The CobInt Trojan is a newly devised malware that has been identified in several ongoing attacks. It is an upgraded version of a previous weapon that has the potential of infecting whole networks of computers. A dangerous characteristic of it is its ability to deploy various modules according to the victim type. Our article illustrates the typical strain behavior and shows infected computers may be recovered.

Threat Summary
| Name | CobInt Trojan |
| Type | Trojan |
| Short Description | The CobInt Trojan is a computer virus that is designed to silently infiltrate computer systems, active infections will spy on the victim users. |
| Symptoms | The victims may not experience any apparent symptoms of infection. |
| Distribution Method | Freeware Installations, Bundled Packages, Scripts and others. |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
| User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss CobInt Trojan. |

CobInt Trojan – Distribution Methods
The CobInt Trojan is the latest malware threat coming it from the Cobalt hacking collective. It is believed that this is merely a next-generation updated threat based on their previous weapons.
The newly updated version was initially discovered in an attack campaign in August focusing on Russian and Romanian banks and financial institutions. Previous versions of it were configured to act against companies such as telecom providers, the manufacturing industry, health care organizations and etc.
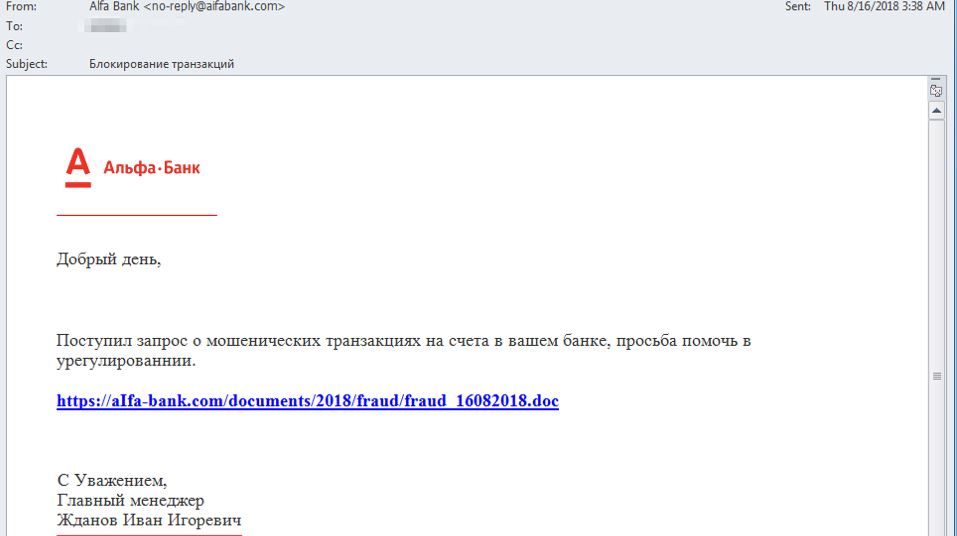
The most prominent distribution method used by the criminals appears to be sending of phishing email messages orchestrated by a special kit used by the hackers. They can spread virus files, infected documents and other payload carriers directly or hyperlink them in the body contents. The emails are designed to appear as being sent by a popular Internet service or
In August four attack campaigns have been observed, most of the leverage an exploit that takes advantage of an vulnerability in the Microsoft Office applications. An analysis of the captured samples indicate that the particular threat is the one described in the CVE-2018-8174 advisory. It reads the following:
A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the VBScript engine handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.
In a web-based attack scenario, an attacker could host a specially crafted website that is designed to exploit the vulnerability through Internet Explorer and then convince a user to view the website. An attacker could also embed an ActiveX control marked “safe for initialization” in an application or Microsoft Office document that hosts the IE rendering engine. The attacker could also take advantage of compromised websites and websites that accept or host user-provided content or advertisements. These websites could contain specially crafted content that could exploit the vulnerability.
As such upon interaction with malicious documents of any popular kind the CobInt Trojan: rich text documents, spreadsheets, presentations and databases. Whenever they are opened a notification box will appear asking the users to enable the built-in scripts, if this is done the infection will follow.
Three other Office related vulnerabilities that are being used are the following:
- CVE-2017-8570 — A remote code execution vulnerability exists in Microsoft Office software when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could use a specially crafted file to perform actions in the security context of the current user. For example, the file could then take actions on behalf of the logged-on user with the same permissions as the current user.
- CVE-2017-11882 — Microsoft Office 2007 Service Pack 3, Microsoft Office 2010 Service Pack 2, Microsoft Office 2013 Service Pack 1, and Microsoft Office 2016 allow an attacker to run arbitrary code in the context of the current user by failing to properly handle objects in memory.
- CVE-2018-0802 — Equation Editor in Microsoft Office 2007, Microsoft Office 2010, Microsoft Office 2013, and Microsoft Office 2016 allow a remote code execution vulnerability due to the way objects are handled in memory.
Related scripts that can help deliver the Trojan threat to the target computers include also web scripts — they can cause the dangerous behavior and can make use of various interactive elements: banners, pop-ups, ads and etc.
As the ongoing attacks target financial institutions the Trojan installation code can be embedded in application installers — they are hacker-created setup files of popular software that the clients or company employees might use. They can uploaded to hacker-controlled download portals that mimic the official vendor download pages. By using similar sounding domain names and security certificates the users can be fooled into downloading the malicious installer packages.

CobInt Trojan – Detailed Description
The CobInt Trojan infection follows a complex infection pattern– that is generally broken into three main stages.
The first stage of infection is the payload delivery itself. Depending on the method of infection this can be done via a script or an application dropper. It would connect to a predefined download server from where on the second stage modules are downloaded. The entire CobInt Trojan is modular in nature and it can interact with components that are downloaded in different stages, this allows the criminals to devise custom parameters according to each individual campaign or target itself. This step acquires the main malicious module and any components that are required during the forthcoming installation.
The CobInt Trojan then be started which is the second step as defined in the behavior pattern. Like other typical strains it will connect to a specific hacker-controlled server. This is done via a secure, stable and encrypted connection which allows the operators to spy on the users, take over control of their machines and deploy other threats.
During its execution the various processes are disguised as Windows functions by employing an advanced protection stealth protection module. It is able to hook up to system processes and impersonate them. By comparing it to other similar threats it can also include a data harvesting process which can harvest information that can be grouped into two main categories:
- Private User Data — The malicious engine can hijack sensitive information that can be used to expose the identity of the victims. An example list includes their name, address, location, interests, location and any stored account credentials.
- Campaign Metrics — The malicious engine can harvest data that can be used to optimize the campaigns. This includes a report of all installed hardware components, operating system values and user settings.
The third step in the infection process is the deployment of all additional modules. They can be different depending on the ongoing campaign instructions.
Future versions can be configured to run several processes such as the following:
- Windows Registry Modifications — A delivered module can be configured into applying various changes to the Windows Registry. If they are made against the operating system then overall performance may degrade. Modifications to individual applications can result in the inability to run certain functions.
- Persistent Installation — The CobInt Trojan can be installed as a persistent threat which will automatically start the engine once the computer is powered on. This can alo disable certain system services and access to the recovery boot menu.
- Delete Commands — The engine can identify and delete Shadow Volume Copies and System Restore points. This can make system restore very difficult.
- Additional Modules Deployment — Infected host can be ordered into downloading other threats automatically.
We anticipate that the Trojan will be updated in the future with additional functionality.

Remove CobInt Trojan Trojan
If your computer system got infected with the CobInt Trojan Trojan, you should have a bit of experience in removing malware. You should get rid of this Trojan as quickly as possible before it can have the chance to spread further and infect other computers. You should remove the Trojan and follow the step-by-step instructions guide provided below.
Note! Your computer system may be affected by CobInt Trojan and other threats.
Scan Your PC with SpyHunter
SpyHunter is a powerful malware removal tool designed to help users with in-depth system security analysis, detection and removal of CobInt Trojan.
Keep in mind, that SpyHunter’s scanner is only for malware detection. If SpyHunter detects malware on your PC, you will need to purchase SpyHunter’s malware removal tool to remove the malware threats. Read our SpyHunter 5 review. Click on the corresponding links to check SpyHunter’s EULA, Privacy Policy and Threat Assessment Criteria.
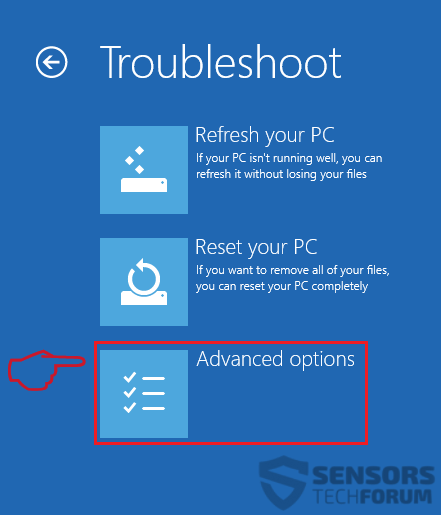
To remove CobInt Trojan follow these steps:
Use SpyHunter to scan for malware and unwanted programs
Preparation before removing CobInt Trojan.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
Step 1: Scan for CobInt Trojan with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
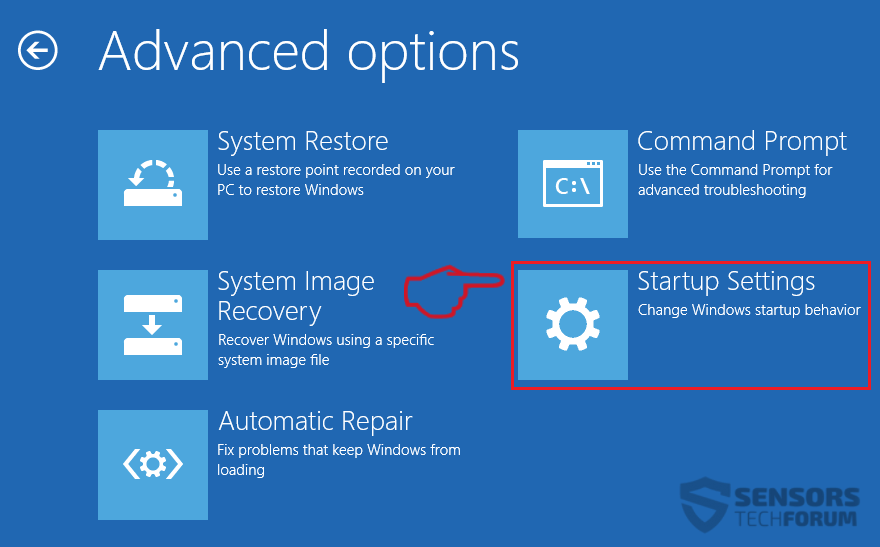
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by CobInt Trojan on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
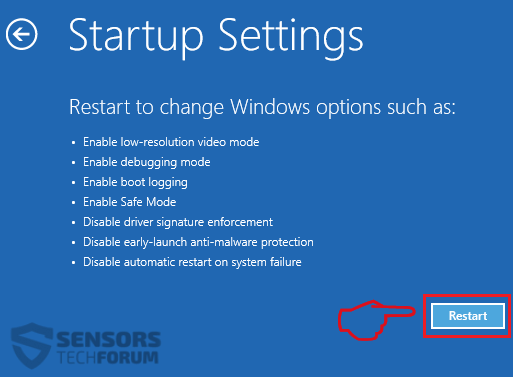
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by CobInt Trojan there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
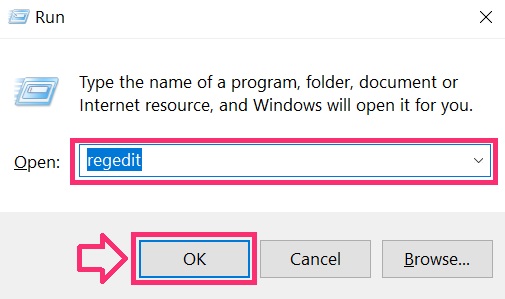
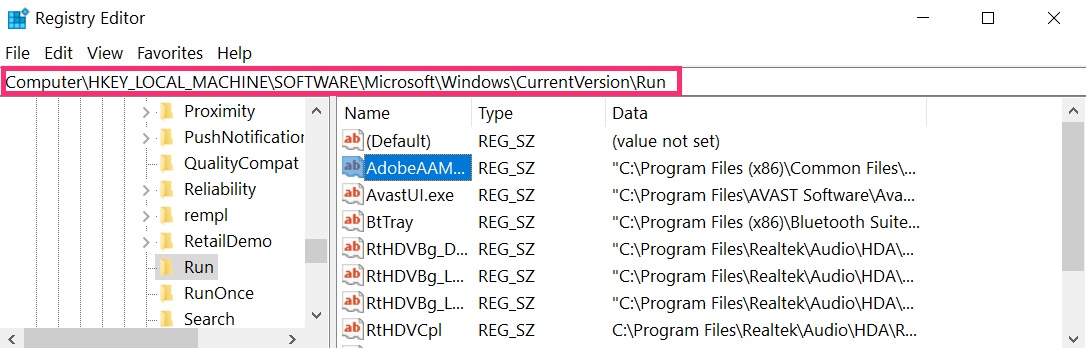
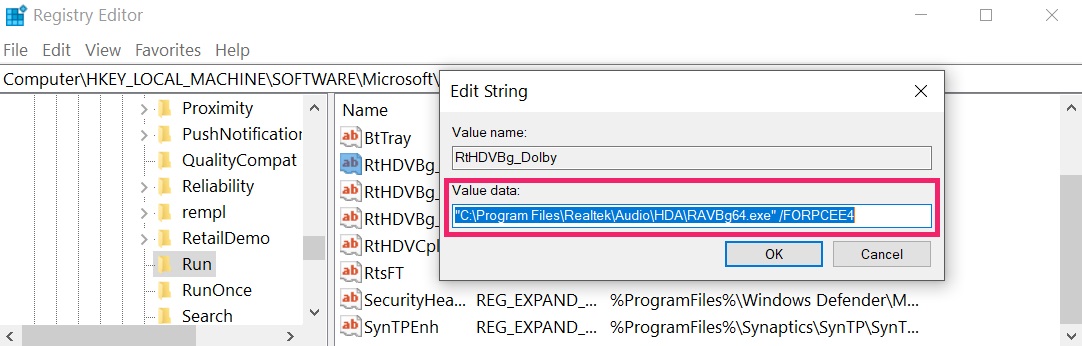 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by CobInt Trojan on your PC.
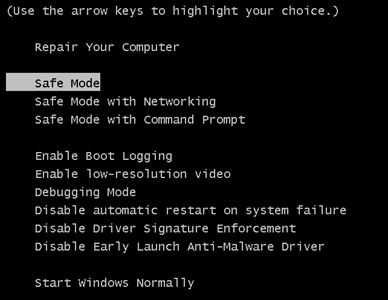
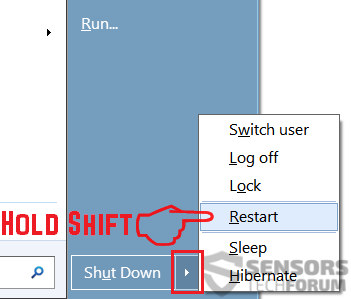
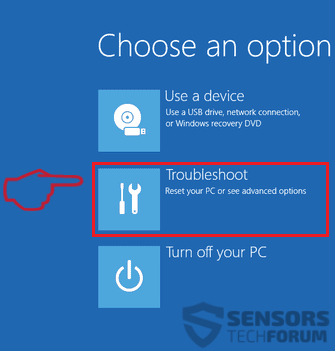
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
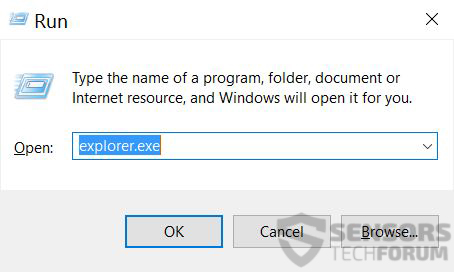
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
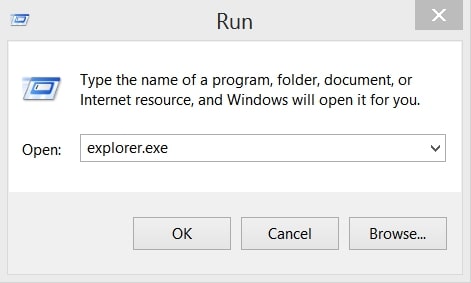
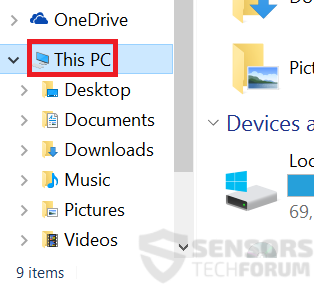
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
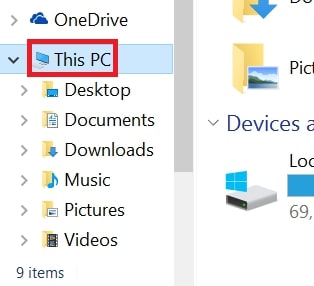
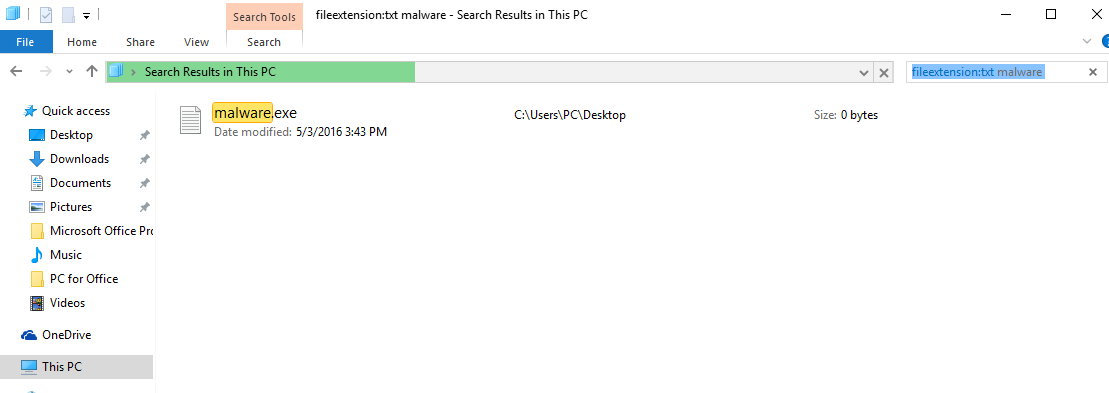
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
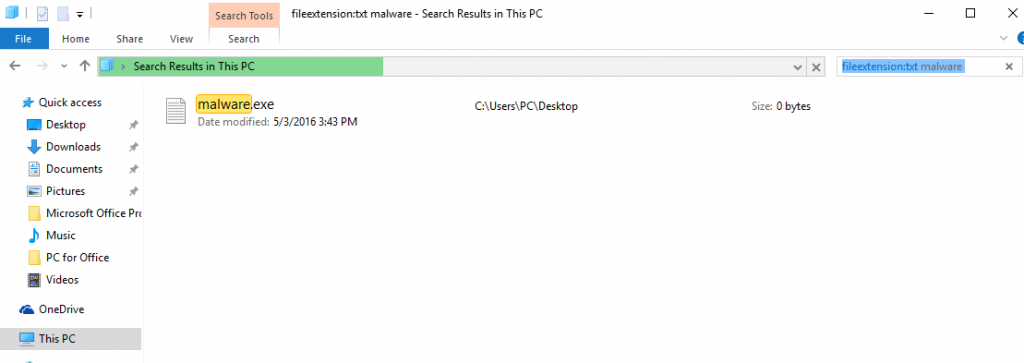
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
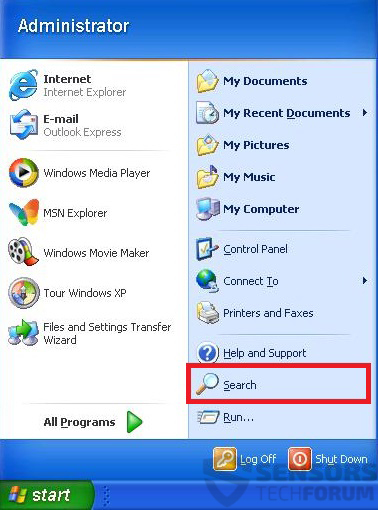
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
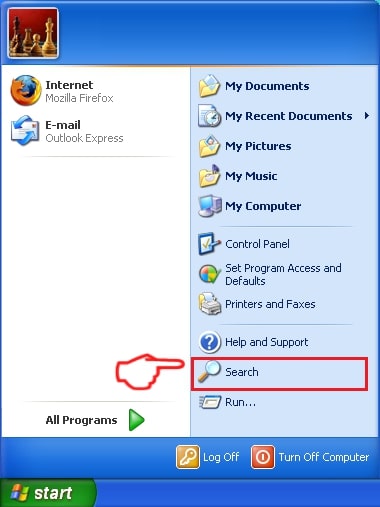
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
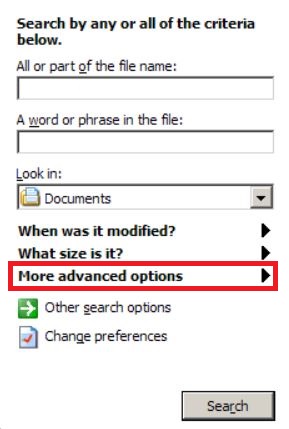
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
CobInt Trojan FAQ
What Does CobInt Trojan Trojan Do?
The CobInt Trojan Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like CobInt Trojan, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can CobInt Trojan Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can CobInt Trojan Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the CobInt Trojan Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this CobInt Trojan how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on CobInt Trojan?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the CobInt Trojan threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.



 1. For Windows XP, Vista and 7.
1. For Windows XP, Vista and 7. 2. For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
2. For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10. Fix registry entries created by malware and PUPs on your PC.
Fix registry entries created by malware and PUPs on your PC.

 1. Install SpyHunter to scan for CobInt Trojan and remove them.
1. Install SpyHunter to scan for CobInt Trojan and remove them.