This article aims to provide insight on phishing web pages that aim for your information and display how to remove such fake sites from your computer plus protect it in the future.
There have so far been millions if not billions of phishing websites out there looking exactly like the original ones and many inexperienced users tend to fall for their trap and give away their personal information and financial details which are sent to the hackers’ servers via tracking technology. Antivirus companies have integrated phishing protection against such threats, but since the hosts spreading phishing spit out multiple URLs with an extreme rate, not all the phishing pages are blocked. This is why we have created this educational material which aims to make you an expert in phishing protection because more users become victims due to their behavior and we can’t blame security software all the time.

How Do Phishing Web Links Spread
Cyber-criminals have invested all of their imagination and potential into creating phishing web pages that will pass the trick. And they use cunning tactics to spread them as well. The tactics are many and the web pages are almost identical.
Method 1 – Via Referrer Spam
One of the most widespread methods of spreading phishing web pages is naturally via manipulating Google to conduct massive spam campaigns via spambots. Such spambots are usually either Web Crawlers also known as spiders and Ghost Referrers. Crawlers aim to crawl different web pages and spam only on those that lack certain security features and are more harmless than Ghosts which are a persistent spam and cannot be blocked easily. Here is an example of a spammed URL via referral spam bots that leads to a phishing AliExpress webpage:

Method 2 – Via PUPs (Ad-supported Programs)
Such software is extremely high in variety of programs that may exist. They may range from browser extensions, toolbars, programs installed on the computer, fake web browsers and many others.
Usually, such potentially unwanted programs are created for multiple different benefits of the interests of their makers:
- To generate hoax traffic by displaying ads and causing browser redirects to third-party websites who may have paid for such service.
- To display advertisements of affiliate links that generate revenue by being clicked on.
- To infect your computer with malware by advertising malicious web links.
- To display phishing web pages that aim for your information.
The displaying of such phishing pages may occur via a browser redirect or via a fake page posted on a toolbar as a favorite bookmark. This includes fake phishing pages such as Facebook login pages, PayPal, Amazon, Apple, LinkedIn and multiple other services.
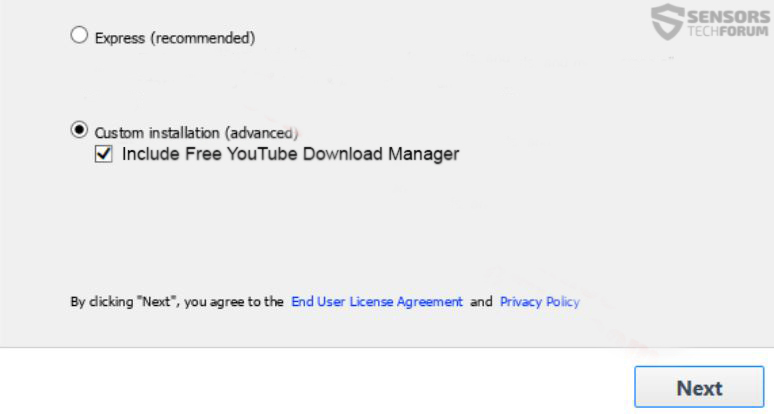
Such unwanted software can be replicated via multiple different methods, primarily via bundling. Bundling is a service that aims to push third-party programs by embedding their installation along other free software downloaded online. One example can be seen on the image below, advertising an app as a “useful extra”. Such bundled programs can be seen on suspicious software download sites or torrent sites.
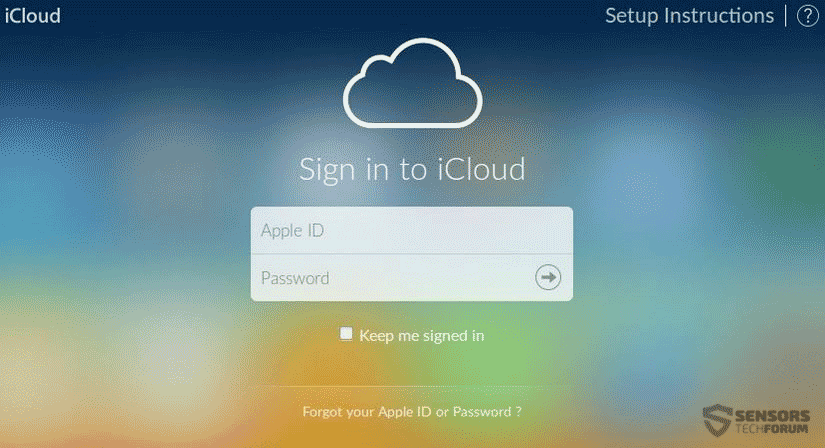
And Mac users are also endangered by such unwanted applications or malware coming from malicious apps. Such may display phishing web pages, like the fake iCloud login below:
Method 3 – Via Malware
The most effective and the smartest method of all of the phishing attacks is conducted via multiple types of malware being spread out In the wild. One of those viruses which is extremely dangerous is banking malware or banking Trojans. Such may phish for your financial information after infecting your computer. One of the latest viruses in this segment, known as the BlackMoon banking trojan uses a very cunning technique. The virus has a pre-configured list of hashes of websites that the user may visit. As soon as the victim visits the original website, for example a purchase page from online retailer, the Trojan detects it and then displays an error message:
As soon as the victim clicks on the “OK” button, BlackMoon redirects to an identically looking phishing web page with the financial credentials. Some malware which is better developed may generate such web pages on the spot by copying the “page source” code:
Other malware which may cause the spreading of such phishing web pages are botnet viruses and although not as effective, may be worms which spread automatically from a computer to another computer. Such worms may also display phishing web pages in a similar manner or even install Trojans, like the BlackMoon.
Method 4 – Via E-mails
Probably the most widespread method out there, phishing e-mails often tend to trick many inexperienced victims and also experienced corporate users into entering their credentials for a banking institution or online payment service. You won’t even believe how many have fallen to the trap of socially engineered e-mails purely because the scheme is created in a very clever way.
For example, one scheme may be to spread phishing e-mails to users who use only payment service, like PayPal. Such schemes were reported to be spread since the year 2014 and are evolving. One of those e-mails can have a subject such as:
- Your account has been logged in from another device.
- Verify that you have made the PayPal transfer.
- Suspicious activity on your account.
- Purchasing receipt from Apple Store Australia.
The body of the e-mail appear to be exactly the same as a legitimate e-mail sent by PayPal, for example. And even experienced users would not be able to tell the difference. And since those phishing pages are generally not malicious and associated with malware, they are not blocked by antivirus programs or web browser companies. So you might be visiting such as website, thinking “Oh, well, I have antivirus protection”, but the site may be completely different from the original.

How to Detect Phishing (Fake) Web Links
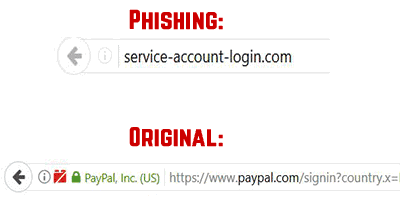
Usually, the detection of such web links should happen manually. If you have doubts that a web page is phishing or just want to check such page, the first action that should be performed by you, is check the URL for phishing. There are multiple ways to do it, the most simple of which is to compare the original URL with the URL of the phishing page. You should preferably do this on another device that is safe or via another web browser. If the web link you see differs from the original, then you most likely have a phishing page:
Also, another sign of copying a phishing page is that the web pages that are phishing are often not HTTPs (s for secured). This can be detected by the green padlock icon that usually appears In the address bar, like the image above displays.
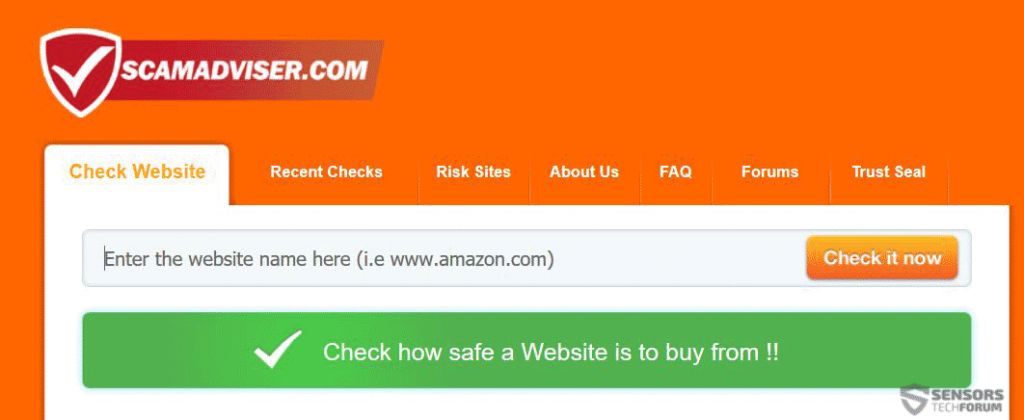
Another method to check phishing e-mails is via using different online services. One in particular is Scamadviser.com which also has a build in browser extension. On the site you may paste the URL to see if it a malicious URL or if it has been detected for being a phishing or scam web page:
In addition to this, you can also check your web browsers for suspicious browser extensions added to them an check your PC if it has a suspicious ad-supported program embedded within it, by following the steps below:

How to Get Rid of Phishing Websites Permanently
After checking for suspicious browser extensions and you find suspicious such, recommendations are to clean your web browsers cache to completely clean them up from any unwanted software. This is achievable by following the instructions for web browsers in this video:
The instructions are to remove a specific potentially unwanted program, but they will also help you clean your web browsers and get rid of any suspicious software residing on your computer.
In addition to this, to further remove phishing websites from your computer, recommendations are to scan it for any suspicious software and malware that keeps causing them to appear. According to experts this is the best method to detect if any harmful objects causing the URLs to appear on your PC may be residing on your system. The best method to do this is to download and install an advanced anti-malware software, after which boot your PC in safe mode with networking and scan it for malware:

How to Protect Myself in The Future
Protection against phishing attacks is basically protection against suspicious web links, malware and harmful software. This is why it comes down primarily to what combination of protection tactics you apply. This is why, for maximum protection, we strongly suggest you to follow the below-mentioned advises. If implemented in combination, the security of your data and your credentials will significantly improve and may save you a lot of headaches:
Advice 1: Make sure to read our general protection tips and try to make them your habit and educated others to do so as well.
Advice 2: Install an advanced anti-malware program that has an often updated real-time shield definitions and malware and phishing protection.
Spy Hunter scanner will only detect the threat. If you want the threat to be automatically removed, you need to purchase the full version of the anti-malware tool.Find Out More About SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool / How to Uninstall SpyHunter
Advice 3: Make sure to change all of your passwords from a secure device. If you do not have such, you can boot a live Ubuntu or other OS. The new passwords should be strong and connected one to another, so that you can remember them easily, for example P@55w0rd1, P@66w0rd2 and so on. You can also use colors and other words to remember them easily.
Advice 4: Backup your files using one of the methods in this article.
Advice 5: : Make sure to use a security-oriented web browser while surfing the world wide web.
- Windows
- Mac OS X
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari
- Internet Explorer
- Stop Push Pop-ups
How to Remove from Windows.
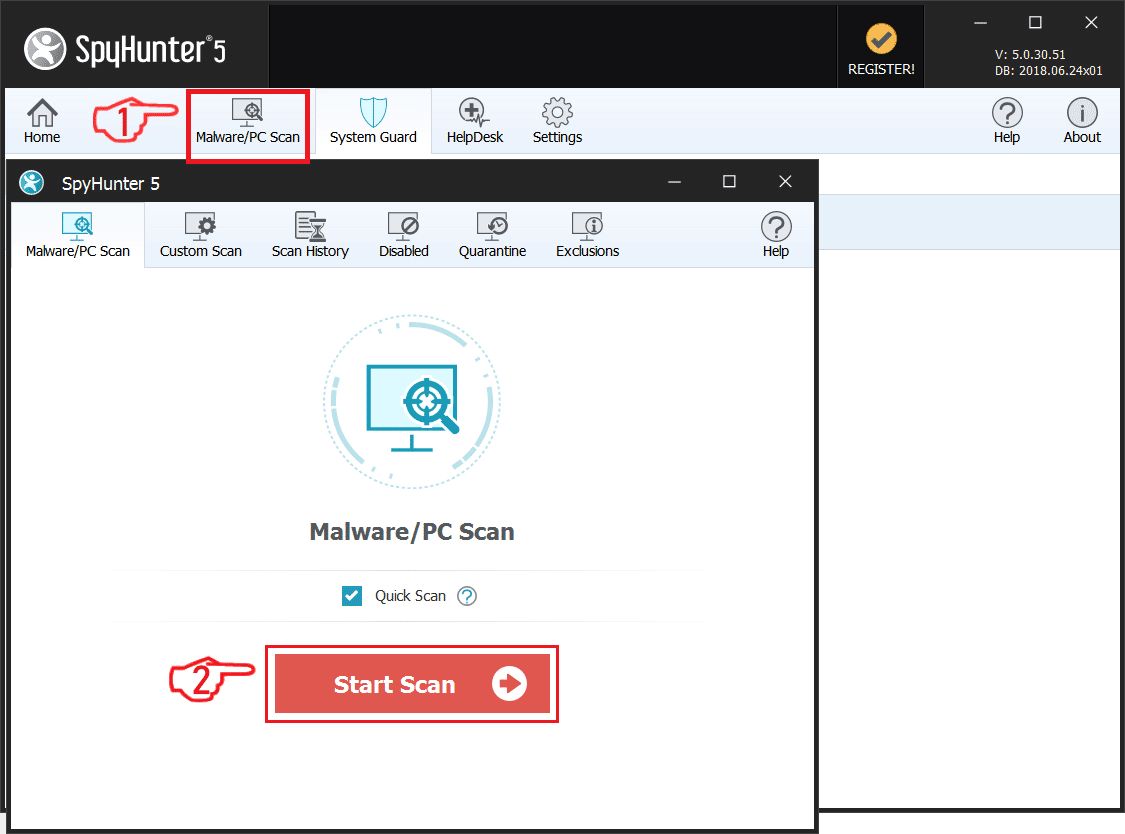
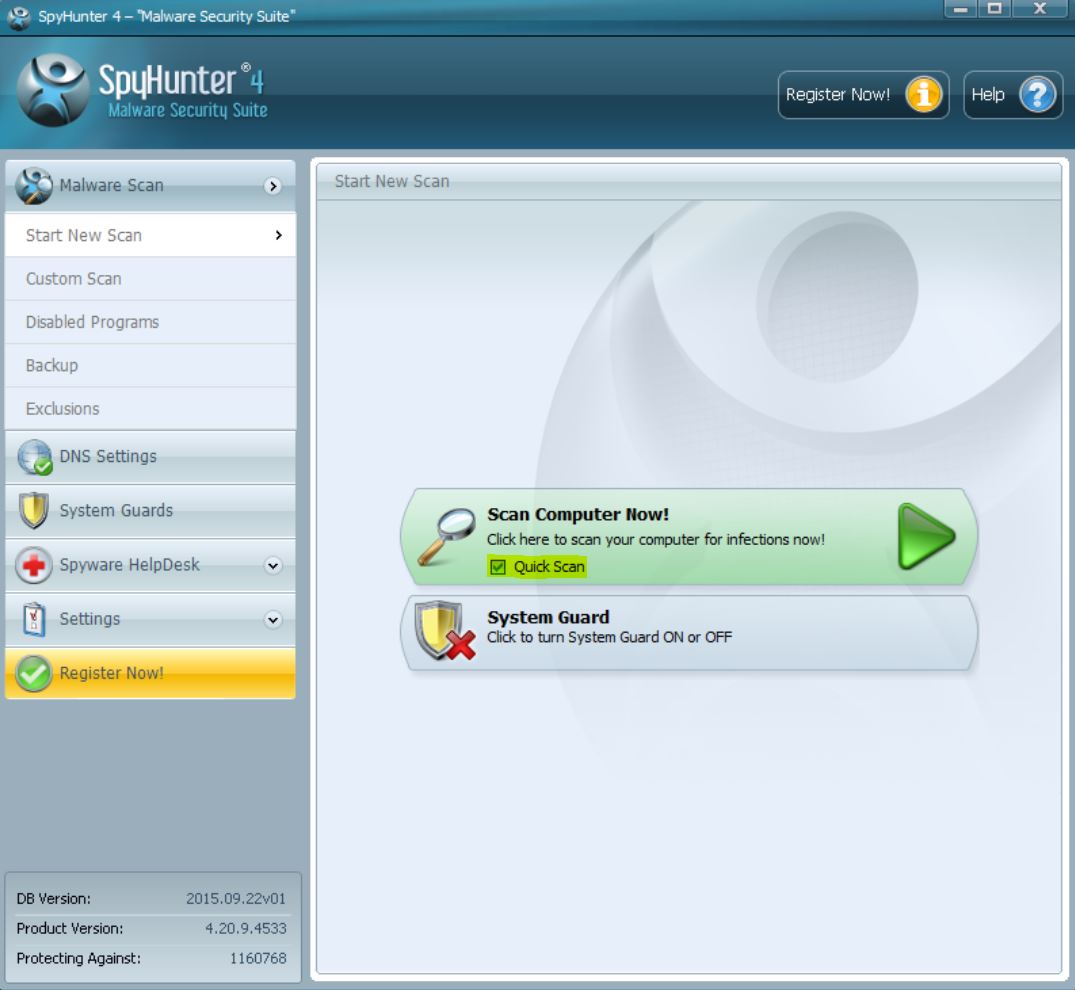
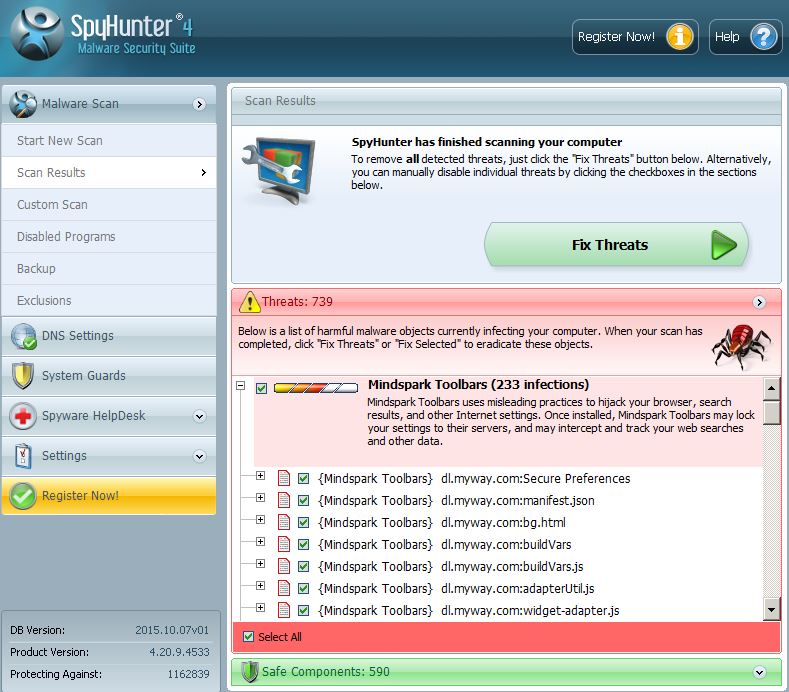
Step 1: Scan for with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
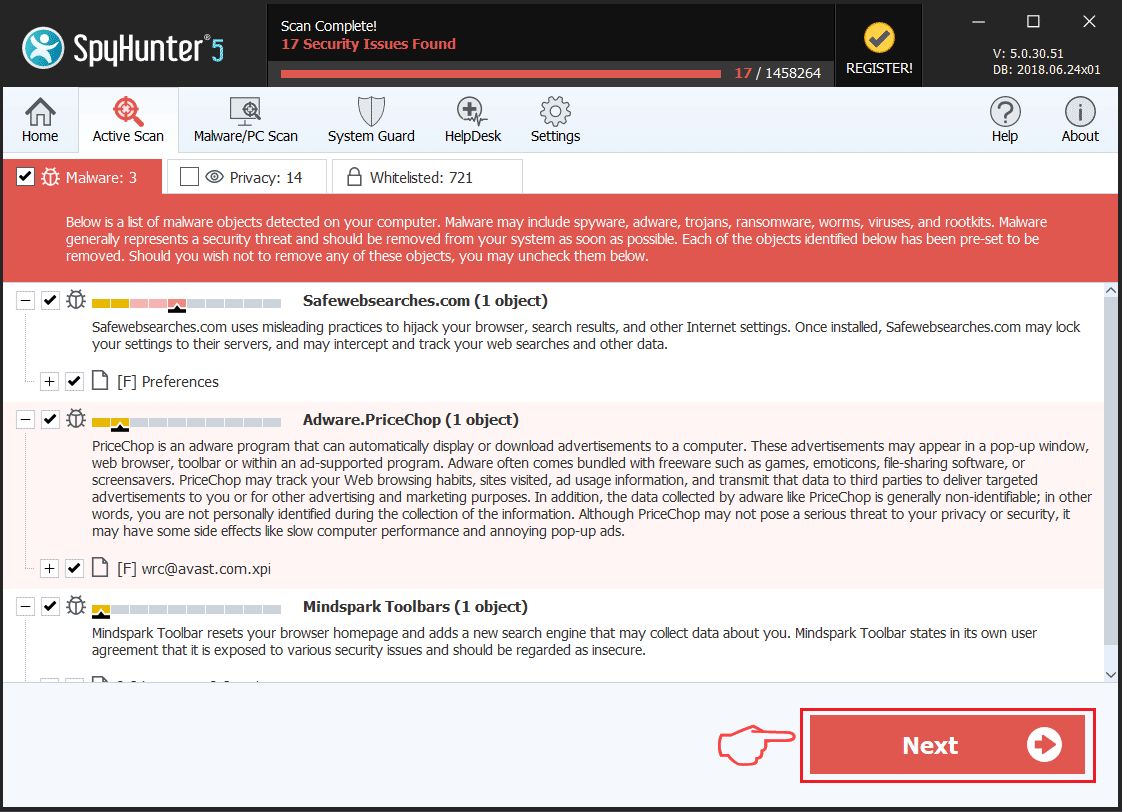
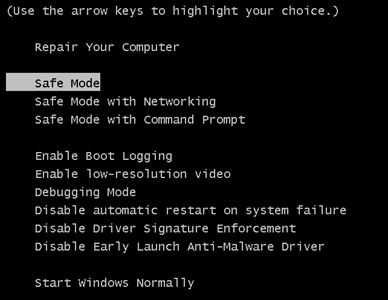
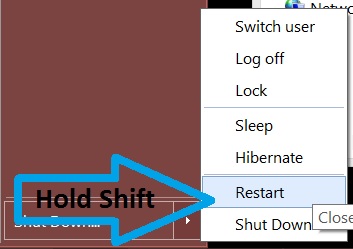
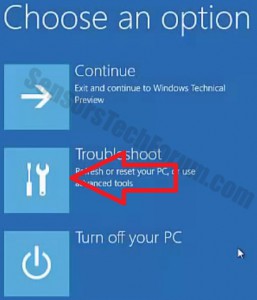
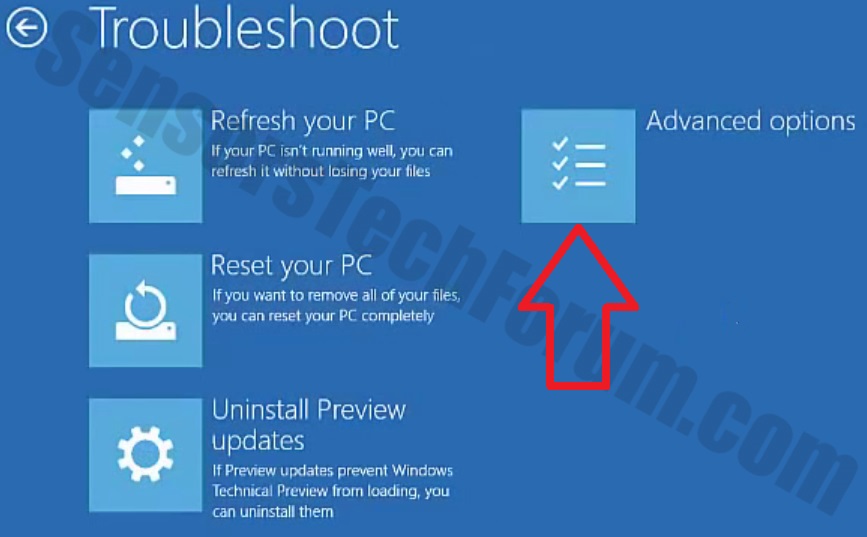
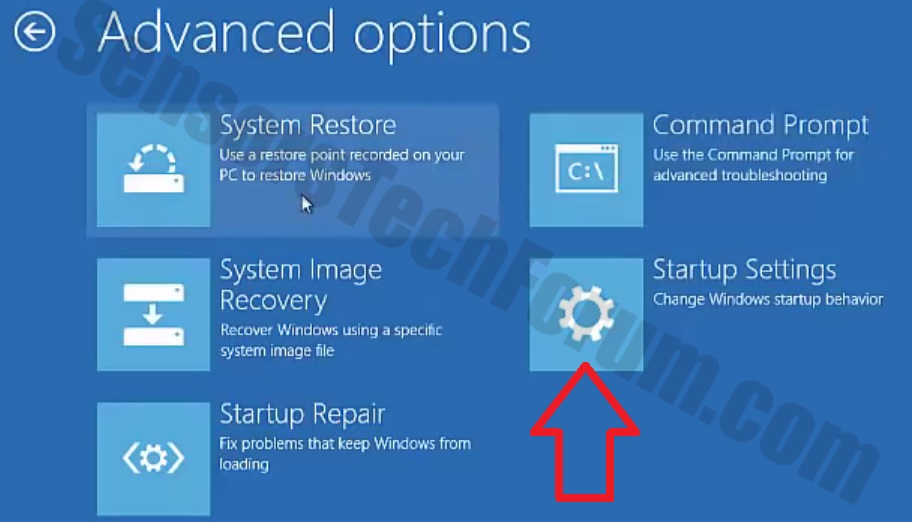
Step 2: Boot Your PC In Safe Mode

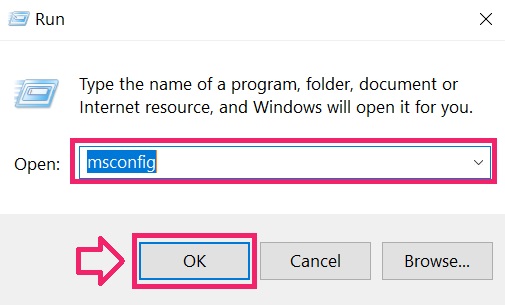
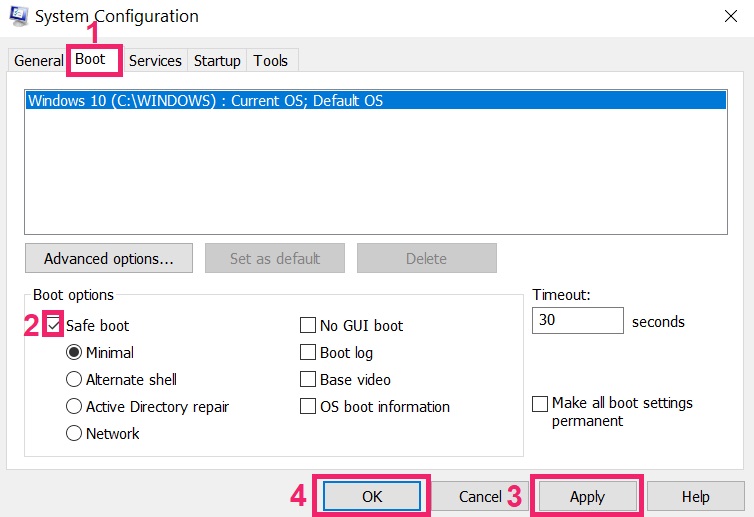
Step 3: Uninstall and related software from Windows
Uninstall Steps for Windows 11
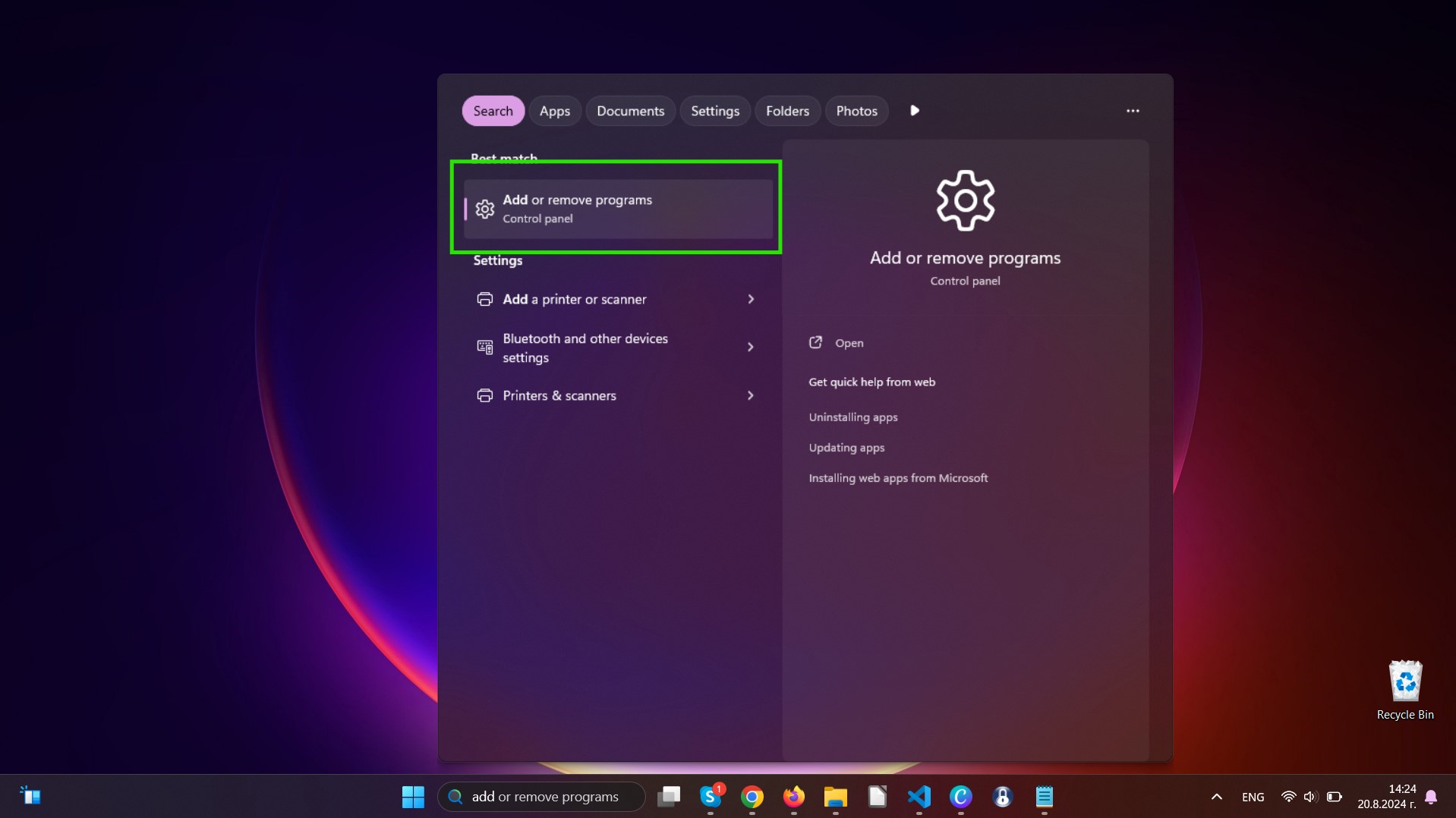
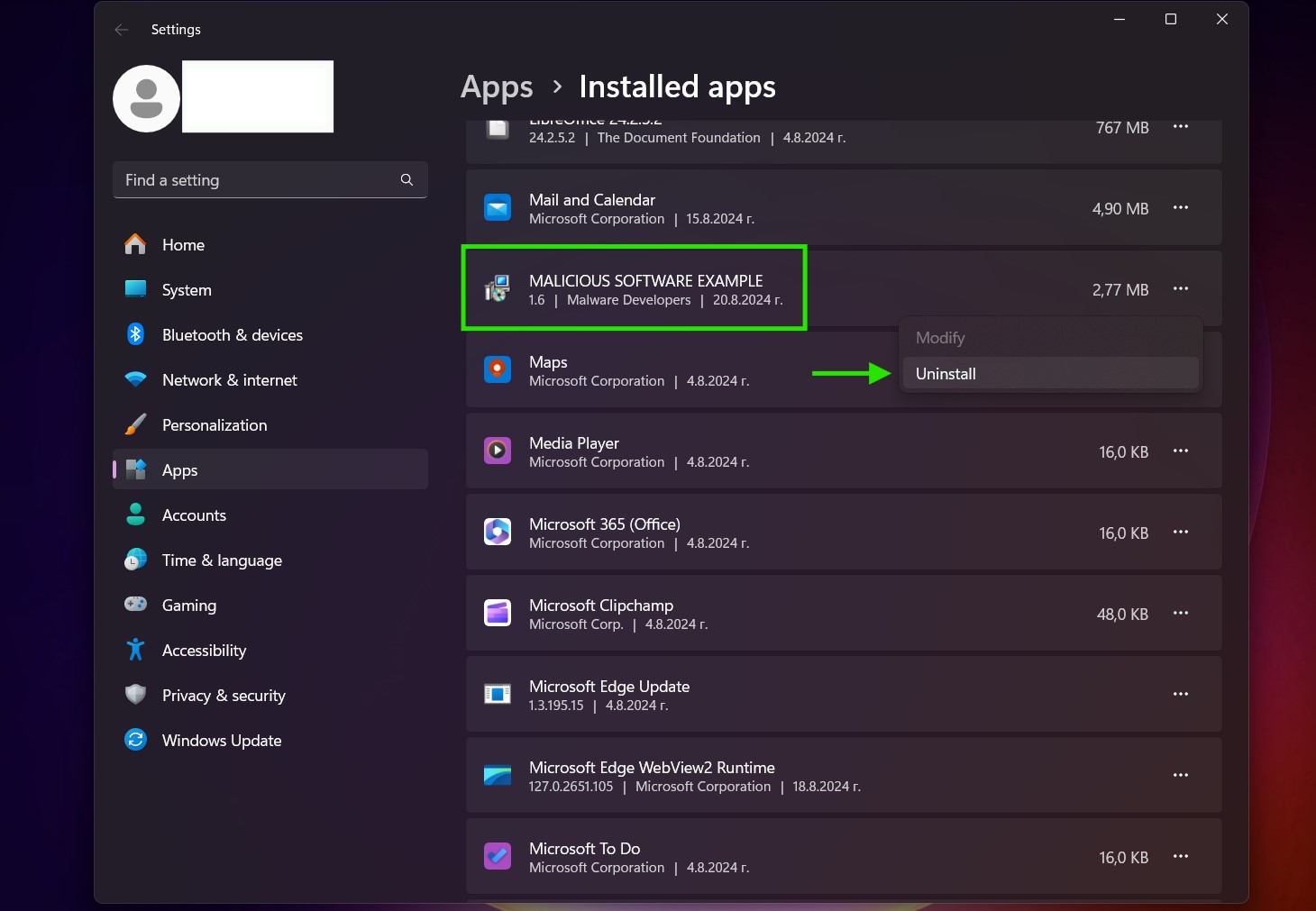
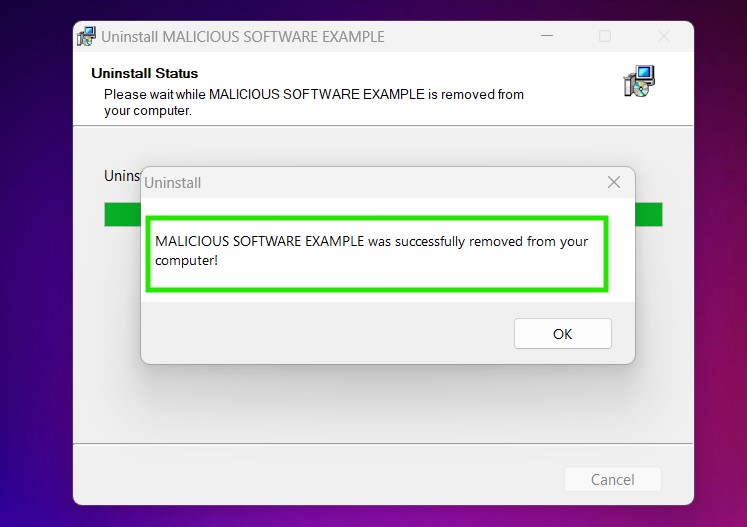
Uninstall Steps for Windows 10 and Older Versions
Here is a method in few easy steps that should be able to uninstall most programs. No matter if you are using Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista or XP, those steps will get the job done. Dragging the program or its folder to the recycle bin can be a very bad decision. If you do that, bits and pieces of the program are left behind, and that can lead to unstable work of your PC, errors with the file type associations and other unpleasant activities. The proper way to get a program off your computer is to Uninstall it. To do that:

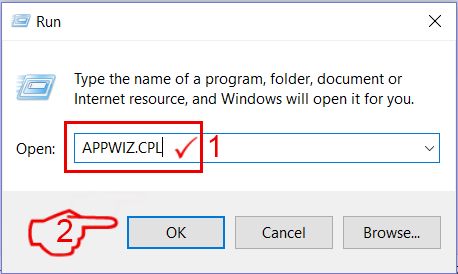
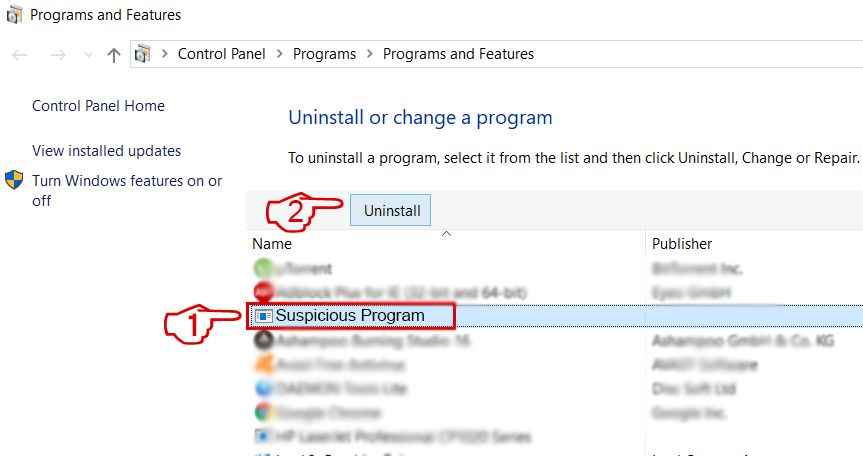 Follow the instructions above and you will successfully uninstall most programs.
Follow the instructions above and you will successfully uninstall most programs.
Step 4: Clean Any registries, Created by on Your PC.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
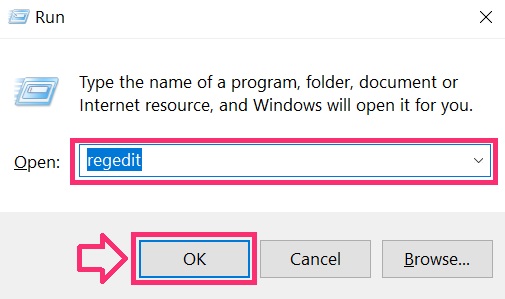
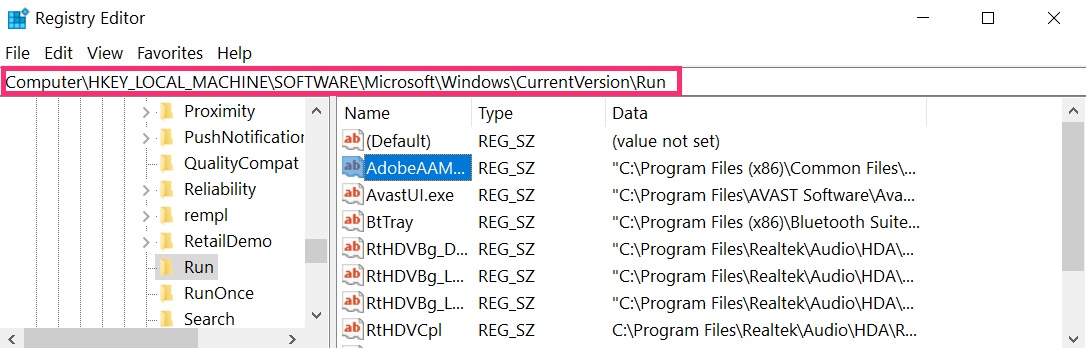
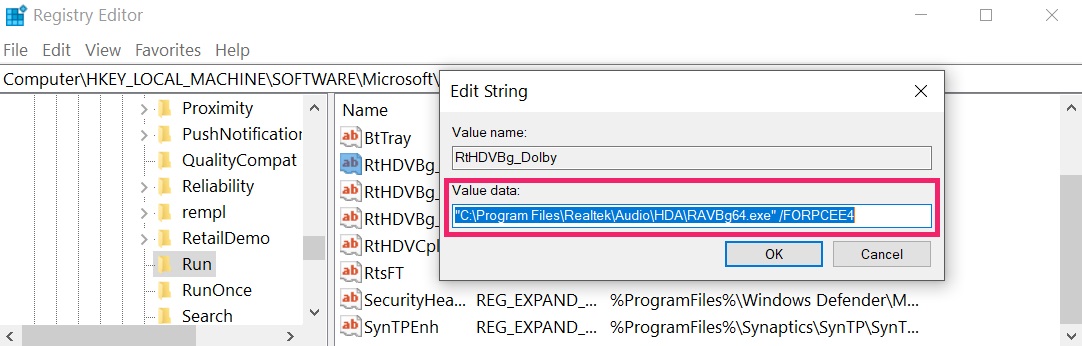 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Video Removal Guide for (Windows).
Get rid of from Mac OS X.
Step 1: Uninstall and remove related files and objects
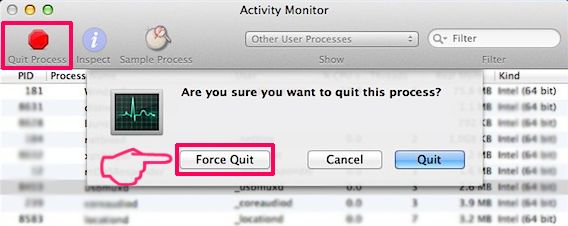
Your Mac will then show you a list of items that start automatically when you log in. Look for any suspicious apps identical or similar to . Check the app you want to stop from running automatically and then select on the Minus (“-“) icon to hide it.
- Go to Finder.
- In the search bar type the name of the app that you want to remove.
- Above the search bar change the two drop down menus to “System Files” and “Are Included” so that you can see all of the files associated with the application you want to remove. Bear in mind that some of the files may not be related to the app so be very careful which files you delete.
- If all of the files are related, hold the ⌘+A buttons to select them and then drive them to “Trash”.
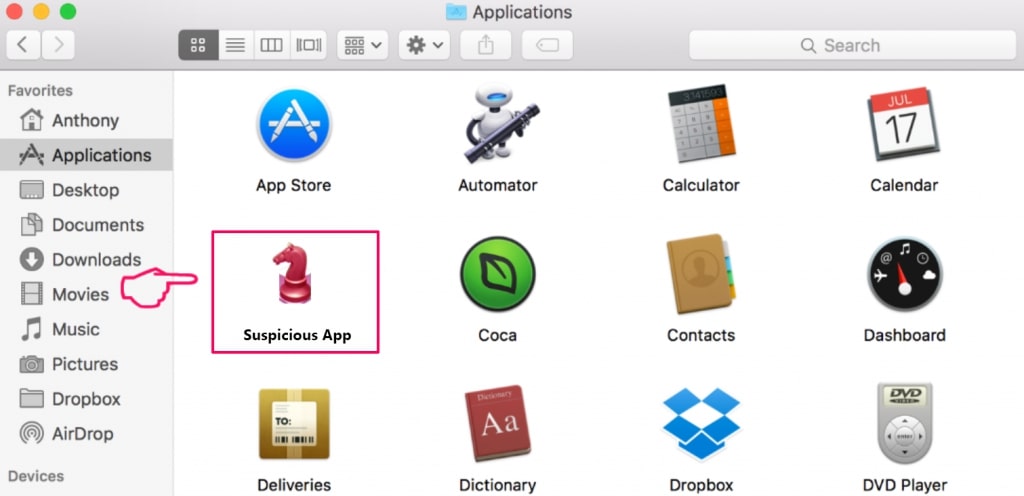
In case you cannot remove via Step 1 above:
In case you cannot find the virus files and objects in your Applications or other places we have shown above, you can manually look for them in the Libraries of your Mac. But before doing this, please read the disclaimer below:
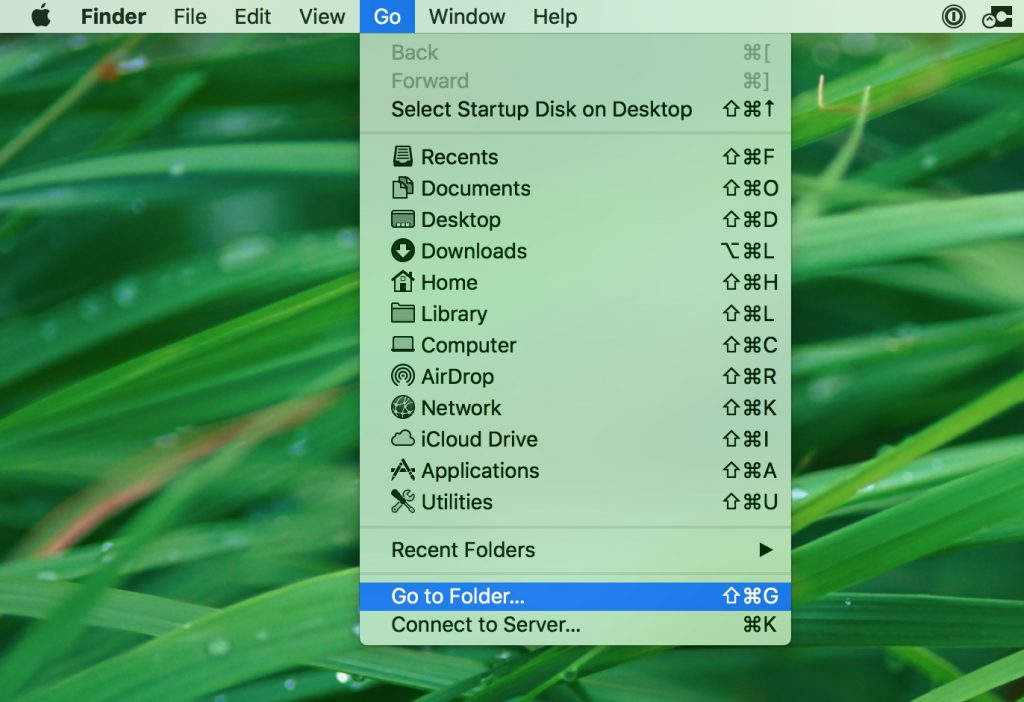
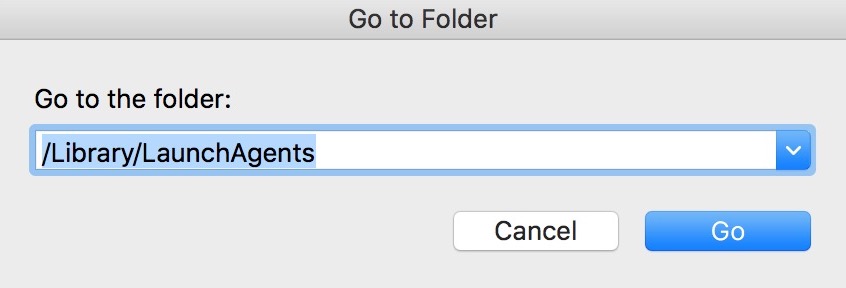
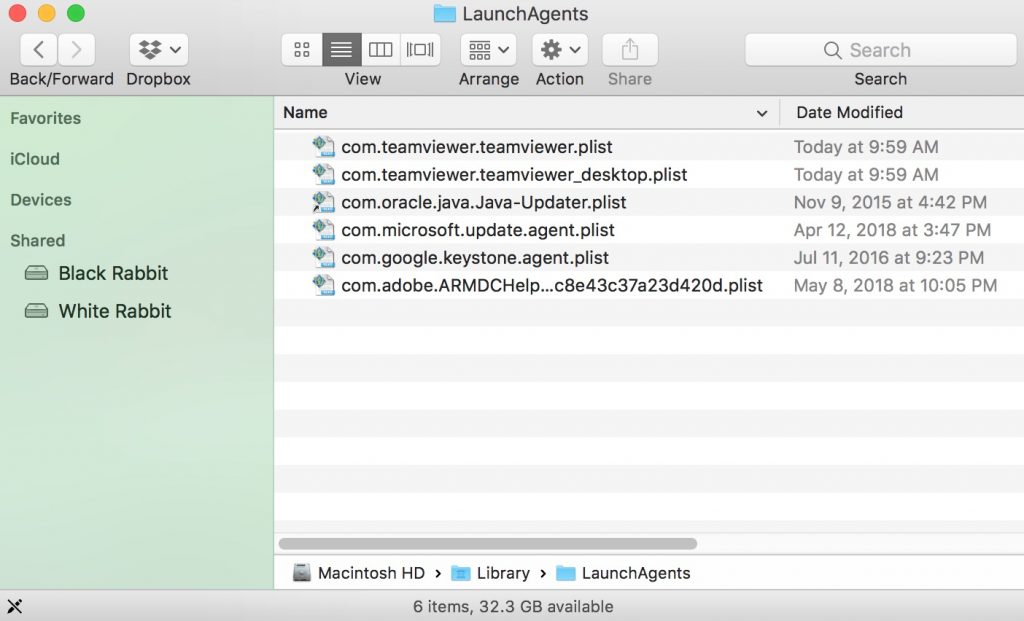
You can repeat the same procedure with the following other Library directories:
→ ~/Library/LaunchAgents
/Library/LaunchDaemons
Tip: ~ is there on purpose, because it leads to more LaunchAgents.
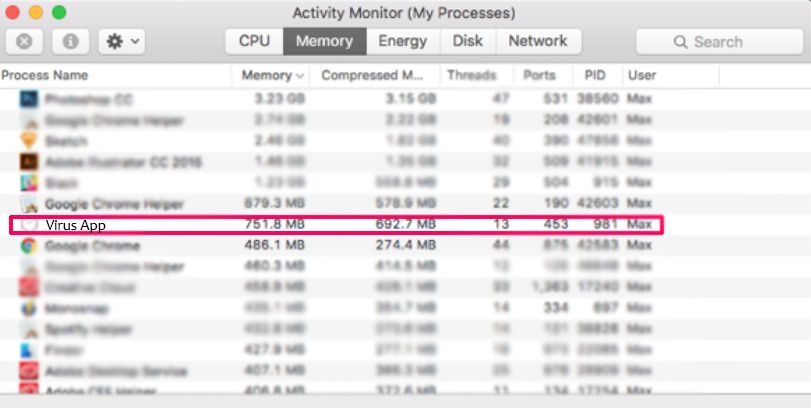
Step 2: Scan for and remove files from your Mac
When you are facing problems on your Mac as a result of unwanted scripts and programs such as , the recommended way of eliminating the threat is by using an anti-malware program. SpyHunter for Mac offers advanced security features along with other modules that will improve your Mac’s security and protect it in the future.
Video Removal Guide for (Mac)
Remove from Google Chrome.
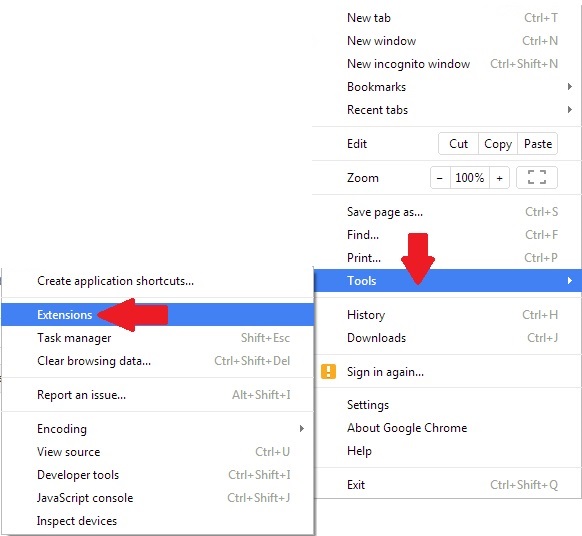
Step 1: Start Google Chrome and open the drop menu
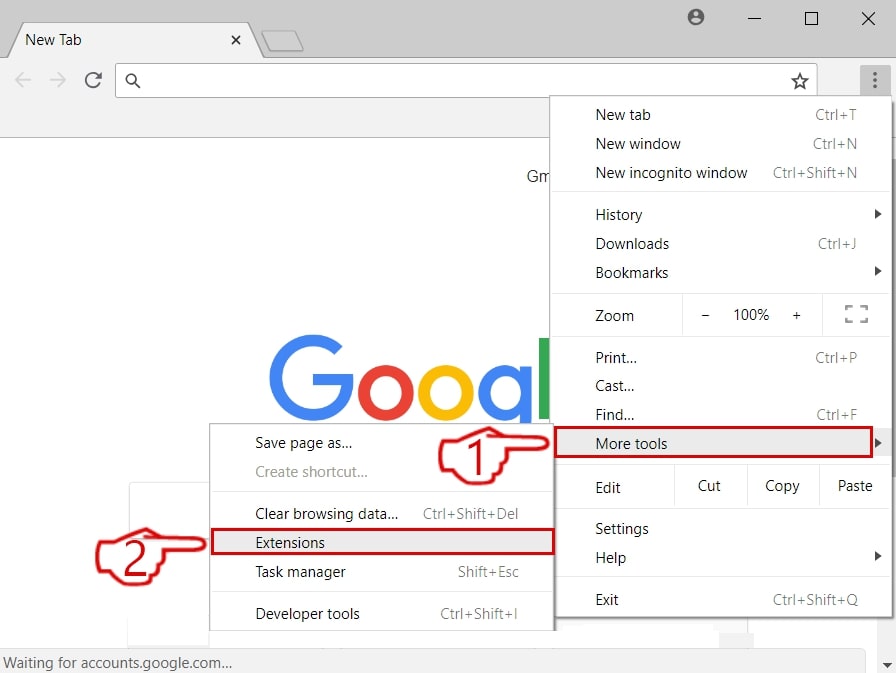
Step 2: Move the cursor over "Tools" and then from the extended menu choose "Extensions"
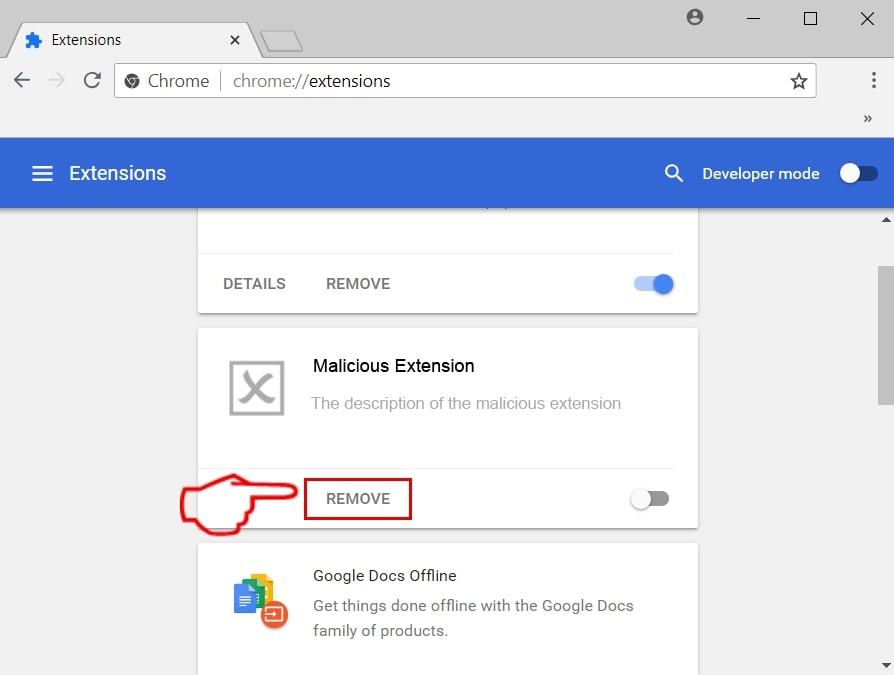
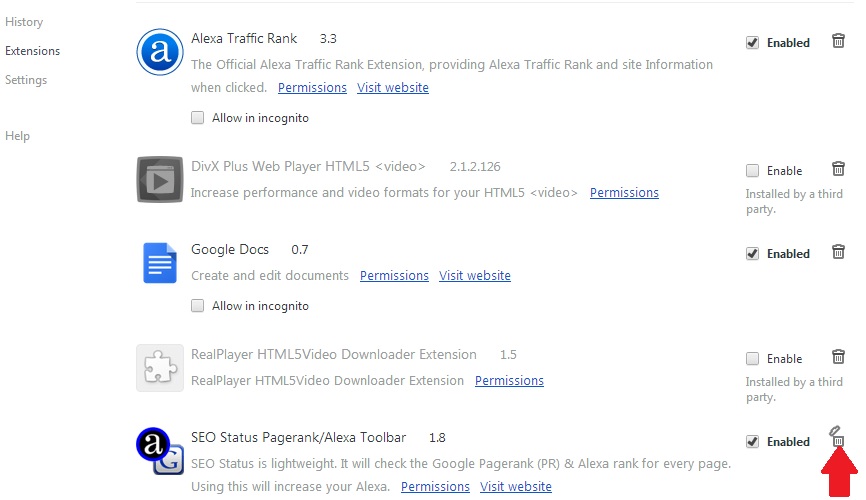
Step 3: From the opened "Extensions" menu locate the unwanted extension and click on its "Remove" button.
Step 4: After the extension is removed, restart Google Chrome by closing it from the red "X" button at the top right corner and start it again.
Erase from Mozilla Firefox.
Step 1: Start Mozilla Firefox. Open the menu window:
Step 2: Select the "Add-ons" icon from the menu.
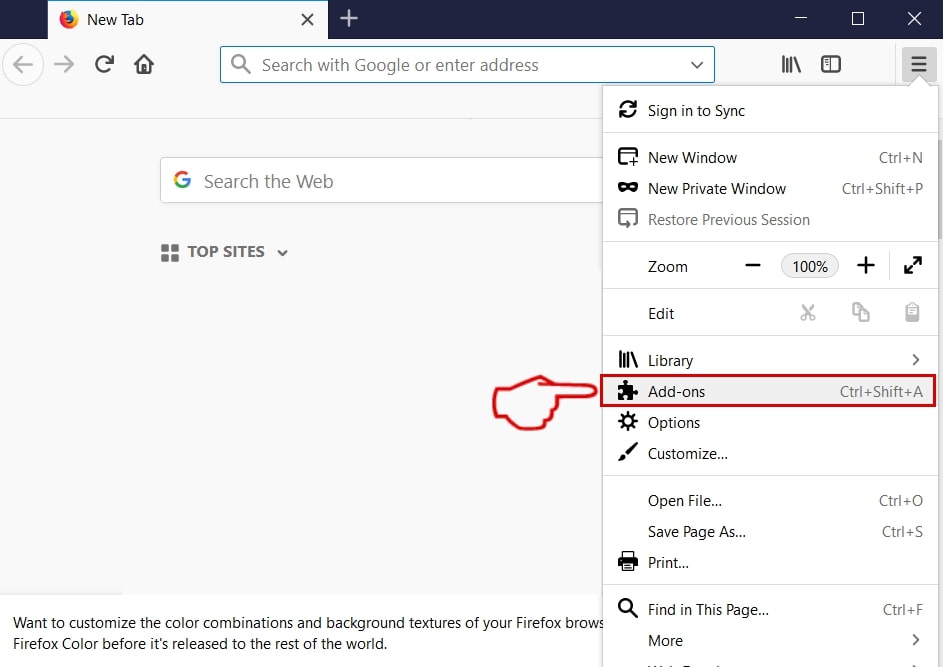
Step 3: Select the unwanted extension and click "Remove"

Step 4: After the extension is removed, restart Mozilla Firefox by closing it from the red "X" button at the top right corner and start it again.
Uninstall from Microsoft Edge.
Step 1: Start Edge browser.
Step 2: Open the drop menu by clicking on the icon at the top right corner.
Step 3: From the drop menu select "Extensions".
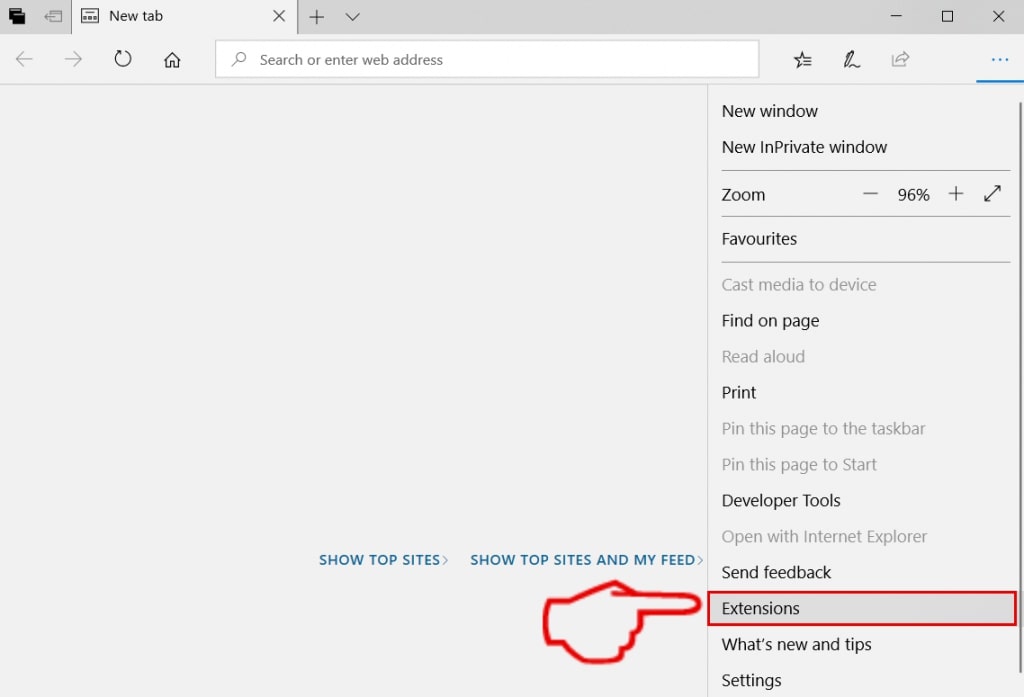
Step 4: Choose the suspected malicious extension you want to remove and then click on the gear icon.
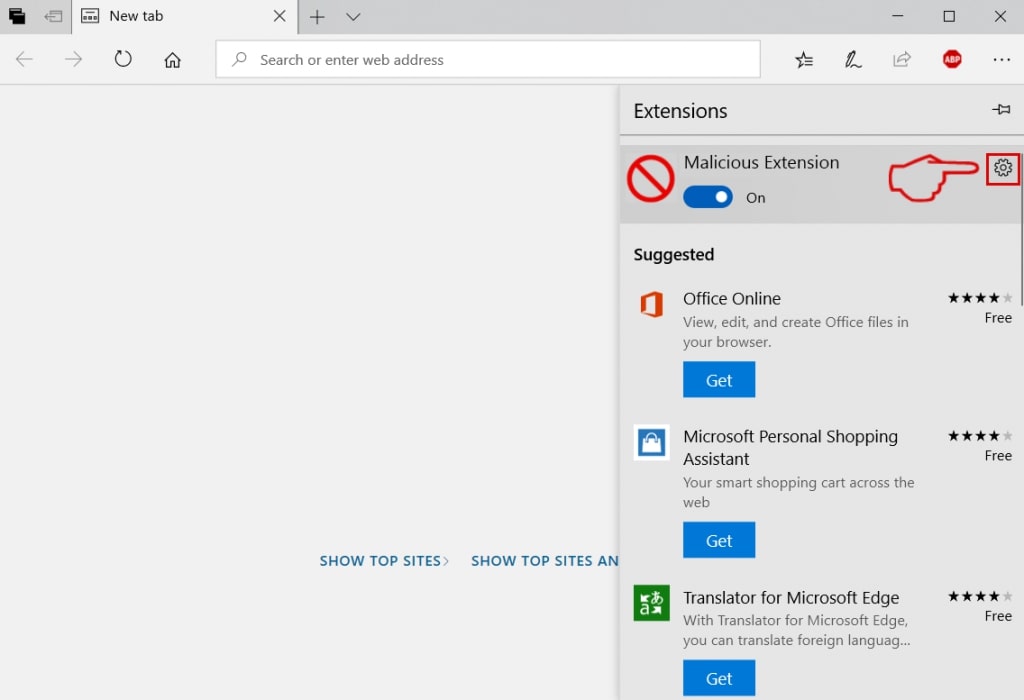
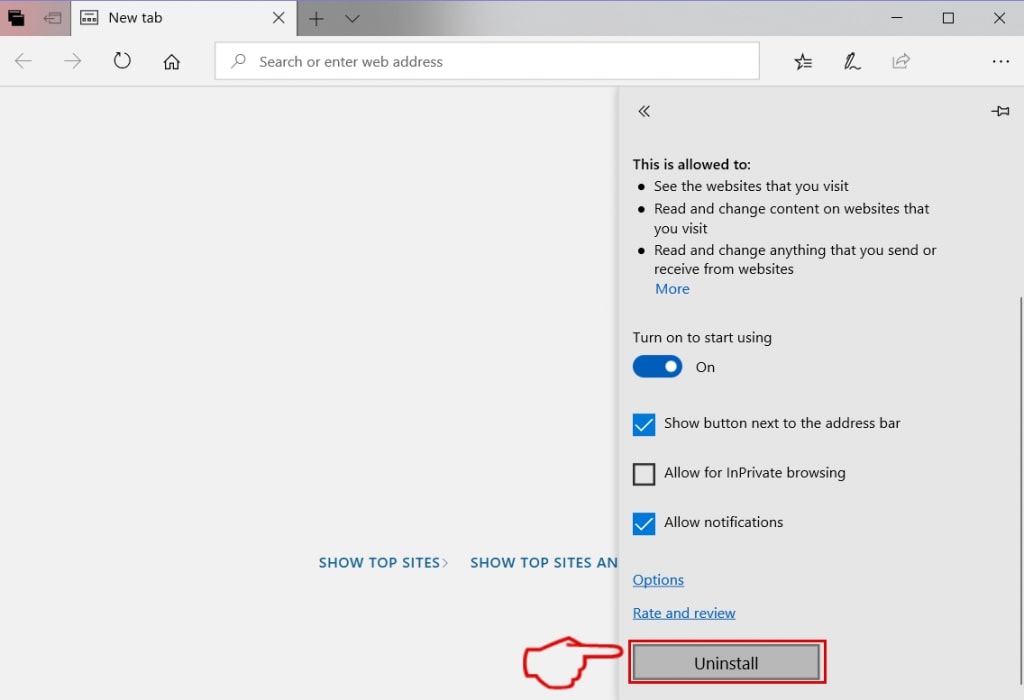
Step 5: Remove the malicious extension by scrolling down and then clicking on Uninstall.
Remove from Safari
Step 1: Start the Safari app.
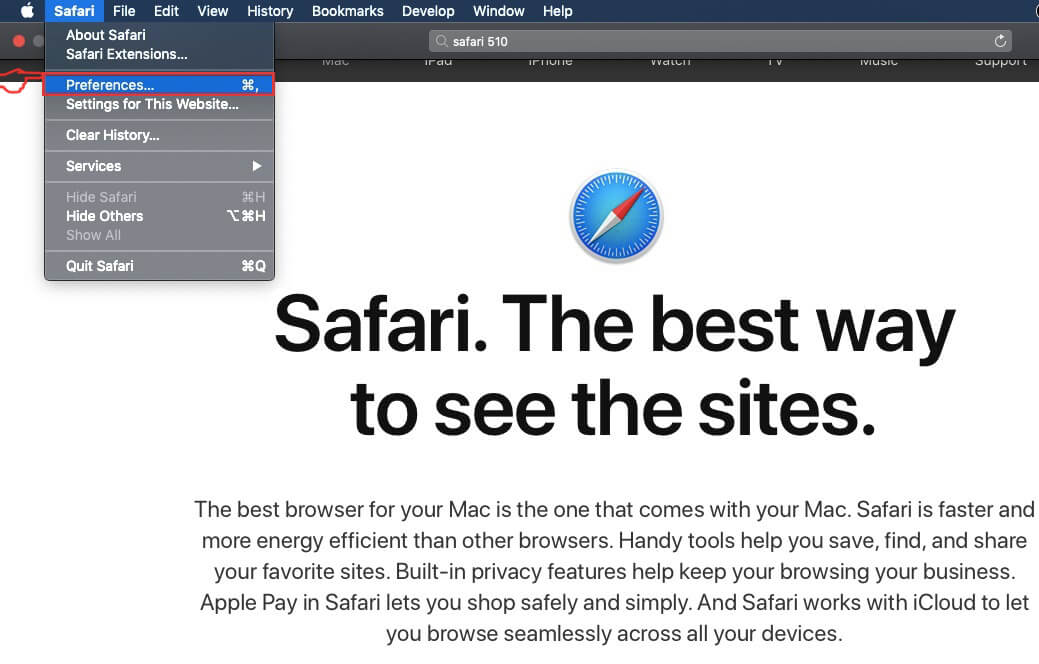
Step 2: After hovering your mouse cursor to the top of the screen, click on the Safari text to open its drop down menu.
Step 3: From the menu, click on "Preferences".
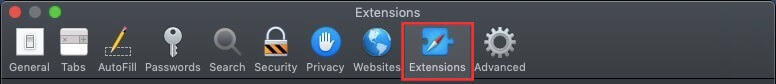
Step 4: After that, select the 'Extensions' Tab.
Step 5: Click once on the extension you want to remove.
Step 6: Click 'Uninstall'.
A pop-up window will appear asking for confirmation to uninstall the extension. Select 'Uninstall' again, and the will be removed.
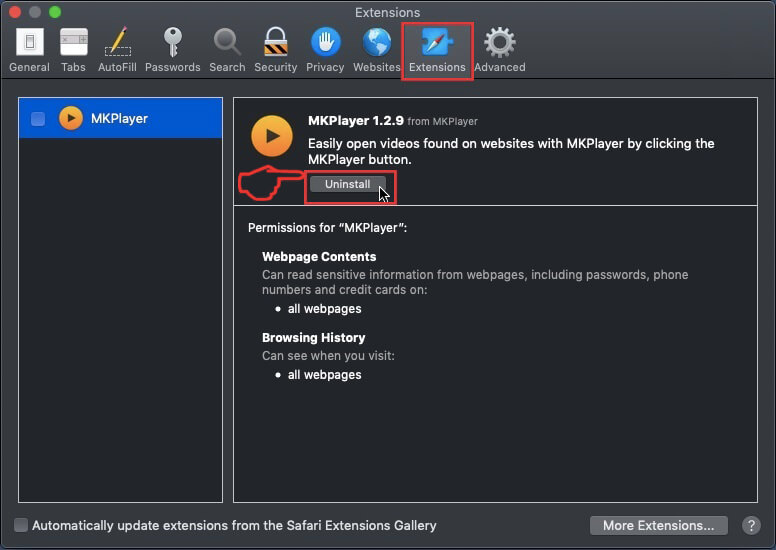
Eliminate from Internet Explorer.
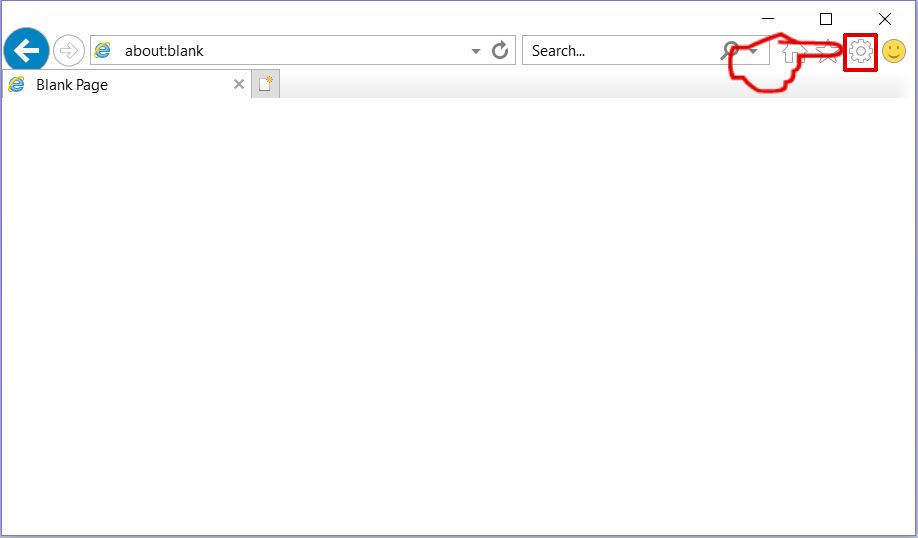
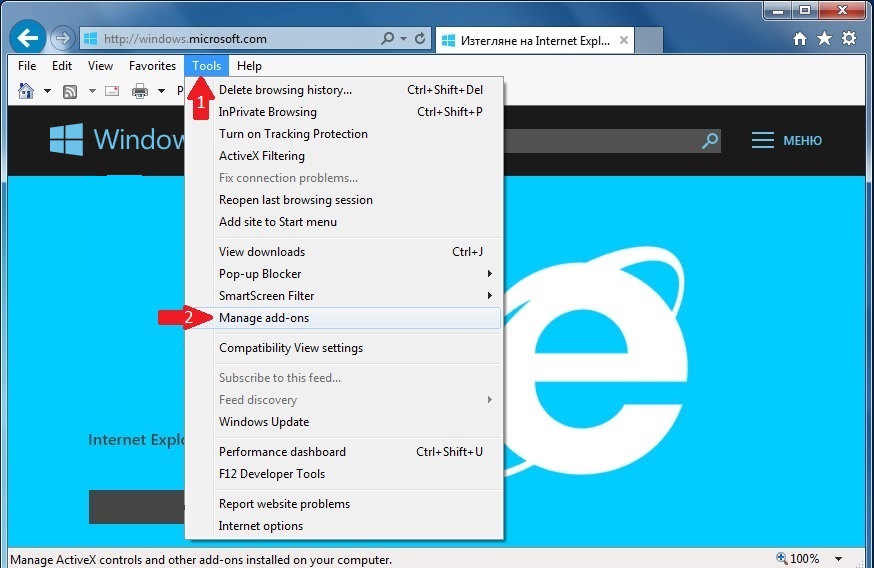
Step 1: Start Internet Explorer.
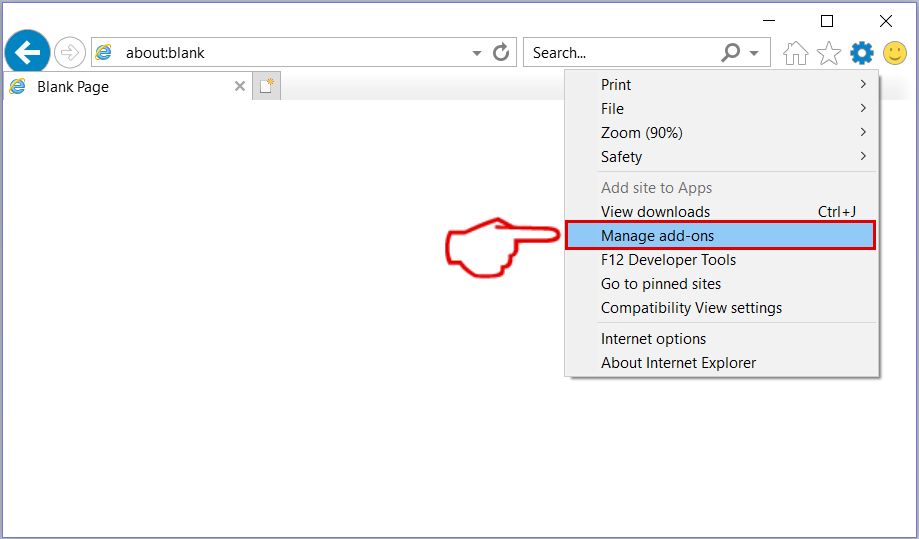
Step 2: Click on the gear icon labeled 'Tools' to open the drop menu and select 'Manage Add-ons'
Step 3: In the 'Manage Add-ons' window.
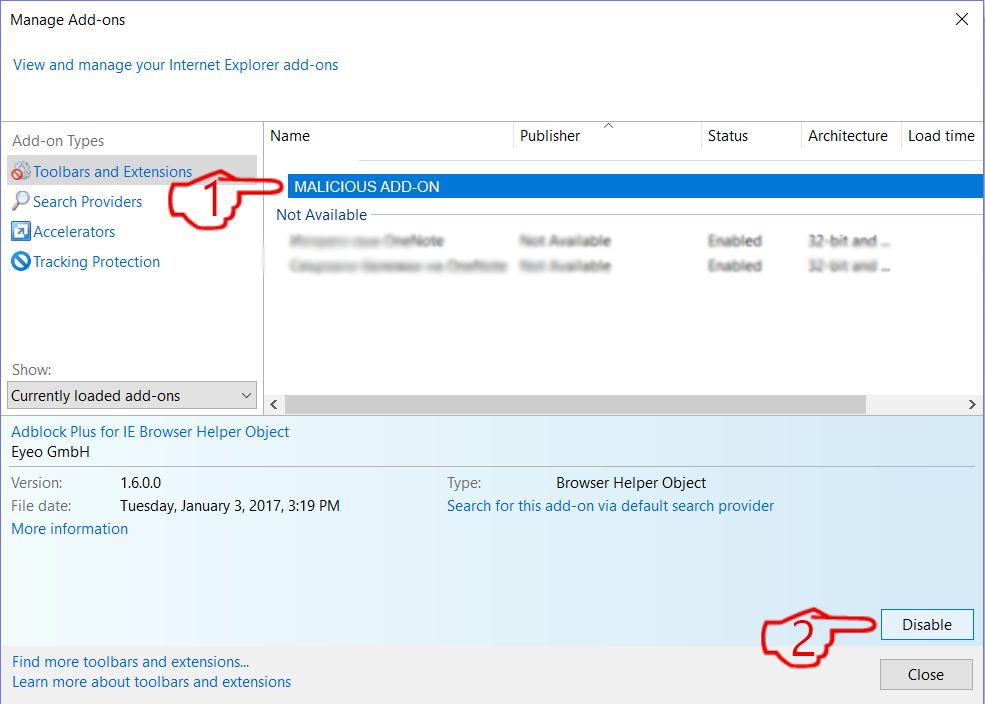
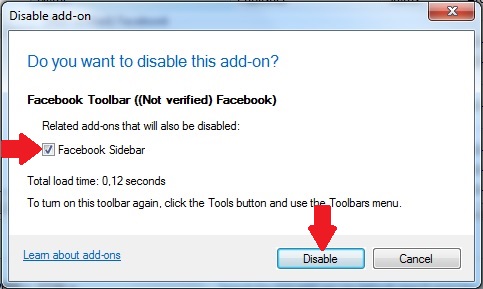
Step 4: Select the extension you want to remove and then click 'Disable'. A pop-up window will appear to inform you that you are about to disable the selected extension, and some more add-ons might be disabled as well. Leave all the boxes checked, and click 'Disable'.
Step 5: After the unwanted extension has been removed, restart Internet Explorer by closing it from the red 'X' button located at the top right corner and start it again.
Remove Push Notifications from Your Browsers
Turn Off Push Notifications from Google Chrome
To disable any Push Notices from Google Chrome browser, please follow the steps below:
Step 1: Go to Settings in Chrome.
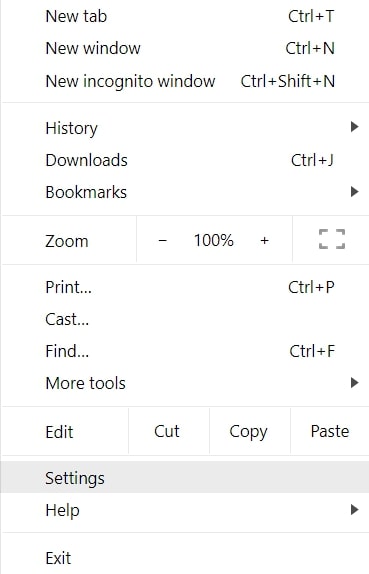
Step 2: In Settings, select “Advanced Settings”:
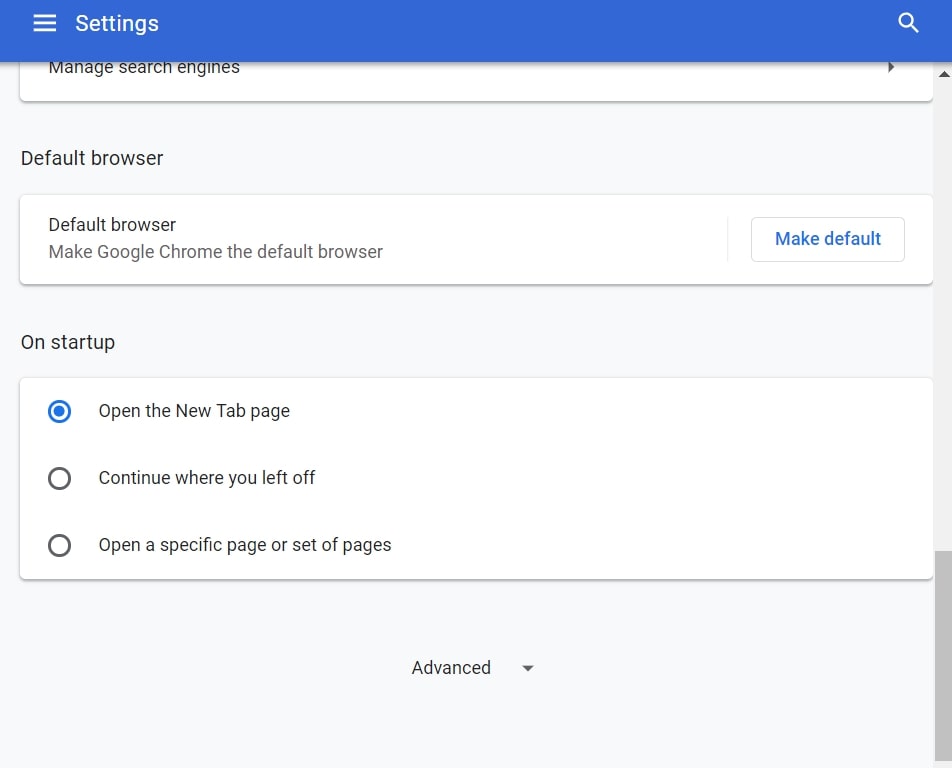
Step 3: Click “Content Settings”:
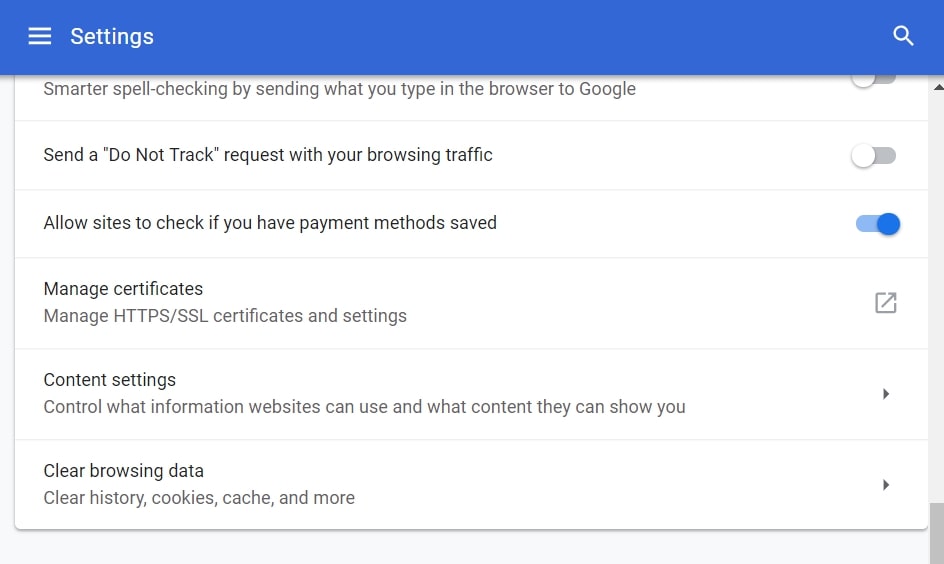
Step 4: Open “Notifications”:
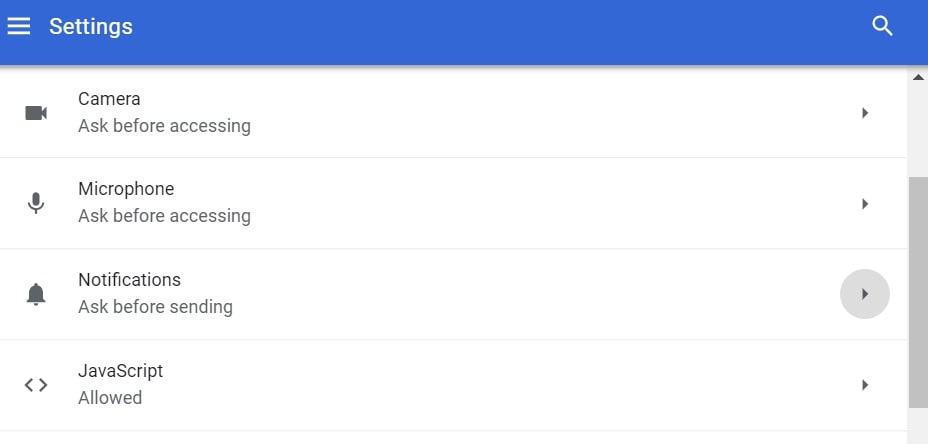
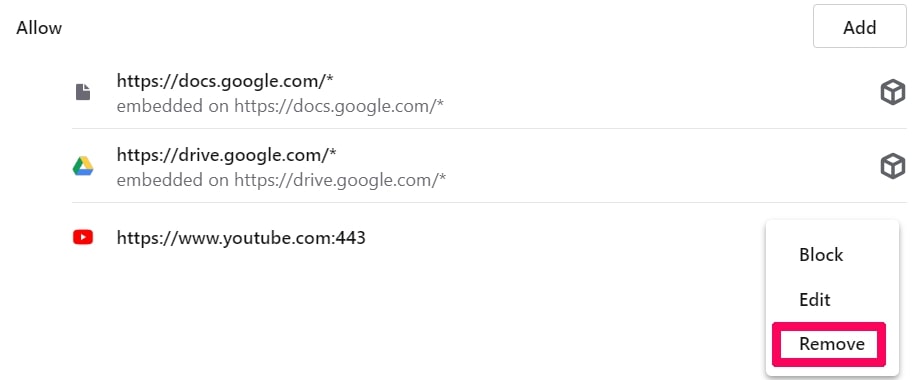
Step 5: Click the three dots and choose Block, Edit or Remove options:

Remove Push Notifications on Firefox
Step 1: Go to Firefox Options.
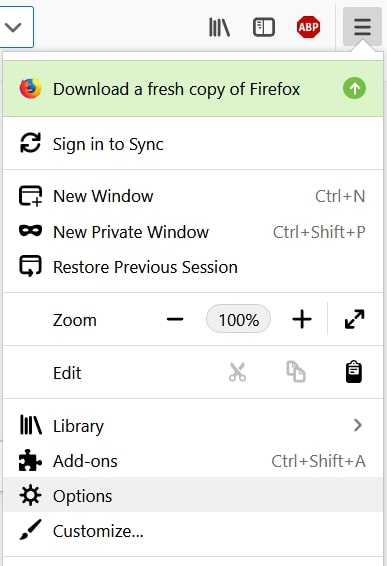
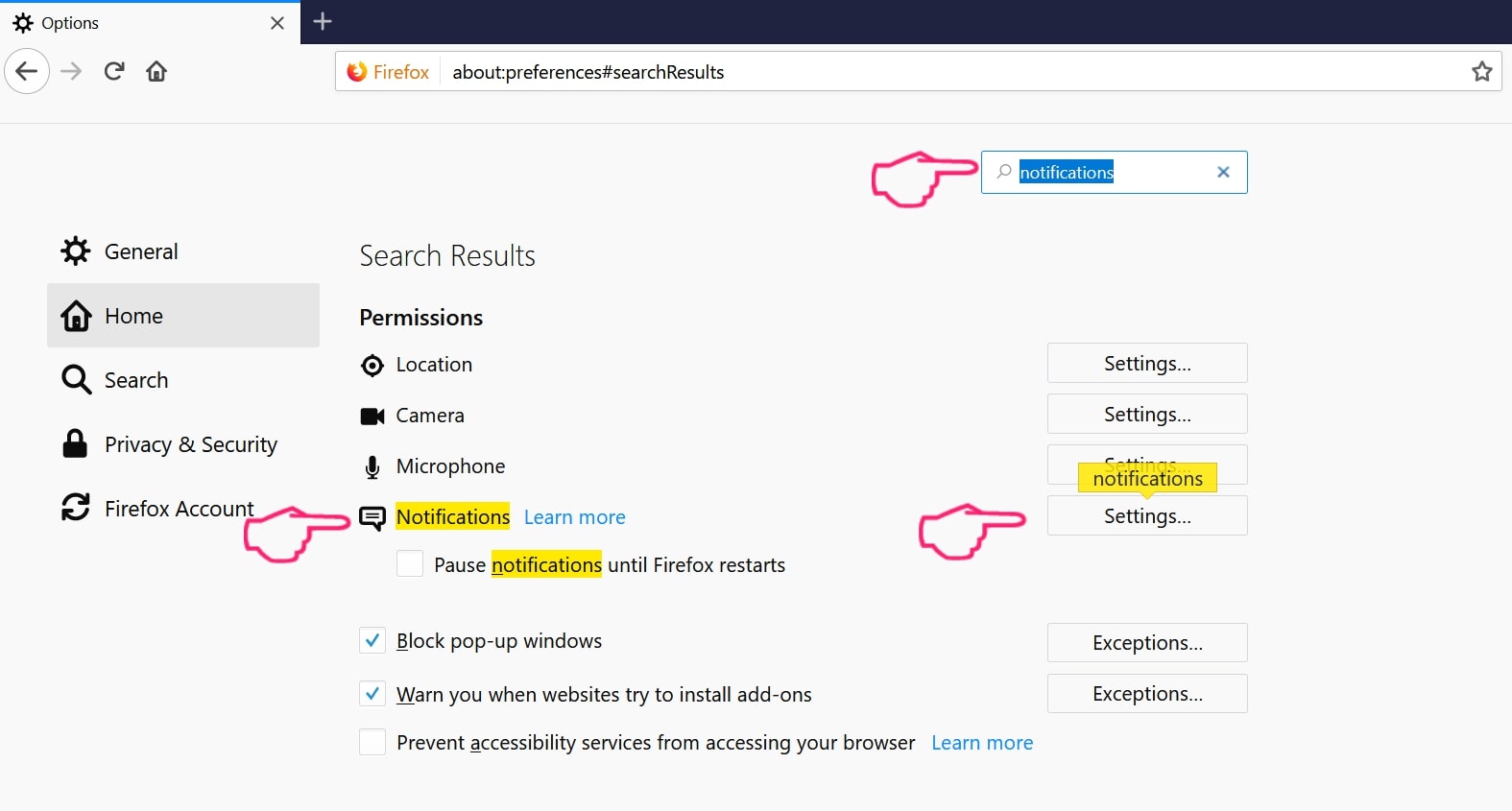
Step 2: Go to “Settings”, type “notifications” in the search bar and click "Settings":
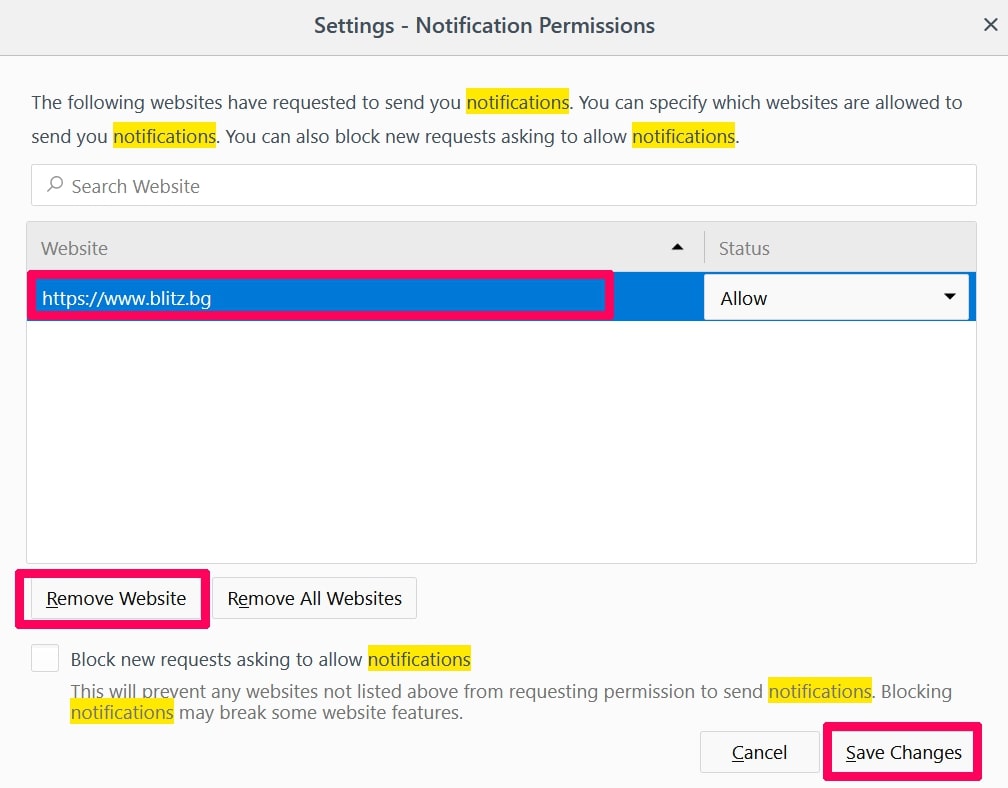
Step 3: Click “Remove” on any site you wish notifications gone and click “Save Changes”
Stop Push Notifications on Opera
Step 1: In Opera, press ALT+P to go to Settings.
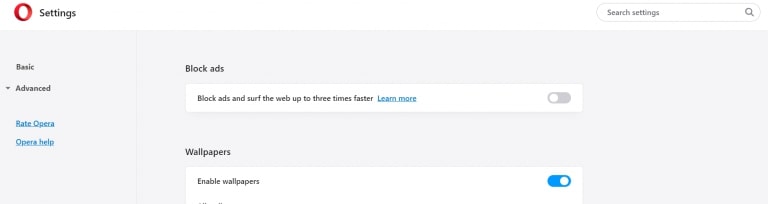
Step 2: In Setting search, type “Content” to go to Content Settings.
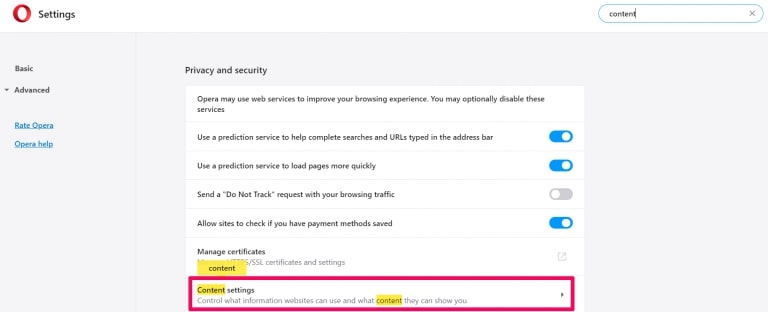
Step 3: Open Notifications:
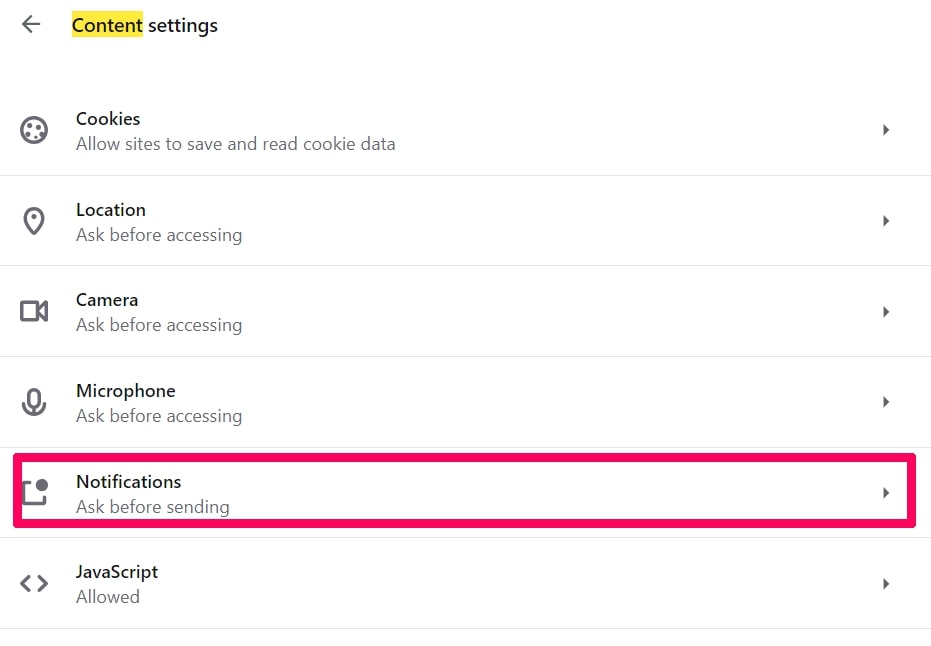
Step 4: Do the same as you did with Google Chrome (explained below):
Eliminate Push Notifications on Safari
Step 1: Open Safari Preferences.
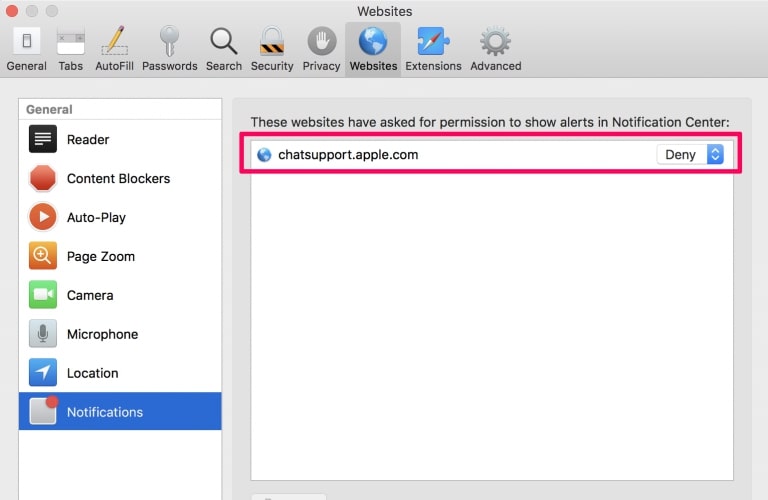
Step 2: Choose the domain from where you like push pop-ups gone and change to "Deny" from "Allow".
-FAQ
What Is ?
The threat is adware or browser redirect virus.
It may slow your computer down significantly and display advertisements. The main idea is for your information to likely get stolen or more ads to appear on your device.
The creators of such unwanted apps work with pay-per-click schemes to get your computer to visit risky or different types of websites that may generate them funds. This is why they do not even care what types of websites show up on the ads. This makes their unwanted software indirectly risky for your OS.
What Are the Symptoms of ?
There are several symptoms to look for when this particular threat and also unwanted apps in general are active:
Symptom #1: Your computer may become slow and have poor performance in general.
Symptom #2: You have toolbars, add-ons or extensions on your web browsers that you don't remember adding.
Symptom #3: You see all types of ads, like ad-supported search results, pop-ups and redirects to randomly appear.
Symptom #4: You see installed apps on your Mac running automatically and you do not remember installing them.
Symptom #5: You see suspicious processes running in your Task Manager.
If you see one or more of those symptoms, then security experts recommend that you check your computer for viruses.
What Types of Unwanted Programs Are There?
According to most malware researchers and cyber-security experts, the threats that can currently affect your device can be rogue antivirus software, adware, browser hijackers, clickers, fake optimizers and any forms of PUPs.
What to Do If I Have a "virus" like ?
With few simple actions. First and foremost, it is imperative that you follow these steps:
Step 1: Find a safe computer and connect it to another network, not the one that your Mac was infected in.
Step 2: Change all of your passwords, starting from your email passwords.
Step 3: Enable two-factor authentication for protection of your important accounts.
Step 4: Call your bank to change your credit card details (secret code, etc.) if you have saved your credit card for online shopping or have done online activities with your card.
Step 5: Make sure to call your ISP (Internet provider or carrier) and ask them to change your IP address.
Step 6: Change your Wi-Fi password.
Step 7: (Optional): Make sure to scan all of the devices connected to your network for viruses and repeat these steps for them if they are affected.
Step 8: Install anti-malware software with real-time protection on every device you have.
Step 9: Try not to download software from sites you know nothing about and stay away from low-reputation websites in general.
If you follow these recommendations, your network and all devices will become significantly more secure against any threats or information invasive software and be virus free and protected in the future too.
How Does Work?
Once installed, can collect data using trackers. This data is about your web browsing habits, such as the websites you visit and the search terms you use. It is then used to target you with ads or to sell your information to third parties.
can also download other malicious software onto your computer, such as viruses and spyware, which can be used to steal your personal information and show risky ads, that may redirect to virus sites or scams.
Is Malware?
The truth is that PUPs (adware, browser hijackers) are not viruses, but may be just as dangerous since they may show you and redirect you to malware websites and scam pages.
Many security experts classify potentially unwanted programs as malware. This is because of the unwanted effects that PUPs can cause, such as displaying intrusive ads and collecting user data without the user’s knowledge or consent.
About the Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific, adware-related problem, and restore your browser and computer system.
How did we conduct the research on ?
Please note that our research is based on independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware, adware, and browser hijacker definitions.
Furthermore, the research behind the threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand this online threat, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.





 Fix registry entries created by on your PC.
Fix registry entries created by on your PC.
 1. Install SpyHunter to scan for and remove .
1. Install SpyHunter to scan for and remove .
 1. For Windows 7,XP and Vista.
1. For Windows 7,XP and Vista. 2. For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
2. For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.