Trojan Operations
Apart from disabling the security software that can interfere with its execution the Trojan also creates a secure connection with a hacker-controlled server. It is used to automatically report the infections, harvested information and other gathered data. The analysis shows that the following strings are one of the first that are transferred:
- Computer name
- Public IP address
- Path of the installed Rakhni Trojan on the infected hosts
- Current Date and Time
- Trojan Built Date

The local instance is able to communicate three states of current status — a confirmation that the Trojan components have been downloaded; a message showing that the network infiltration has been begun or an error message.
A network worm instance is executed which scans the local network and attempts to infiltrate other machines on the networks using various vulnerabilities. It performs automated penetration testing by using the built-in scripts.
The Trojan module is also responsible for the advanced stealth protection mechanism that can instruct the virus to automatically delete itself. This is done if the underlying engine suspects that the users maybe trying to scan their systems for malware or attempt to remove via both manual or automated means.
Preparation before removing Rakhni Trojan.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
Step 1: Scan for Rakhni Trojan with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
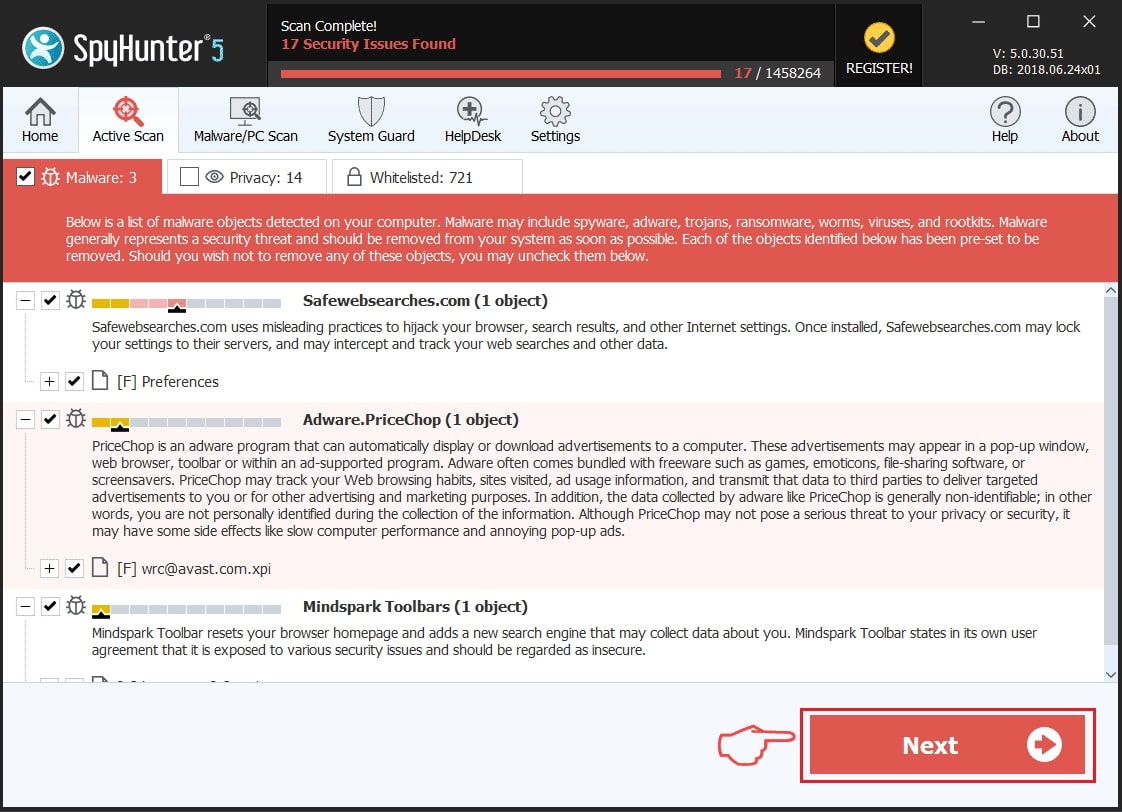
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by Rakhni Trojan on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by Rakhni Trojan there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
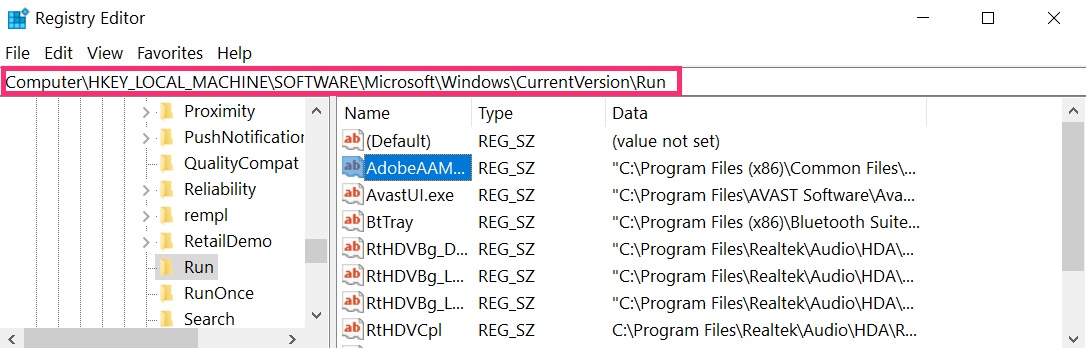
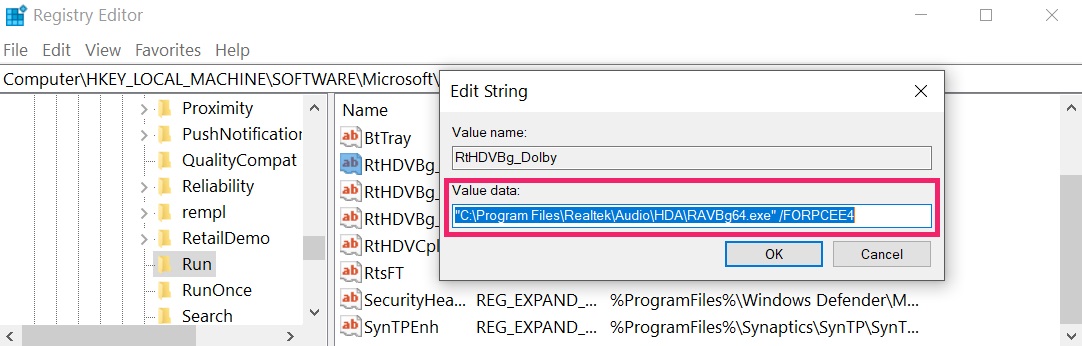 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by Rakhni Trojan on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
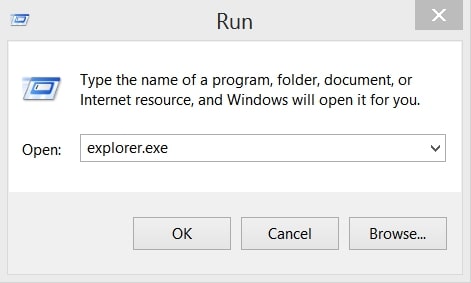
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
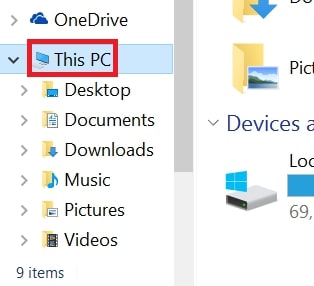
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
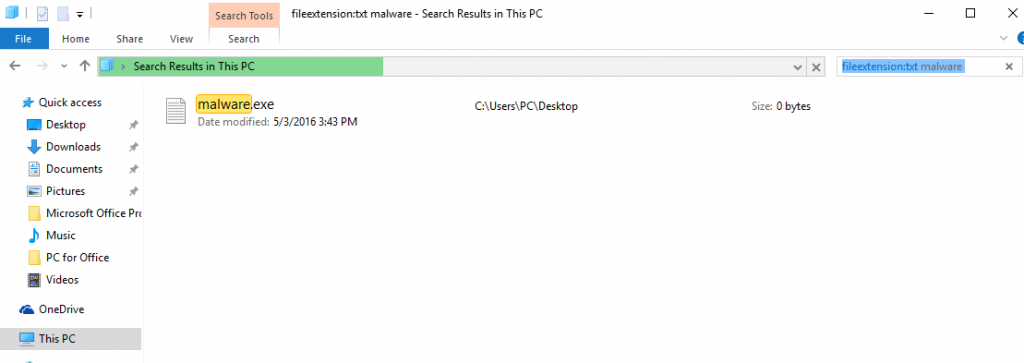
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
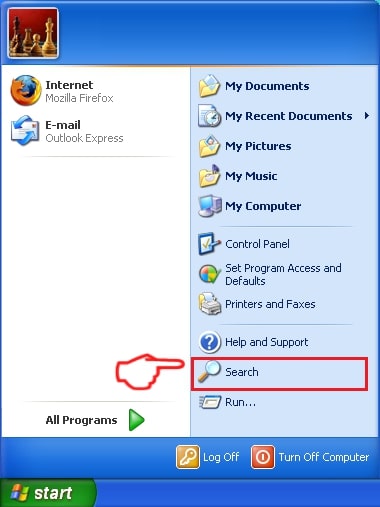
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
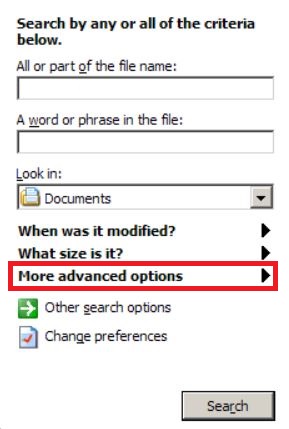
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
Rakhni Trojan FAQ
What Does Rakhni Trojan Trojan Do?
The Rakhni Trojan Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like Rakhni Trojan, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can Rakhni Trojan Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can Rakhni Trojan Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the Rakhni Trojan Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this Rakhni Trojan how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on Rakhni Trojan?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the Rakhni Trojan threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.



