Another malvertising campaign has been detected, redirecting users to the HanJuan exploit kit (EK) also known as Timba Trojan and Fobber. An advertising service – Ad.fly has been compromised and exploited to link users to a piece of malicious software designed to harvest login details. The attack itself may be considered a man-in-the-middle one since the user’s browser is disposed to seize various credentials. Ad.fly is a URL shortener that displays an ad before the user reaches the final content via the shortened link.
URL shortening services are often employed by cyber criminals to masquerade malicious links. However, the present malvertising campaign is designed to exploit not the short link but an embedded advertisement within the Ad.fly service. Hence, the malicious advertising happens and the user is redirected to the exploit kit.
The HanJuan EK Malvertising Campaign Description
As just mentioned, the attack begins with the exploitation of the Ad.fly service. Basically, the shortener uses interstitial advertising. Interstitials are web pages that are shown to the user before or after he reaches the desired content. Usually, interstitials are controlled by an ad server.
The malvertising redirection system to the exploit kit is quite sophisticated, as indicated by Malwarebytes research. The first four sessions load the interstitial ad via an encoded JavaScript blurb: Once the HanJuan kit is loaded, Flash Player and Internet Explorer are fired before the final payload is dropped onto the hard disk. According to Segura, a senior security researcher at Malwarebytes, the vulnerability exploited in Flash Player is said to be CVE-2015-0359, and the one in IE – CVE-2014-1776. Each can be employed, depending on the user’s profile. Furthermore, the payload most likely contains various layers of encryption – both in the binary itself and the C&C communications, making the whole malicious campaign a tad more complex.
Login Details Theft
As with most malicious campaigns of the scale, the final goal is the stealing of sensitive information.
The malicious interstitial ad is loaded via an encoded JavaScript. Moreover, the final URL is embarked via CORS – Cross Origin Resource Sharing. CORS is defined as a mechanism that permits restricted resources on a web page such as JavaScript to be demanded by an outside domain, different from the original one.
Another version of the Tinba Trojan
According to the Dutch security company Fox-IT, the threat is yet another variant of the Tinba banking Trojan also known as Tiny Banker and Trojan.Tinba.B. Tinba was detected by Symantec back in September 2014. Its threat level was considered low, its primary purpose being the theft of banking credentials.
Another malicious campaign associated with HanJuan EK was detected in March this year. Any user who had visited the New York Daily website, Metacafe and several other less popular ones, could have been compromised by a malvertising campaign redirecting to the HanJuan EK. An Adobe Flash Player vulnerability was similarly exploited.
HanJuan Exploit Kit Detection and Removal
To stay protected against exploit kits, users can follow some security tips such as:
- Frequently update Java, Adobe products, and Flash.
- Turn off Java and Flash when not needed.
- Implement a routine patching program.
- Sustain a powerful anti-malware solution.
The following security tip goes to business owners:
- Eliminate or restrict admin-level rights for non-expert employees.
To make sure the computer hasn’t been affected by the HanJuan EK, performing a full system scan is recommended. Several removal steps that apply to information stealing Trojans are also provided.

Spy Hunter scanner will only detect the threat. If you want the threat to be automatically removed, you need to purchase the full version of the anti-malware tool.Find Out More About SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool / How to Uninstall SpyHunter
Preparation before removing HanJuan Exploit Kit.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
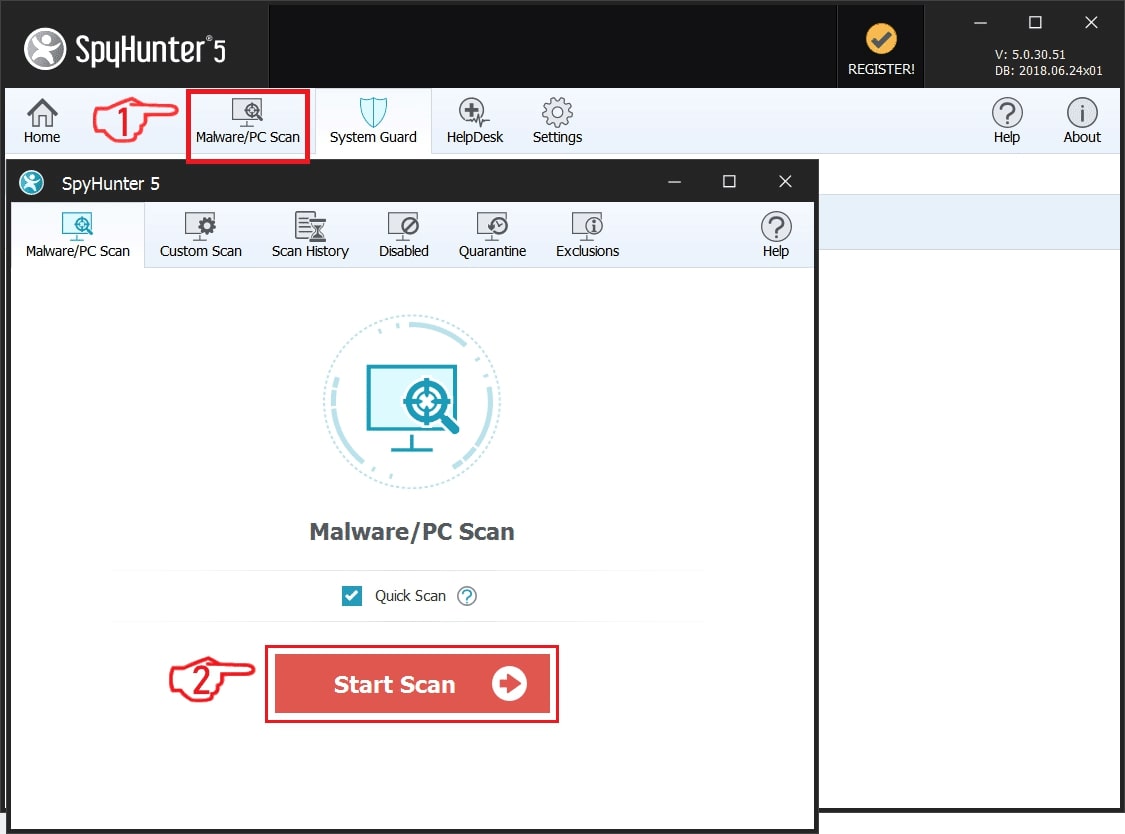
Step 1: Scan for HanJuan Exploit Kit with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
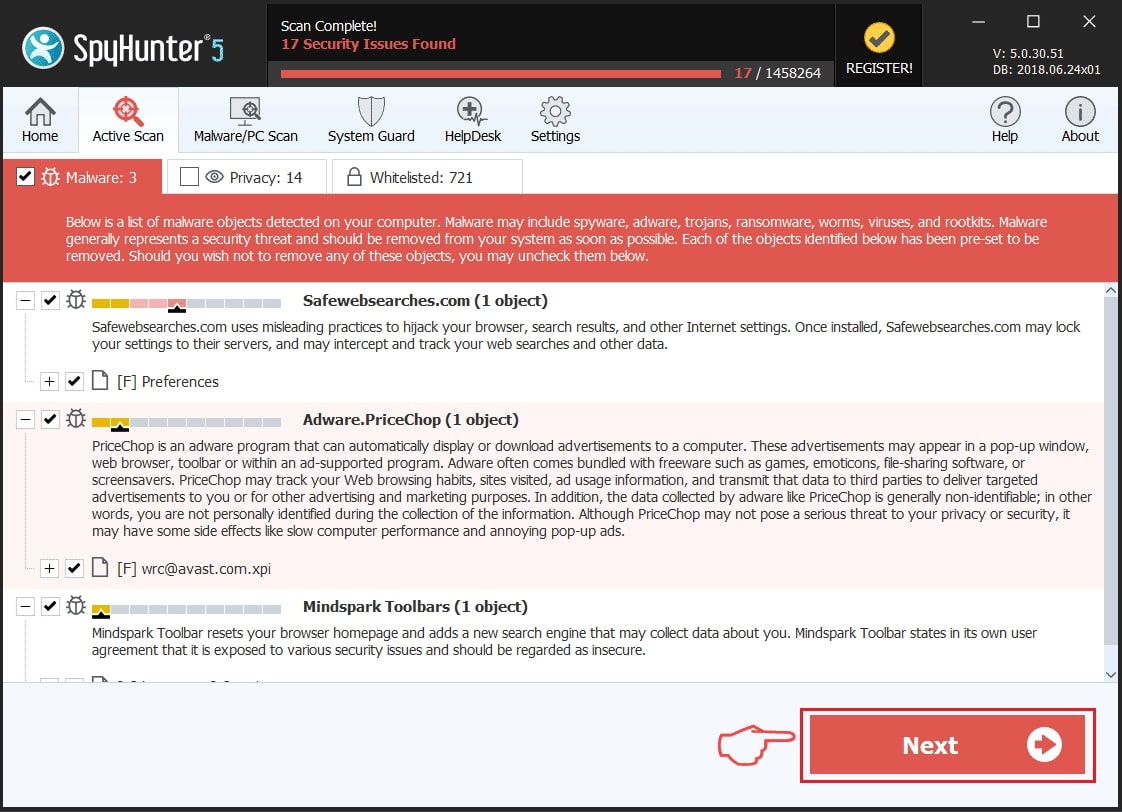
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by HanJuan Exploit Kit on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by HanJuan Exploit Kit there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
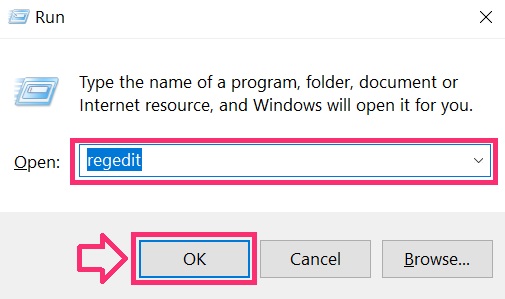
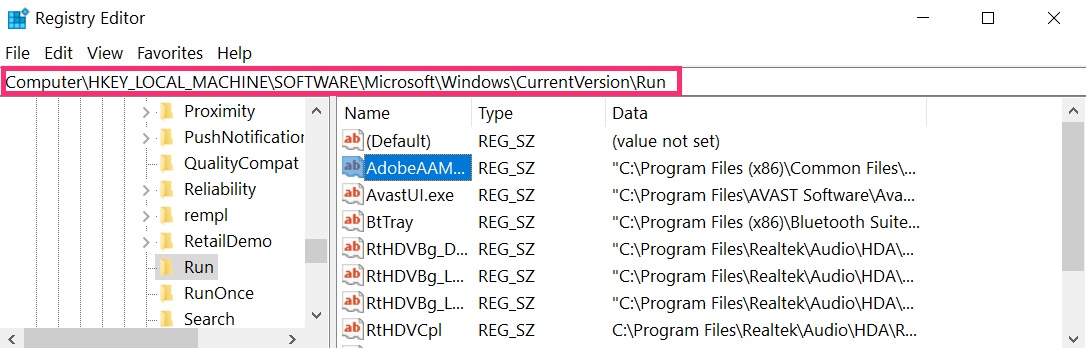
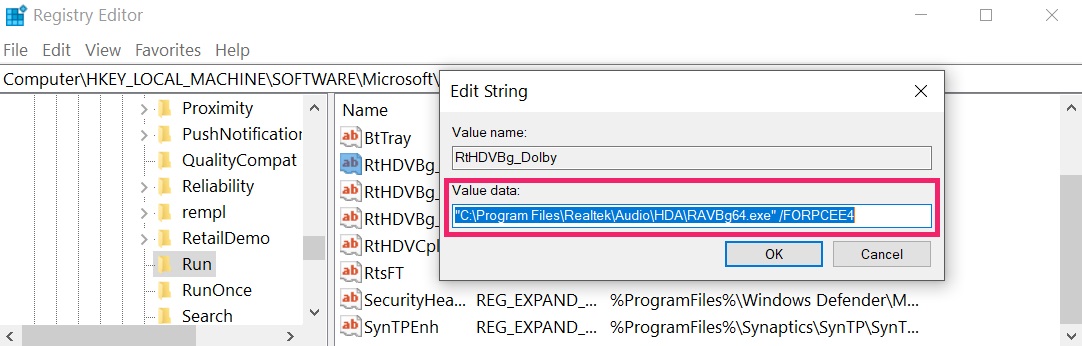 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by HanJuan Exploit Kit on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
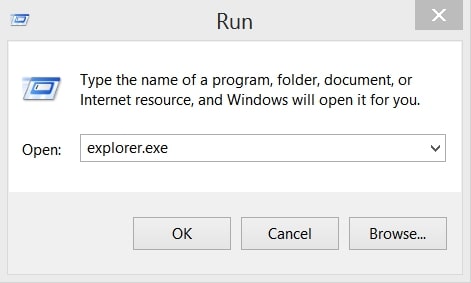
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
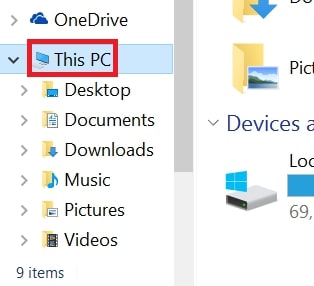
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
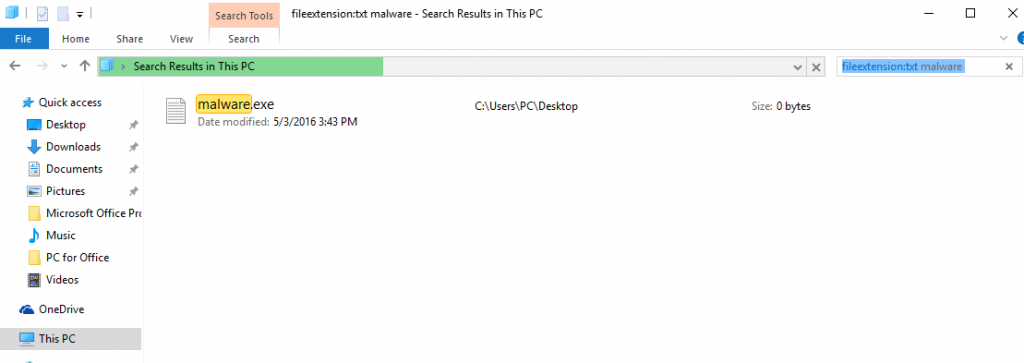
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
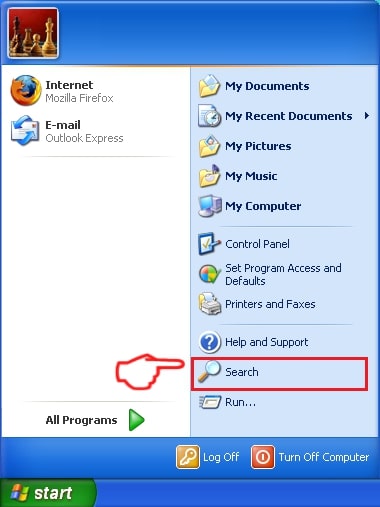
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
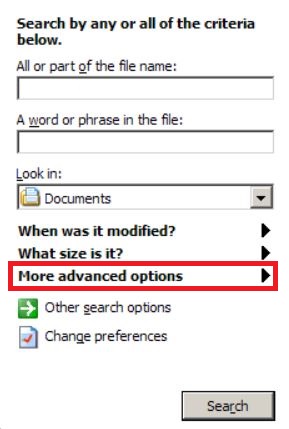
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
HanJuan Exploit Kit FAQ
What Does HanJuan Exploit Kit Trojan Do?
The HanJuan Exploit Kit Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like HanJuan Exploit Kit, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can HanJuan Exploit Kit Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can HanJuan Exploit Kit Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the HanJuan Exploit Kit Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this HanJuan Exploit Kit how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on HanJuan Exploit Kit?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the HanJuan Exploit Kit threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.


