When a web browser is facing a major update, there are two decisions that developers usually face: whether to optimize the code or to add new features to the browser. It all sounds great up until the moment when the inevitable exploits and security gaps arise from the depths of the code. In this article, we have managed to identify the latest security flaws that have been discovered in the two most commonly used web browsers – Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome.

Buffer Overflow in the XML Parser in All Versions Before 38.0
What is specific about the exploit is that an attacker could be able to insert and activate any random code, without requiring any specific skills to do so. As a result of that, the potential attacker could have gained access to valuable information, stored in the browser. Thus, personal information could be exposed partially. However, there also had been a possibility that the attacker was able to modify system files and make them available for cyber criminals.
The update.exe Flaw
This flaw was very critical since it was connected to one of the most exploited vulnerabilities in any software – that hackers can exploit and assume control over your system. The specifics about this flaw is that on Windows OS systems, the browser did not confirm and ensure that the pathway of the executable is located in its original position in the app directory. To evaluate, this means that it was open for modifications or even replacements with a Trojan Horse by users in the network (worst case scenario), giving hackers full control over your computer without your consent.
The asm.js Flaw
The asm.js is the programming language that allows computer engines, based on C++ and JavaScript such as your online games on Facebook, run through your browser as if they were installed on your PC. The particular security gap that was discovered with this exploit was that it could allow individuals with talents in coding and JavaScript to steal information such as website and banking credentials, email addresses, etc.
Given that Firefox experienced many changes over the years, we should not neglect its Rival Google Chrome because it is the most widely used browser out there.
The Row-hammer Exploit
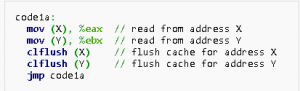
Row-hammer represents a vulnerability in Dynamic Random-Access Memory, which has a lot to do with the manual override of the memory cells of the DRAM organization. Google security experts have recently discovered that a .cc sandbox file did not have limits for NaCl (native client). Furthermore, this exploit is based on gaps in the DRAM, which could cause errors and provide access to the user without any security authentication and disclose vital information to hackers. Below we see the clflush commands that are used to perform the attack:
The DDoS Exploits
Google experts and other anonymous professionals have uncovered multiple exploits in Google Chrome in various locations of the program that create prerequisites for sending multiple packets and crashing the browser known as DDoS attack.
All of the exploits gave way to partial exposure of user credentials and other information, as well as possible modification over some system files and degraded browser performance.
HTMLConstructionsite.cpp Weakness
The code of the HTMLConstructionside.Cpp represented a weakness in regards to the fact that in the executeReparentTask scripts which manage child and parent task, according to the script language, can easily be modified by hackers and set to do variety of damages to the user. By having modified the ‘child’ script below, a malicious code could have been able to steal information from the user and, to some extent, modify the system files. Below is a small portion of the task script of HTMLConstructionside.cpp.
It is crucial to raise awareness, regarding those web exploits, because, even though they have already been fixed in the newer updates, you never know when a new exploit is going to create an opportunity for black hats to exploit and infect your computer with the various types of malware. That is why frequently updating your anti-malware program is always recommended by security experts.

