 Ransomware encryptions and infections have created havoc worth around 18 million USD. These type of attacks come from Trojan horses with preprogrammed scripts that encrypt the user files in mainly AES and RSA encryption algorithms. Ransomware infections have become a grave danger to inexperienced users who usually open email attachments without carefully thinking about their legitimacy. The threat itself can be removed with a particular anti-malware program, however, the encrypted files remain. This is a tutorial to help users in decrypting RSA encrypted data. The methods below were recommended by experts and were tried several times by users with a good result. However this is no guarantee that it will work for you.
Ransomware encryptions and infections have created havoc worth around 18 million USD. These type of attacks come from Trojan horses with preprogrammed scripts that encrypt the user files in mainly AES and RSA encryption algorithms. Ransomware infections have become a grave danger to inexperienced users who usually open email attachments without carefully thinking about their legitimacy. The threat itself can be removed with a particular anti-malware program, however, the encrypted files remain. This is a tutorial to help users in decrypting RSA encrypted data. The methods below were recommended by experts and were tried several times by users with a good result. However this is no guarantee that it will work for you.

What Is RSA Encryption Algorhytm?
RSA encryption algorithm is a type of language that, in this case, changes the normal code of the file with a unique key. This key can be decrypted via special software, but it requires a powerful machine since it is a time-costly process. RSA algorithm has been employed by the most traditional ransomware viruses that have caused massive devastations on a global scale – The CryptoWall Variants(2.0, 3.0), Bitcrypt and others. In this tutorial, we show you a possible method of decrypting your files and restoring them to their previous working state in case you have no backup on your operating system (OS). After the tutorial, we have provided instructions on how to enable Windows file history so your files can be backed up so you can protect yourself from future attacks. Make sure you take your time and do everything from the steps below and things should be fine for you.

Ransomware Removal Manual
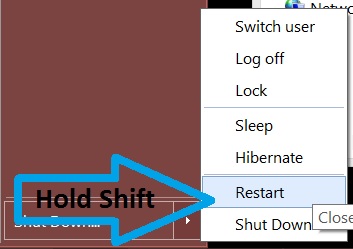
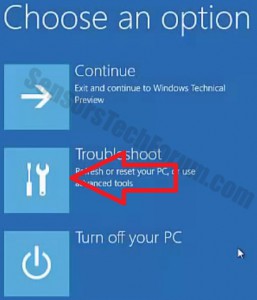
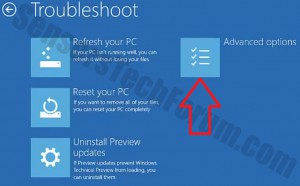
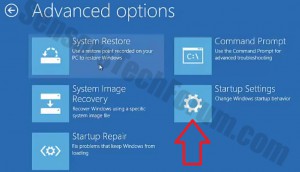
Before doing this, make sure you backup your information on a USB stick or anything of this similarity. After that, make sure you download a reputable anti-malware software that will detect anything out of the ordinary and assist you with the removal of the threat. Download it to a safe PC and put it on yours and boot your computer in Windows online Safe Mode using the following manual:

Ransomware Files Restoration
For this particular tutorial, we have used .bitcrypt extension files, encrypted by ransomware, called Bitcrypt. We have also used Ubuntu version 14.04 which assisted us in using special software appropriate for this distribution. You can get it from their website’s download page and you can either:
-Install it along with your operating system by booting a live USB drive.
-Install it on a virtual drive (Recommended).
Here we have brief tutorials for both:
Installation of Ubuntu on your machine:
Step1: Get a USB flash drive that has above 2GB of space.
Step2: Download the free software, called Rufus and install it on your windows.
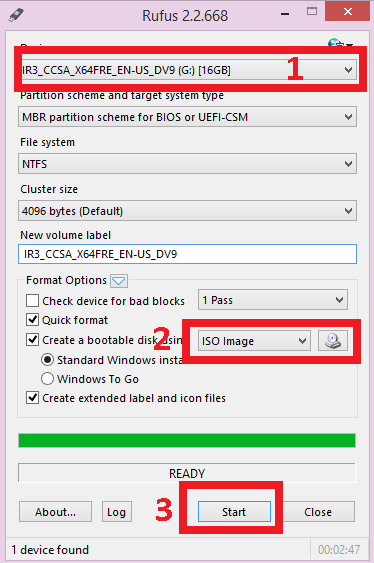
Step3: Configure Rufus by choosing NTFS as a system and selecting the USB drive as the one to be created as a bootable USB. After that boot the Linux image from the following button:
Make sure you locate it and select it from where you downloaded it.
Step4: After the flash drive is ready, restart your computer, and it should run the Ubuntu installation. If it does not, you should go to the BIOS menu by pressing the BIOS hotkey on startup for your PC (Usually it is F1) and from there select the first boot option to be the USB bootable drive or CD/DVD in case you have burnt Ubuntu on such.
Installation Of Ubuntu on your Virtual Drive
For this installation, you need to download VMware Workstation from their download page or any other Virtual Drive Management program. After installed you should:
Step1: Create a new virtual drive.
Step2: Set the drive size. Make sure you have a minimum of 20 gigabytes of free space fro Ubuntu on your computer. Also choose ‘Run as a single drive’.
Step 3: Select the ISO image. For this option, you should know where it is.
Step 4: After that play the Virtual Machine and it will install automatically.
File Decryption
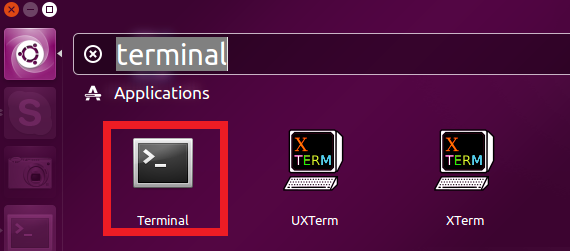
Once you have Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution on your computer open the terminal by doing the following:
Then update your Linux and install greater version than Python 3.2 by typing the following in the terminal:
→sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3.2
Also, if your Linux does not have sqlite3 module, install it by typing:
→sudo apt-get install sqlite3 libsqlite3-dev
sudo gem install sqlite3-ruby
Now after we have Python installed, we need to download a script created by 2014 Airbus Defence and Space Cybersecurity. To do this click on this link. Download the file in your ‘Home’ folder after it prompts you where to save it. Keep this as decrypt.py in case it is not saved in this format.
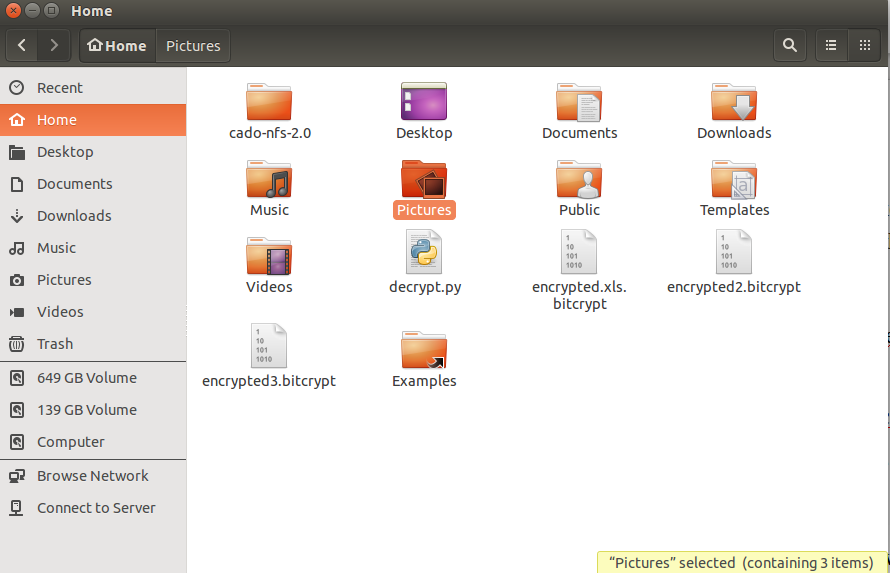
Now that we have Python and the script, it is time to find out the key of the .bytrcypt encrypted file. To do this move your encrypted files ot the home folder by using the file manager:
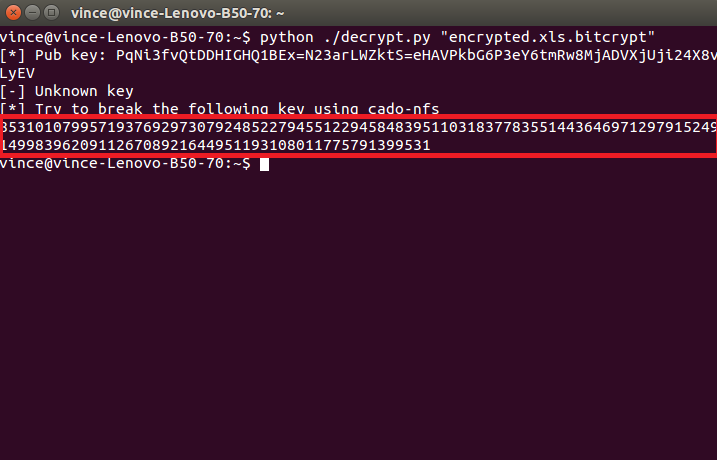
After you located all of the encrypted files there along with the “decrypt.py” file type the following into the terminal to initiate the script:
→python ./decrypt.py “Your_Encrypted_Document_Name_and_Format”
It will show an error, and this is entirely normal as long as you see this code:
This is the RSA code for this file. Now, we need to decrypt it, and we are halfway there. To do this download a program called cado-nfs2.0.tar.gz from their download page here. We recommend the 2.0 version. However, the newest version is also on a good level.
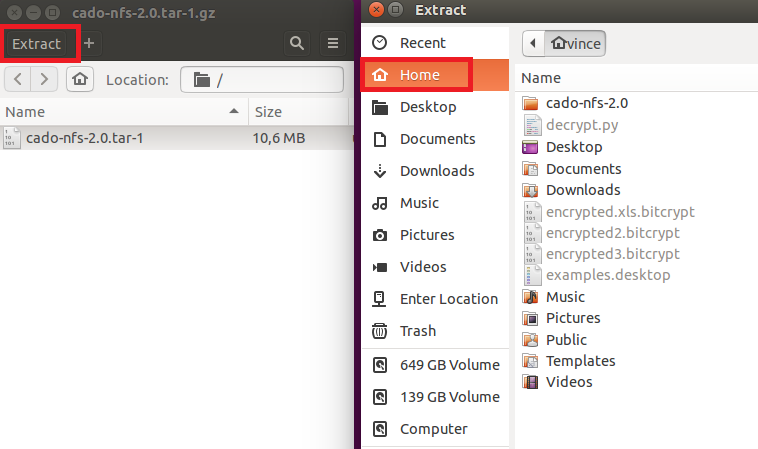
It will download a .tar archive file (.tar files are very similar to .rar or .zip files). Simply open it and click on the Extract button on top and choose the ‘Home’ folder. It should look like this:
After the we have all the files extracted in the ‘Home’ folder, we need to compile cado-nfs. To do this, open another terminal and type:
→cd cado-nfs-2.0
make
After this is set, it is time to run the key cracker. Important – this process can take from several hours to days to be finished. To begin the process type in your cd cado-nfs terminal:
→./factor.sh YOUR_UNIQUE_KEY_WHICH_IS_LETTERS_OR_NUMBERS_HERE -s 4 -t 6
After the process completes, you should see the following:
→Info:Complete Factorization: Total cpu/real-time for everything: hhhh/dddd
LongNumber1 LongNumber2
After we have the decrypted key, we need to insert in the “decrypt.py” script. Do this by opening decrypt.py in a text editor and finding this part of it:
→known_keys = { many long numbers }
We need to add before the second bracket (“}”) these lines:
The Previous Key, a column, opened parenthesis, LongNumber1, Comma, LongNumber2, closed parenthesis. It should look like this:
→The Previous Key:(LongNumber1,LongNumber2)
Be advised that you should do this only one time. After this it is time to decode the files. To do this type:
→python ./decrypt.py “Your_Encrypted_Document.docx.bitcrypt”
Executing this command will make a file that is called “Your_Encrypted_Document.docx.bitcrypt.CLEAR”
Just rename the file by removing the .clear extension and you should be all set. Repeat the process for your other files as well. But remember that first you should find out their initial keys to decrypt them. You should be able to open them now. We hope this works for you.

Conclusion
The best defense against Ransomware threats is always the user himself. It is crucial to know which files you open and whether or not the locations of those files are safe or not. However if you are in an organization or somewhere where the computer is located in a public or work environment, it always opens it up to a direct attack that is even more dangerous. A real expert will say that the best computer is the one that is switched off, because it may have the best defenses, but the one who makes the errors is not the machine, it’s the man. This is why you should always keep enough knowledge and build up PC usage behavior that is security oriented.
Spy Hunter scanner will only detect the threat. If you want the threat to be automatically removed, you need to purchase the full version of the anti-malware tool.Find Out More About SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool / How to Uninstall SpyHunter




Hi,
I have the same problem. My files are also infected by the Cryptowall 3.0. And the extension is ccc. Can I use this python script to decrypt ? Are there other possible solutions ?
thx a lot
Patrick