 This article has been created to help you remove Red CERBER ransomware’s _READ_THIS_FILE_ variant and help you restore files that have been encrypted by this virus.
This article has been created to help you remove Red CERBER ransomware’s _READ_THIS_FILE_ variant and help you restore files that have been encrypted by this virus.
One of the most devastating ransomware infections out there, called Red CERBER ransomware has been reported to be released in a new malicious version. Ever since the Red wallpaper Cerber variants were released, the previous versions were using different names for ransom notes – _{random}_README_.hta,_HELP_DECRYPT_{RANDOM}.hta or _HELP_HELP_HELP_{RANDOM}.hta. Now, the format of the ransom notes is _READ_THIS_FILE_{random}.hta and the virus has other incremental changes in addition to these ones. It aims to encrypt the files on compromised computers and leave a 4 A-Z 0-9 file extension after the encrypted files, for example .bfO5. The victim is always asked to pay for a program that is special and will decrypt the encoded files which are no longer openable after infection. In case you have become a victim of this Cerber ransomware variant, recommendations are to read this article carefully.

Threat Summary
| Name | Red CERBER |
| Type | Ransomware Virus |
| Short Description | This Cerber ransomware variant encrypts files with the RSA-512 cipher and an RC4 encryption algorithm adding four randomly generated A-Z 0-9 characters(ex. .b43s) as a file extension to the encrypted files and asks a ransom payoff for decryption. |
| Symptoms | Files are enciphered and become inaccessible by any type of software. A ransom note with instructions for paying the ransom shows as a _READ_THIS_FILE_{random}.hta file. Also may add the following audio message after encryption: |
| Distribution Method | Spam Emails, Email Attachments, File Sharing Networks, Malicious Executable in Torrent Trackers. |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
| Data Recovery Tool | Windows Data Recovery by Stellar Phoenix Notice! This product scans your drive sectors to recover lost files and it may not recover 100% of the encrypted files, but only few of them, depending on the situation and whether or not you have reformatted your drive. |

Red CERBER 2017 – How Does It Infect
The infection procedure of this Red CERBER ransomware variant is still a very widespread and powerful e-mail and other forms of spam. To assist with this, there are multiple forms of .ZIP and other archived type of files that are send via multiple methods:
- The Nemucod Trojan downloader.
- The pseudoDarkleech Rig EK.
- Rig EK version 4.0.
The latest reports of infections by Red CERBER ransomware are also connected with the usage of a so-called “BLANK SLATE” malicious spam. These particular messages are blank e-mails without any content what so ever carrying the malicious attachment with themselves. The way the attack is carried is that the malicious attachments are .ZIP files. The zip files are carrying either a document or a malicious javascript type of files (.js). The malicious JavaScript causes infection immediately after being opened and the .doc file which is a Microsoft Word file says you need to enable the content. As reported by PaloAlto networks the files are spread with double archives. The first archive in which are the malicious file has a name, like 1223_ZIP.zip and it is also archived in another .zip archive with a name that has 9 random digits, for example 38285032.zip.
To learn how to protect yourself from malicious archives without having to open them, please read the following related article:

Red CERBER 2017’s Infection – What Has Changed
Not much has changed when an infection with the Red CERBER virus takes place, but there are some changes, indeed. The first change is the C2 servers which are used to connect and download the malicious payload. The latest variant of Red CERBER using _READ_THIS_FILE_.hta ransom note has been reported to connect to the following remote hosts:
→ 11.11.127.0 with a subnet mask 27
14.77.242.0 with a subnet mask 27
87.98.148.0 with a subnet mask 22
What follows through is the standard Red CERBER infection procedure. Numerous files are downloaded by connecting to distribution sites. These sites are not online for long periods of time and they are used to download the malicious payload onto the computer of the user via unsecured ports on it. The payload may consist of the following type of files:
- Three executables, one with single digit as a name, for example 3.exe, one with three digits, for example 232.exe and one with random digits and letters, for example 52Si7.exe.
- Two .dat files, named read.php and user.php.
After the files of this Red CERBER variant are dropped on the computer which has been infected, the malware activates scripts that perform different unauthorized by the user activities:
- It drops files that appear as if they are legitimate.
- It reads the allowing and trusted programs lists on Windows.
- It looks for different processes that are running and spawns new processes with legitimate names to avoid detection. May even spawn concealed processes that do not appear in the Windows Task Manager.
It modifies the following system files – wscript.exe, WScript.exe, WScript.exe,mui, sortdefault.nls, wshom.ocx, stdole2.tlb, KERNELBASE.dll.mui, msxml3.dll.
In addition to this, the virus(https://sensorstechforum.com/remove-cerber-4-1-5-ransomware-restore-files/) may also attack the following Windows Registry Editor sub-keys to modify settings that will suit it’s needs which are to encrypt the files uninterruptedly:
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
→HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
→HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes
→HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes
→HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography
Amongst other activities of the Red CERBER 2017 virus may be included the before-seen shutting down of significant database processes which may be running. It was previously detected in the code of the ransomware that the following processes are scanned for and if detected, ended as tasks, to ensure database encryption:
→ msftesql.exe sqlagent.exe sqlbrowser.exe sqlservr.exe sqlwriter.exe oracle.exe ocssd.exe dbsnmp.exe synctime.exe mydesktopqos.exe agntsvc.exeisqlplussvc.exe xfssvccon.exe mydesktopservice.exe ocautoupds.exe agntsvc.exeagntsvc.exe agntsvc.exeencsvc.exe firefoxconfig.exe tbirdconfig.exe ocomm.exe mysqld.exe mysqld-nt.exe mysqld-opt.exe dbeng50.exe sqbcoreservice.exe

Red CERBER 2017 – The Encryption Process
The encryption procedure of Red CERBER has remained rather the same, with the exclusion that there was an intermediary version of it’s previous HELP_HELP_HELP ransomware variant. This version initially began with changing the names on the encrypted files, but it later stopped changing their names and changed only their file extensions. Then, the ones who are behind the virus, if the same hackers, may have decided to switch back to changing the names of the files in this version.
Whatever the case may be, files encrypted by the _READ_THIS_FILE_ Red CERBER variant appear in a completely random way and cannot be recognized at all, for example:
For the encryption process, the virus may still use the same RSA-512 encryption algorithm. It is combined with an RC4 encryption mode and results in the files becoming no longer openable. What is worse about this is that after the virus encrypts the files on the compromised computer, it generates two types of RSA keys – public and private. Both are required to decrypt your files, especially the private key. While the public key could be factorized, using Python in Ubuntu, it is very difficult to calculate the private key, especially, because of the fact that a unique type of key has been used for each file or set of files – it is simply because of the configuration.
Similar to the other Red CERBER ransomware iterations, the virus still targets files that are used very often on user PC’s:
→ ” .123″, ” .1cd”, “.3dm”, “.3ds”, “.3fr”, “.3g2”, “.3gp”, “.3pr”, “.602”, “.7z”, “.7zip”, “.aac”, “.ab4”, “.abd”, “.acc”, “.accdb”, “.accde”, “.accdr”, “.accdt”, “.ach”, “.acr”, “.act”, “.adb”, “.adp”, “.ads”, “.aes”, “.agdl”, “.ai”, “.aiff”, “.ait”, “.al”, “.aoi”, “.apj”, “.apk”, “.arc”, “.arw”, “.ascx”, “.asf”, “.asm”, “.asp”, “.aspx”, “.asset”, “.asx”, “.atb”, “.avi”, “.awg”, “.back”, “.backup”, “.backupdb”, “.bak”, “.bank”, “.bat”, “.bay”, “.bdb”, “.bgt”, “.bik”, “.bin”, “.bkp”, “.blend”, “.bmp”, “.bpw”, “.brd”, “.bsa”, “.bz2”, “.c”, “.cash”, “.cdb”, “.cdf”, “.cdr”, “.cdr3”, “.cdr4”, “.cdr5”, “.cdr6”, “.cdrw”, “.cdx”, “.ce1”, “.ce2”, “.cer”, “.cfg”, “.cfn”, “.cgm”, “.cib”, “.class”, “.cls”, “.cmd”, “.cmt”, “.config”, “.contact”, “.cpi”, “.cpp”, “.cr2”, “.craw”, “.crt”, “.crw”, “.cry”, “.cs”, “.csh”, “.csl”, “.csr”, “.css”, “.csv”, “.d3dbsp”, “.dac”, “.das”, “.dat”, “.db”, “.db3”, “.db_journal”, “.dbf”, “.dbx”, “.dc2”, “.dch”, “.dcr”, “.dcs”, “.ddd”, “.ddoc”, “.ddrw”, “.dds”, “.def”, “.der”, “.des”, “.design”, “.dgc”, “.dgn”, “.dif”, “.dip”, “.dit”, “.djv”, “.djvu”, “.dng”, “.doc”, “.docb”, “.docm”, “.docx”, “.dot”, “.dotm”, “.dotx”, “.drf”, “.drw”, “.dtd”, “.dwg”, “.dxb”, “.dxf”, “.dxg”, “.edb”, “.eml”, “.eps”, “.erbsql”, “.erf”, “.exf”, “.fdb”, “.ffd”, “.fff”, “.fh”, “.fhd”, “.fla”, “.flac”, “.flb”, “.flf”, “.flv”, “.forge”, “.fpx”, “.frm”, “.fxg”, “.gbr”, “.gho”, “.gif”, “.gpg”, “.gray”, “.grey”, “.groups”, “.gry”, “.gz”, “.h”, “.hbk”, “.hdd”, “.hpp”, “.html”, “.hwp”, “.ibank”, “.ibd”, “.ibz”, “.idx”, “.iif”, “.iiq”, “.incpas”, “.indd”, “.info”, “.info_”, “.iwi”, “.jar”, “.java”, “.jnt”, “.jpe”, “.jpeg”, “.jpg”, “.js”, “.json”, “.k2p”, “.kc2”, “.kdbx”, “.kdc”, “.key”, “.kpdx”, “.kwm”, “.laccdb”, “.lay”, “.lay6”, “.lbf”, “.lck”, “.ldf”, “.lit”, “.litemod”, “.litesql”, “.lock”, “.ltx”, “.lua”, “.m”, “.m2ts”, “.m3u”, “.m4a”, “.m4p”, “.m4u”, “.m4v”, “.ma”, “.mab”, “.map “.max”, “.mbx”, “.md”, “.mdb”, “.mdc”, “.mdf”, “.mef”, “.mfw”, “.mid”, “.mkv”, “.mlb”, “.mml”, “.mmw”, “.mny”, “.money”, “.moneywell”, “.mos”, “.mov”, “.mp3”, “.mp4”, “.mpeg”, “.mpg”, “.mrw”, “.ms11”, “.msf”, “.msg”, “.mts”, “.myd”, “.myi”, “.nd”, “.ndd”, “.ndf”, “.nef”, “.nk2”, “.nop”, “.nrw”, “.ns2”, “.ns3”, “.ns4”, “.nsd”, “.nsf”, “.nsg”, “.nsh”, “.nvram”, “.nwb”, “.nx2”, “.nxl”, “.nyf”, “.oab”, “.obj”, “.odb”, “.odc”, “.odf”, “.odg”, “.odm”, “.odp”, “.ods”, “.odt”, “.ogg”, “.oil”, “.omg”, “.one”, “.onenotec2”, “.orf”, “.ost”, “.otg”, “.oth”, “.otp”, “.ots”, “.ott”, “.p12”, “.p7b”, “.p7c”, “.pab”, “.pages”, “.paq”, “.pas”, “.pat”, “.pbf”, “.pcd”, “.pct”, “.pdb”, “.pdd”, “.pdf”, “.pef”, “.pem”, “.pfx”, “.php”, “.pif”, “.pl”, “.plc”, “.plus_muhd”, “.pm”, “.pm!”, “.pmi”, “.pmj”, “.pml”, “.pmm”, “.pmo”, “.pmr”, “.pnc”, “.pnd”, “.png”, “.pnx”, “.pot”, “.potm”, “.potx”, “.ppam”, “.pps”, “.ppsm”, “.ppsx”, “.ppt”, “.pptm”, “.pptx”, “.prf”, “.private”, “.ps”, “.psafe3”, “.psd”, “.pspimage”, “.pst”, “.ptx”, “.pub”, “.pwm”, “.py”, “.qba”, “.qbb”, “.qbm”, “.qbr”, “.qbw”, “.qbx”, “.qby”, “.qcow”, “.qcow2”, “.qed”, “.qtb”, “.r3d”, “.raf”, “.rar”, “.rat”, “.raw”, “.rb”, “.rdb”, “.re4”, “.rm”, “.rtf”, “.rvt”, “.rw2”, “.rwl”, “.rwz”, “.s3db”, “.safe”, “.sas7bdat”, “.sav”, “.save”, “.say”, “.sch”, “.sd0”, “.sda”, “.sdb”, “.sdf”, “.secret”, “.sh”, “.sldm”, “.sldx”, “.slk”, “.slm”, “.sql”, “.sqlite”, “.sqlite-shm”, “.sqlite-wal”, “.sqlite3”, “.sqlitedb”, “.sr2”, “.srb”, “.srf”, “.srs”, “.srt”, “.srw”, “.st4”, “.st5”, “.st6”, “.st7”, “.st8”, “.stc”, “.std”, “.sti”, “.stl”, “.stm”, “.stw”, “.stx”, “.svg”, “.swf”, “.sxc”, “.sxd”, “.sxg”, “.sxi”, “.sxm”, “.sxw”, “.tar”, “.tax”, “.tbb”, “.tbk”, “.tbn”, “.tex”, “.tga”, “.tgz”, “.thm”, “.tif”, “.tiff”, “.tlg”, “.tlx”, “.txt”, “.uop”, “.uot”, “.upk”, “.usr”, “.vb”, “.vbox”, “.vbs”, “.vdi”, “.vhd”, “.vhdx”, “.vmdk”, “.vmsd”, “.vmx”, “.vmxf”, “.vob”, “.vpd”, “.vsd”, “.wab”, “.wad”, “.wallet”, “.war”, “.wav”, “.wb2”, “.wk1”, “.wks”, “.wma”, “.wmf”, “.wmv”, “.wpd”, “.wps”, “.x11”, “.x3f”, “.xis”, “.xla”, “.xlam”, “.xlc”, “.xlk”, “.xlm”, “.xlr”, “.xls”, “.xlsb”, “.xlsm”, “.xlsx”, “.xlt”, “.xltm”, “.xltx”, “.xlw”, “.xml”, “.xps”, “.xxx”, “.ycbcra” “.yuv”, “.zip”
What is interesting is that Red CERBER is configured so that it skips certain Windows folders to encrypt, so that your operating system is still inact:
\\appdata\\roaming\\microsoft\\office\\
\\excel\\
\\microsoft sql server\\
\\onenote\\
\\outlook\\
\\powerpoint\\
\\steam\\
\\the bat!\\
\\thunderbird\\
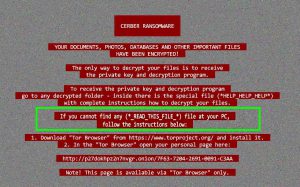
After an encryption takes place, just like with other Red CERBER ransomware variants, the ransom notes are dropped, with the following names:
- _READ_THIS_FILE_{random}.jpg
- _READ_THIS_FILE_{random}.txt
- _READ_THIS_FILE_{random}.hta
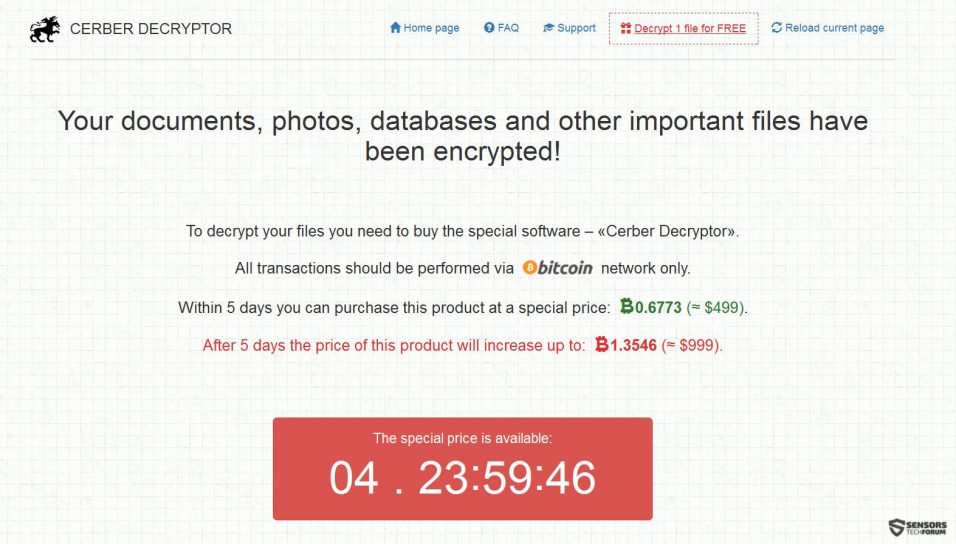
The virus is also very thorough in it’s Tor-based payment web page, which can be accessed from the instruction files:
There, you are requested to pay a hefty ransom fee for a decryptor, which is highly inadvisable, because:
- You cannot trust cyber-criminals.
- You may not get all your files back by paying a hefty ransom fee.

Remove Red CERBER 2017 and Restore Encrypted Files with Random Names
Before attempting any removal or file restoration by this ransomware infection, we would recommend that you backup all your files, even if they are encrypted.
Then, for the removal of the virus, you have two approaches, both illustrated in the instructions below. You can begin to hunt for the files manually by taking advantage of the manual instructions after isolating the threat in safe mode. However, if you lack the time or the experience in malware removal, experts strongly recommend to use a specific anti-malware program which will automatically remove all associated files with CERBER and protect your system in the future too.
In case you are wondering how to restore your files, there are several alternative methods which you can attempt to use in step “2. Restore files encrypted by Red CERBER” below. They are in no way tested, so we advise using them on copies of your files and solely at your own risk. They are not 100% effective, but we have reports on our forums, that indicate that users were able to restore multiple files that were important to them this way.
style>
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
Step 1: Scan for Red CERBER with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
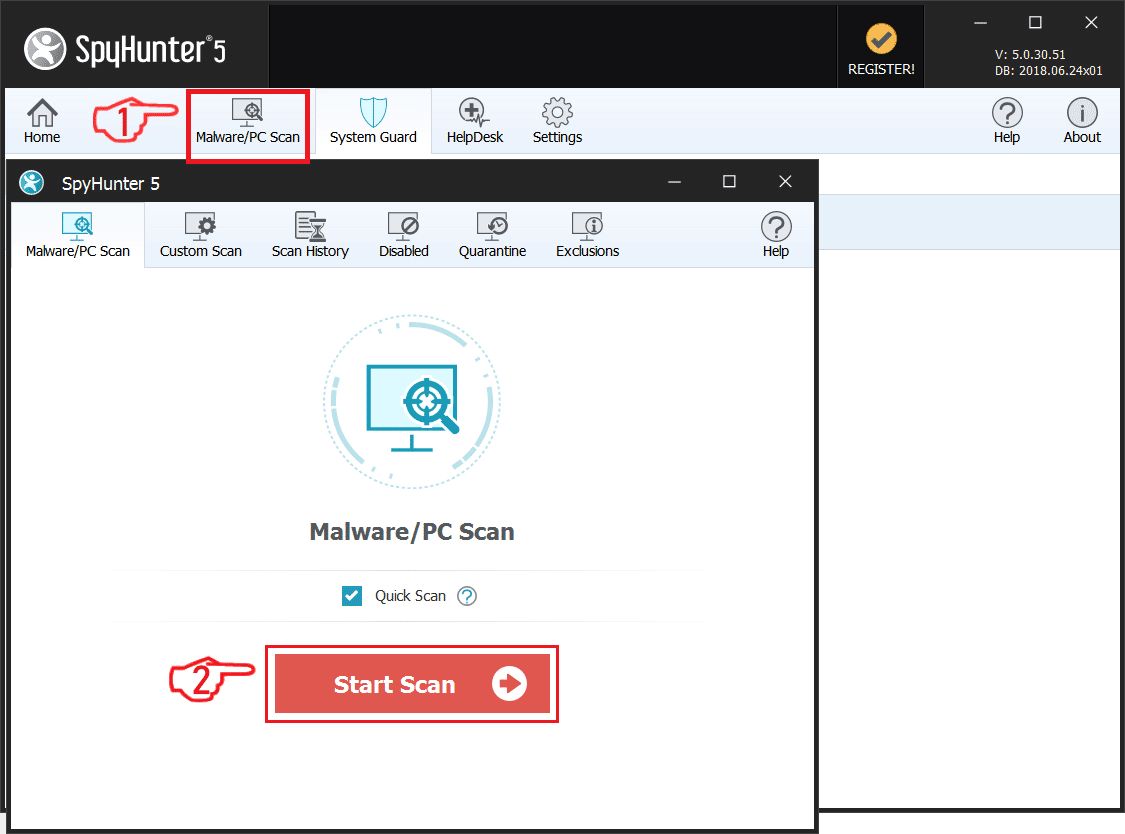
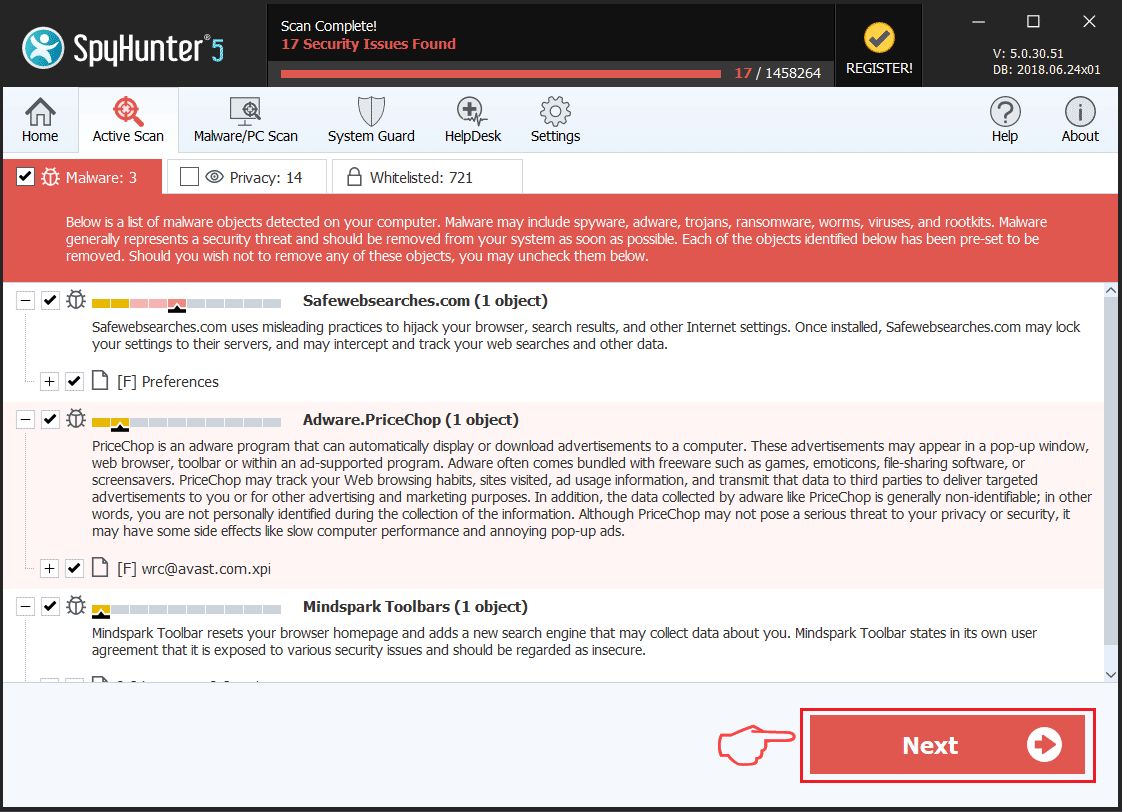
Ransomware Automatic Removal - Video Guide
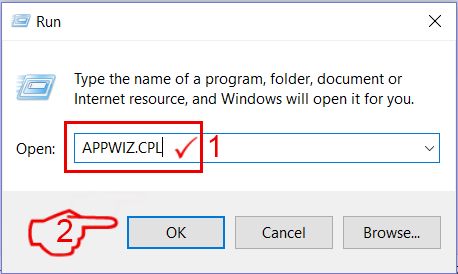
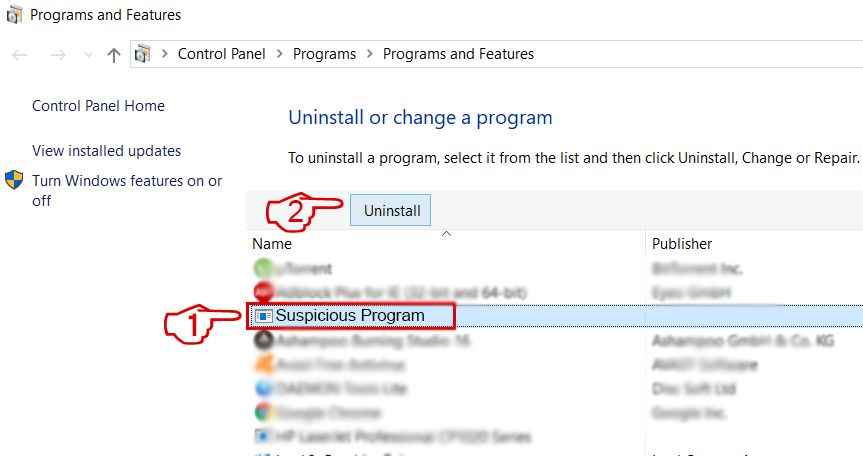
Step 2: Uninstall Red CERBER and related malware from Windows
Here is a method in few easy steps that should be able to uninstall most programs. No matter if you are using Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista or XP, those steps will get the job done. Dragging the program or its folder to the recycle bin can be a very bad decision. If you do that, bits and pieces of the program are left behind, and that can lead to unstable work of your PC, errors with the file type associations and other unpleasant activities. The proper way to get a program off your computer is to Uninstall it. To do that:

 Follow the instructions above and you will successfully delete most unwanted and malicious programs.
Follow the instructions above and you will successfully delete most unwanted and malicious programs.
Step 3: Clean any registries, created by Red CERBER on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by Red CERBER there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
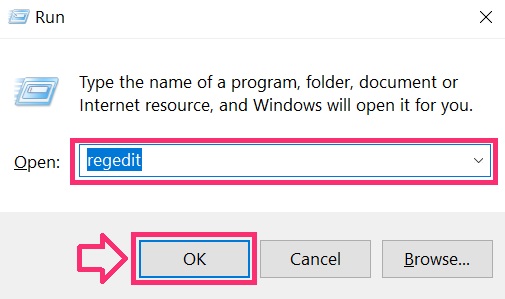
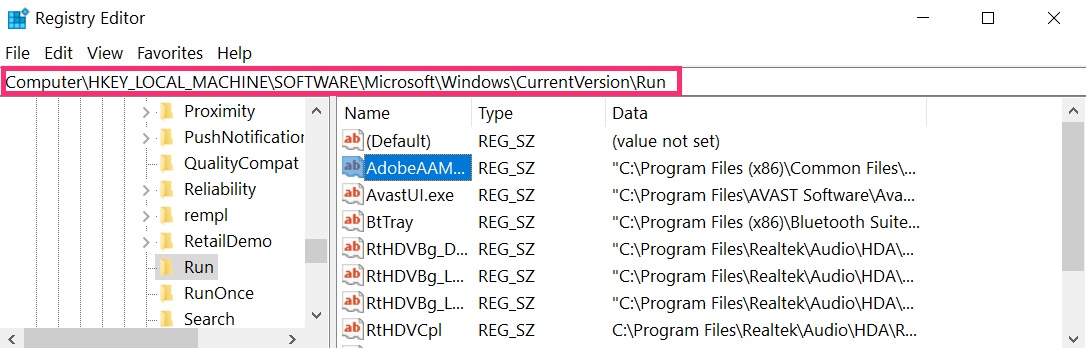
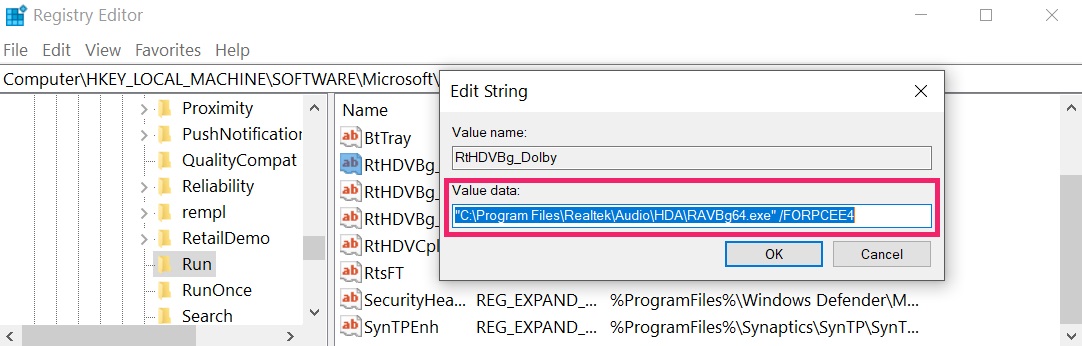 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Before starting "Step 4", please boot back into Normal mode, in case you are currently in Safe Mode.
This will enable you to install and use SpyHunter 5 successfully.
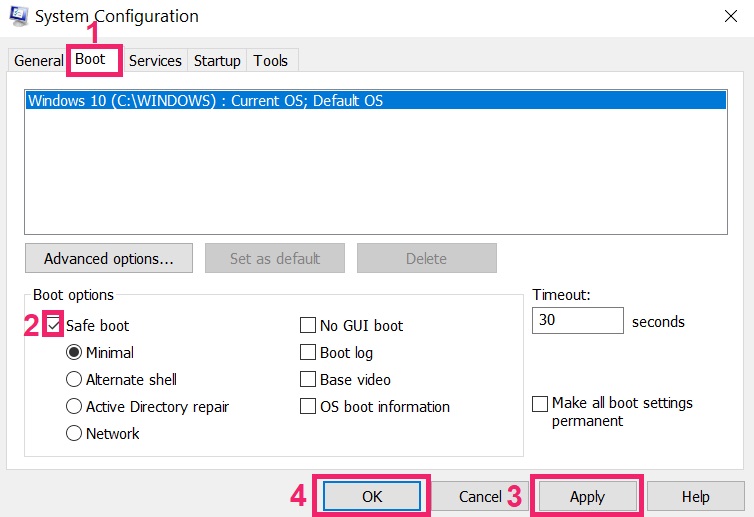
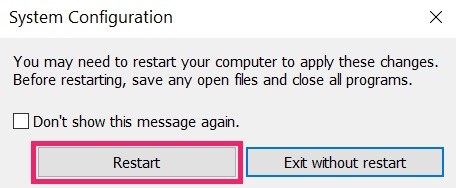
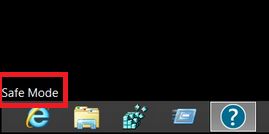
Step 4: Boot Your PC In Safe Mode to isolate and remove Red CERBER

Step 5: Try to Restore Files Encrypted by Red CERBER.
Method 1: Use STOP Decrypter by Emsisoft.
Not all variants of this ransomware can be decrypted for free, but we have added the decryptor used by researchers that is often updated with the variants which become eventually decrypted. You can try and decrypt your files using the instructions below, but if they do not work, then unfortunately your variant of the ransomware virus is not decryptable.
Follow the instructions below to use the Emsisoft decrypter and decrypt your files for free. You can download the Emsisoft decryption tool linked here and then follow the steps provided below:
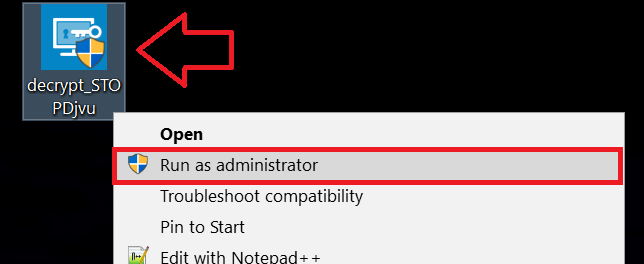
1 Right-click on the decrypter and click on Run as Administrator as shown below:
2. Agree with the license terms:
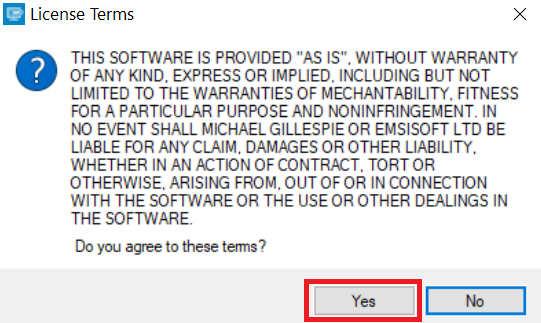
3. Click on "Add Folder" and then add the folders where you want files decrypted as shown underneath:
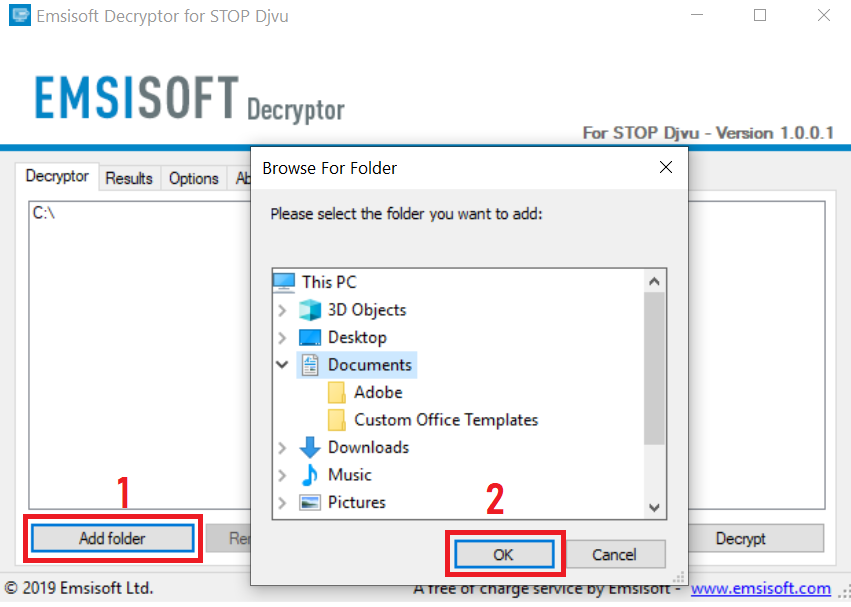
4. Click on "Decrypt" and wait for your files to be decoded.
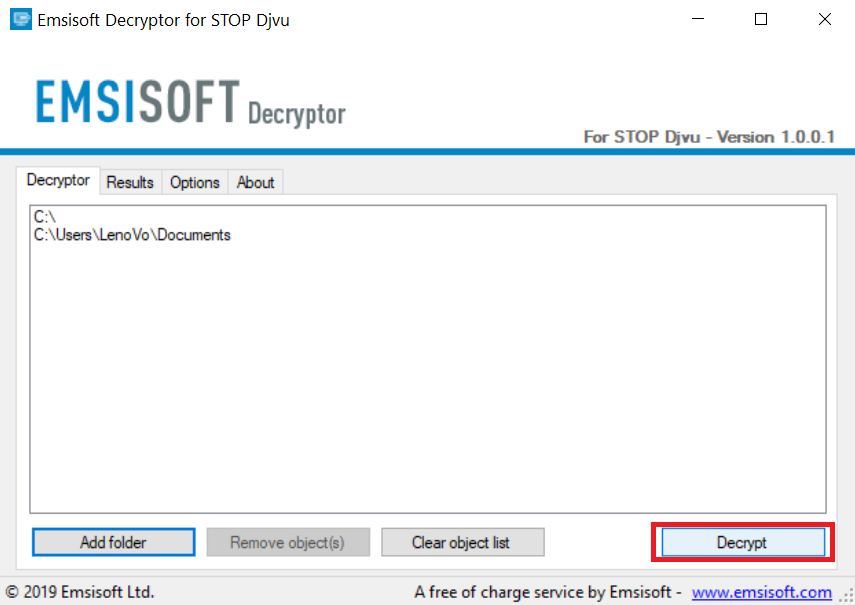
Note: Credit for the decryptor goes to Emsisoft researchers who have made the breakthrough with this virus.
Method 2: Use data recovery software
Ransomware infections and Red CERBER aim to encrypt your files using an encryption algorithm which may be very difficult to decrypt. This is why we have suggested a data recovery method that may help you go around direct decryption and try to restore your files. Bear in mind that this method may not be 100% effective but may also help you a little or a lot in different situations.
Simply click on the link and on the website menus on the top, choose Data Recovery - Data Recovery Wizard for Windows or Mac (depending on your OS), and then download and run the tool.
Red CERBER-FAQ
What is Red CERBER Ransomware?
Red CERBER is a ransomware infection - the malicious software that enters your computer silently and blocks either access to the computer itself or encrypt your files.
Many ransomware viruses use sophisticated encryption algorithms to make your files inaccessible. The goal of ransomware infections is to demand that you pay a ransom payment to get access to your files back.
What Does Red CERBER Ransomware Do?
Ransomware in general is a malicious software that is designed to block access to your computer or files until a ransom is paid.
Ransomware viruses can also damage your system, corrupt data and delete files, resulting in the permanent loss of important files.
How Does Red CERBER Infect?
Via several ways.Red CERBER Ransomware infects computers by being sent via phishing emails, containing virus attachment. This attachment is usually masked as an important document, like an invoice, bank document or even a plane ticket and it looks very convincing to users.
Another way you may become a victim of Red CERBER is if you download a fake installer, crack or patch from a low reputation website or if you click on a virus link. Many users report getting a ransomware infection by downloading torrents.
How to Open .Red CERBER files?
You can't without a decryptor. At this point, the .Red CERBER files are encrypted. You can only open them once they are decrypted using a specific decryption key for the particular algorithm.
What to Do If a Decryptor Does Not Work?
Do not panic, and backup the files. If a decryptor did not decrypt your .Red CERBER files successfully, then do not despair, because this virus is still new.
Can I Restore ".Red CERBER" Files?
Yes, sometimes files can be restored. We have suggested several file recovery methods that could work if you want to restore .Red CERBER files.
These methods are in no way 100% guaranteed that you will be able to get your files back. But if you have a backup, your chances of success are much greater.
How To Get Rid of Red CERBER Virus?
The safest way and the most efficient one for the removal of this ransomware infection is the use a professional anti-malware program.
It will scan for and locate Red CERBER ransomware and then remove it without causing any additional harm to your important .Red CERBER files.
Can I Report Ransomware to Authorities?
In case your computer got infected with a ransomware infection, you can report it to the local Police departments. It can help authorities worldwide track and determine the perpetrators behind the virus that has infected your computer.
Below, we have prepared a list with government websites, where you can file a report in case you are a victim of a cybercrime:
Cyber-security authorities, responsible for handling ransomware attack reports in different regions all over the world:
Germany - Offizielles Portal der deutschen Polizei
United States - IC3 Internet Crime Complaint Centre
United Kingdom - Action Fraud Police
France - Ministère de l'Intérieur
Italy - Polizia Di Stato
Spain - Policía Nacional
Netherlands - Politie
Poland - Policja
Portugal - Polícia Judiciária
Greece - Cyber Crime Unit (Hellenic Police)
India - Mumbai Police - CyberCrime Investigation Cell
Australia - Australian High Tech Crime Center
Reports may be responded to in different timeframes, depending on your local authorities.
Can You Stop Ransomware from Encrypting Your Files?
Yes, you can prevent ransomware. The best way to do this is to ensure your computer system is updated with the latest security patches, use a reputable anti-malware program and firewall, backup your important files frequently, and avoid clicking on malicious links or downloading unknown files.
Can Red CERBER Ransomware Steal Your Data?
Yes, in most cases ransomware will steal your information. It is a form of malware that steals data from a user's computer, encrypts it, and then demands a ransom in order to decrypt it.
In many cases, the malware authors or attackers will threaten to delete the data or publish it online unless the ransom is paid.
Can Ransomware Infect WiFi?
Yes, ransomware can infect WiFi networks, as malicious actors can use it to gain control of the network, steal confidential data, and lock out users. If a ransomware attack is successful, it could lead to a loss of service and/or data, and in some cases, financial losses.
Should I Pay Ransomware?
No, you should not pay ransomware extortionists. Paying them only encourages criminals and does not guarantee that the files or data will be restored. The better approach is to have a secure backup of important data and be vigilant about security in the first place.
What Happens If I Don't Pay Ransom?
If you don't pay the ransom, the hackers may still have access to your computer, data, or files and may continue to threaten to expose or delete them, or even use them to commit cybercrimes. In some cases, they may even continue to demand additional ransom payments.
Can a Ransomware Attack Be Detected?
Yes, ransomware can be detected. Anti-malware software and other advanced security tools can detect ransomware and alert the user when it is present on a machine.
It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest security measures and to keep security software updated to ensure ransomware can be detected and prevented.
Do Ransomware Criminals Get Caught?
Yes, ransomware criminals do get caught. Law enforcement agencies, such as the FBI, Interpol and others have been successful in tracking down and prosecuting ransomware criminals in the US and other countries. As ransomware threats continue to increase, so does the enforcement activity.
About the Red CERBER Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this Red CERBER how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific malware and restore your encrypted files.
How did we conduct the research on this ransomware?
Our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, and as such, we receive daily updates on the latest malware and ransomware definitions.
Furthermore, the research behind the Red CERBER ransomware threat is backed with VirusTotal and the NoMoreRansom project.
To better understand the ransomware threat, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.
As a site that has been dedicated to providing free removal instructions for ransomware and malware since 2014, SensorsTechForum’s recommendation is to only pay attention to trustworthy sources.
How to recognize trustworthy sources:
- Always check "About Us" web page.
- Profile of the content creator.
- Make sure that real people are behind the site and not fake names and profiles.
- Verify Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter personal profiles.