Mac security is once again impacted by a very dangerous threat called the Evilquest ransomware. This is a rare and new malware which has been detected in software installers that have the virus code embedded in them. In comparison with other threats this one has includes advanced functionality.
EvilQuest Mac Ransomware Decryptor Released
Following the numerous virus reports about the discovery of the EvilQuest ransomware a decryptor has been devised by SentinelOne. This malware has remained active for over a month and is being integrated into various carrier files.
Thanks to the captured samples the analysts have been able to take a closer look at all components and modules which are installed on a typical system. One of the components which are run as part of the infection sequence appear to be vulnerable and by following these weaknesses the experts were able to devise a method to restore the affected data.
It appears that the main weak spot of the malware is found in the users tracking mechanism. Apparently the released versions of the malware do not keep track of the users who have paid the decryption sum. The actual decryption mechanism also stored some of the private decryption keys on the local machine using a simpler locking method which allowed the analysts to break the protection and come up with a way to restore the affected files.
At the moment the decryption software is available in binary form, an executable will soon be released.
EvilQuest Ransomware is Specially Designed for Mac Computers, Spreads Via Infected Packages
The EvilQuest ransomware is designed for Mac computers and is now actively being distributed by the hackers in contaminated packages. In this case the target files were pirate versions of commonly installed applications — this includes all common categories of packages such as creativity suites, productivity programs, system utilities and even games.
There are several infection strategies that can be used to spread these virus-infected packages:
- Online Download Portals — These files can be uploaded to various software download portals that are hosted by organizations, communities or individuals.
- Peer-to-Peer Networks — These are popular file-sharing networks that are used by end users to share all kinds of files, including pirate software. The most popular example is BitTorrent which is well-known to desktop users.
- Hacker-Controlled Sites, Media & Content — The computer criminals can devise various types of scam sites, redirects, multimedia and various web elements that can lead to the virus infection. Common elements which are used for the delivery include banners, pop-ups, ads and etc.
This direct delivery via applications and data is a common and effective mechanism especially if the hackers are able to coerce the users into downloading the package. At any time the criminals can choose to change the tactic if they find out that this is not an effective mechanism.
EvilQuest Mac Ransomware Capabilities and Activity
The captured samples that are identified with the threat indicate that the virus includes a lot of advanced features. It does not just simply encrypt target user data and blackmail the users as expected from most standard malware of this category. Some of the functionality that are integrated include the following:
- Keylogger Installation — The EvilQuest Mac Ransomware will install a keylogger module that is capable of hijacking the data that is entered in forms and fields, as well as track the mouse movement of the users. This information will be forwarded to the hacker controllers.
- Information gathering — The security analysis shows that the malware is fully capable of extracting data about the installed cryptocurrency software and attempt to steal the users wallets. This can be further enhanced by adding in the ability to steal personal users information which can be used to blackmail the victims. Another type of information which can be retrieved include machine information that can be used to generate a unique ID for each infected computer.
- Security Evasion — The main engine has been found to be able to run its own process in safeguarded memory regions which may not be scanned by security software. In addition the engine includes the ability to bypass security applications — this is done by identifying installed engines and reconfiguring them or stopping their services. Depending on the exact configuration they can be disabled or entirely removed.
- Trojan Operations — This Mac ransomware includes the ability to overtake control of the victim systems. This is done by launching a local client which will establish a connection to a remote hacker-controlled server.
Some of the copies of the EvilQuest ransomware have been found to be include in a Google Software Update package which is uploaded to file-sharing networks. The other payload carrier has been identified in a pirate copy of a DJ program called Mixed in Key 8. Another report on the matter lists that the virus has been found in a pirate version of Little Snitch, a popular legitimate firewall. The URL to the infected copy was shared on a Russian forum containing a Torrent tracker.
These malware copies of the virus give further details about the malware sequence. The first step is to install an executable file which is called Patch and placed in the Shared users directory. This will trigger a secondary post-installation script which will be retrieved from a remote hacker-controlled server. It is configured to load and install the ransomware executable. It will run all loaded within components mentioned above. One of the important factors related to this is the fact that at any time the hackers may choose to change the configuration, as a result other components may be loaded and run.
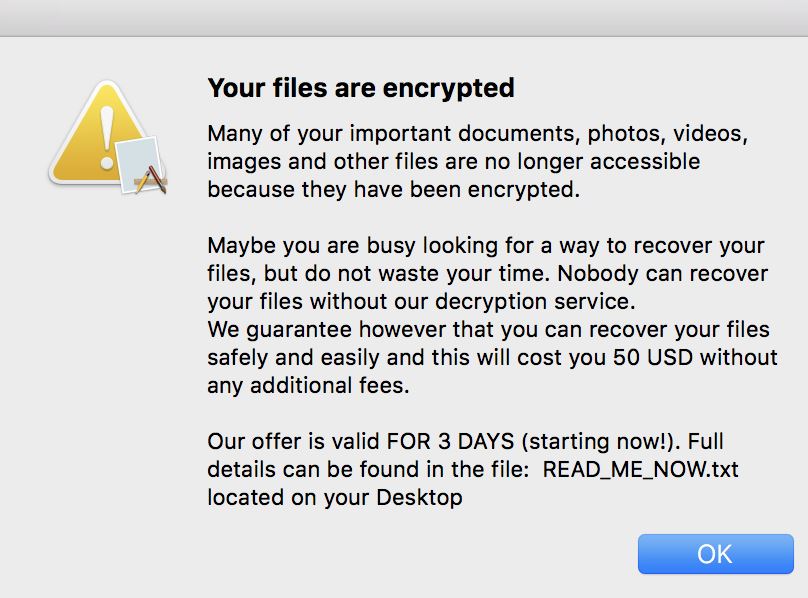
The last component which will be run is the actual file encryption phase. This will process target user data with a strong cipher, the victim files will be selected based on a built-in list of extensions. When the operation has completed running the engine will automatically create a ransom note called READ_ME_NOW which contains the blackmail message. The current version requests the sum of $50.