 This article has been created to explain what exactly is the VPNFilter malware and how to secure your network against this massive infection by protecting your router as well as protecting your computers.
This article has been created to explain what exactly is the VPNFilter malware and how to secure your network against this massive infection by protecting your router as well as protecting your computers.
A new malware, going by the name of VPNFilter has reportedly infected over 500 thousand router devices across most widely used brands such as Linksys, MikroTik, NETGEAR as well as TP-Link, mostly used in homes and offices. The cyber-sec researchers at Cisco Talos have reported that the threat is real and it is live, even thought the infected devices are under investigation at the moment. The malware reportedly has something to do with the BlackEnergy malware, which targeted multiple devices in Ukraine and Industrial Control Systems in the U.S.. If you want to learn more about the VPNFilter malware and learn how you can remove it from your network plus protect your network, we advise that you read this article.

Threat Summary
| Name | VPNFilter |
| Type | IoT Trojan (Infostealer) and Botnet Infection |
| Short Description | Aims to infect complete networks and steal critical network information plus relay it to third-party hosts. |
| Symptoms | Your computer and web browser may lead you to phishing sites via which the crooks may collect important information. |
| Distribution Method | Via worms, botnet and other automated infection methods. |
| Detection Tool |
See If Your System Has Been Affected by malware
Download
Malware Removal Tool
|
User Experience | Join Our Forum to Discuss VPNFilter. |

VPNFilter Malware – How Does It Infect
The VPNFIlter malware uses a very complicated two-stage infection method, the result of which is your computer to become a victim of intelligence gathering and even desctruction operation.
Stage 1 of Infection (Loader)
The first stage of this virus involves a reboot on your router or hub. Since the VPNFilter malware targets primarily routers as well as other internet-of-things devices, just like the Mirai malware it may come as a result of an automated botnet attack that is unleased as a result of central servers being compromised successufully. The infection however is conduced at the aid of an exploit that triggers a reboot of the smart device. The main goal of this Stage 1 is to gain partial control and enable the deployment of the Stage 2 after the reboot process has finished. The phases of Stage 1 are the following:
1.Pulls down a photo from Photobucket.
2.Exploits are triggered and metadata is used in order to call out IP addresses.
3.Connects to the Stage 2 server and downloads the Stage 2 malware after which automatically executes it.
The assoicated URLs with the first stage of infection are reported by researchers to be the libraries of fake photobucket users:
→ photobucket[.]com/user/nikkireed11/library
photobucket[.]com/user/kmila302/library
photobucket[.]com/user/lisabraun87/library
photobucket[.]com/user/eva_green1/library
photobucket[.]com/user/monicabelci4/library
photobucket[.]com/user/katyperry45/library
photobucket[.]com/user/saragray1/library
photobucket[.]com/user/millerfred/library
photobucket[.]com/user/jeniferaniston1/library
photobucket[.]com/user/amandaseyfried1/library
photobucket[.]com/user/suwe8/library
photobucket[.]com/user/bob7301/library
UPDATE JULY 2018: The security reports indicate that the VPNFilter vulnerability affects the following vendors and models:
- ASUS — RT-AC66U, RT-N10, RT-N10E, RT-N10U, RT-N56U, and RT-N66U.
- D-Link — ASUS — RT-AC66U, RT-N10, RT-N10E, RT-N10U, RT-N56U, and RT-N66U.
- Huawei — HG8245.
- Linksys — E1200, E2500, E3000 E3200, E4200, RV082, and WRVS4400N.
- MikroTik — CCR1009, CCR1016, CCR1036, CCR1072, CRS109, CRS112, CRS125, RB411, RB450, RB750, RB911, RB921, RB941, RB951, RB952, RB960, RB962, RB1100, RB1200, RB2011, RB3011, RB Groove, RB Omnitik, and STX5.
- Netgear — DG834, DGN1000, DGN2200, DGN3500, FVS318N, MBRN3000, R6400, R7000, R8000, WNR1000, WNR2000, WNR2200, WNR4000, WNDR3700, WNDR4000, WNDR4300, WNDR4300-TN, and UTM50.
- QNAP — TS251, TS439 Pro, and other QNAP NAS devices running QTS software.
- TP-LINK — R600VPN, TL-WR741ND, and TL-WR841N.
- Ubiquiti — NSM2 and PBE M5.
- ZTE — ZXHN H108N.
The analysts have also uncovered the specific vulnerabilities used for the mentioned devices:
QNAP FTP Service (Authentication Bypass Vulnerability CVE-2015-7261), D-Link DIR-300 (Reaper Remote Code Execution CVE-2011-4723),
ASUS RT-AC66U, RT-N66U (Remote Code Execution CVE-2014-9583),
Linksys E2500 (Reaper OS Command Injection CVE-2013-2678), Vulnerable UPnP Service (e.g. Netgear/TP-Link/D-Link) (Buffer Overflow Vulnerability CVE-2013-0229, Stack Overflow Vulnerability
CVE-2013-0230, Stack Overflow Vulnerability CVE-2012-5958, Stack Overflow VulnerabilityCVE-2012-5959), QNAP QTS before 4.2.4 Build 20170313 (Remote Code Execution CVE-2017-6361),
ASUS RT-AC* and RT-N* (Router JSONP Info Leak CVE-2017-8877), Netgear R6400, R7000, R8000 (Router Password Disclosure CVE-2017-5521),
D-Link DIR-300 (Reaper Router Remote Code Execution),
Netgear WNR2000 (Router Password Disclosure), Netgear R6400, R7000 (Remote Code Execution CVE-2016-6277),
ASUS RT-N66U (Router Session Stealing CVE-2017-6549), Linksys E4200 (OS Command Injection CVE-2013-2679),
Netgear WNR1000 (Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, Router Password Disclosure),
TP-Link TL-WR841N (Unauthenticated Router Access Vulnerability).
Stage 2 of Infection
Once the second stage of infection Is triggered the actual capabilities of the VPNFilter malware are unleashed. They include the usage of the virus in the following activities:
- Connects to a C&C server.
- Connects to a Stage 3 Server.
- Executes Tor, P.S. and other plugins.
- Performs the malicious activities of the malware, which include data collection, command execution, file theft, device management.
- Able to perform self-destructions activity.
The associated IP addresses with the second stage of infection are reported by the researchers to be the following:
→ 91.121.109[.]209
217.12.202[.]40
94.242.222[.]68
82.118.242[.]124
46.151.209[.]33
217.79.179[.]14
91.214.203[.]144
95.211.198[.]231
195.154.180[.]60
5.149.250[.]54
91.200.13[.]76
94.185.80[.]82
62.210.180[.]229
In addition to those two stages, the cyber-security researchers at Cisco Talos have also reported of a 3rd Stage Server in play, the purpose of which so far remains to be unknown. From what it seems, this malware is already shaping up to be a very sophisticated infection and it is not to be underestimated as it’s infection rate may rise.

VPNFilter Botnet Malware – Malicious Activities
The main activities which have been associated with the VPNFilter malware have been reported to be divided In two parts by malware researchers, the first set of which are preoperational activities that gather information before actually performing the end goal activities. In addition to this, the Cisco Talos experts have also reported similarities in the VPNFilter malware and the previously reported BlackEnergy IoT botnet, which was used to target organizations and governments in the U.S. and Ukraine. The malware used the same saparate stage type of infection modules which is a sign it may be used by the same people behind the BlackEnergy infection.
The activity of the VPNFilter malware begins with it’s preparational stage which firstly checks the outbound and inbound TCP/IPv4 traffic. It does that check in order to understand that the destination IP address matches what it has found when the listener is active. If this is so, the virus procedes to make sure that the packed has eight or more bytes and scanss the data for specific bytes afterwards. As soon as this is done, the virus initiates a call process to a newly received IP address which was basically those bytes it checked and this results in it’s stage 2 to start.
The the second stage, this malware does a lot more than the first one, which is basically, VPNFilter’s loader. The stage includes the creating of the following diredctory in the victim’s device:
→ /var/run/vpnfilterm (m is for modules directory)
/var/run/vpnfilterw (w is for working directory)
Then, the malware starts to kill different modules and overwrite data in them, one of those modules is:
→ /dev/mtdblock0 (It’s first 5,000 bytes are overwritten with zeros and the device is rebooted)
After this is done, the VPNFilter malware executes a shell command and then sets up It’s Tor configuration which in it’s turn ensures that the anonymity is enabled. AS soon as this is done, the virus copies a file from it’s client directly to the server. VPNFilter does not stop there however – the botner malware goeas as far as to set two types of URLs:
- Set a URL in the configuration panel of the current configuration of the device.
- Set a custom URL in the current proxy configuration.
When the virus has set a URL, it proceeds towards tinkering with the port settings, by changing the default proxy port and setting a delay between the main loop executions.
After doing all these nefarious actions, the malware reboots the IoT device for longer than normal and then downloads a URL after which saves it into a file. In addition to all of this, it can stop the infection process mid-infection or possibly delay it.
The malware then proceeds to it’s third stage which has not yet been disclosed by the researchers as they may still be in the process of analyzing it, but it is believed that the third-stage is related with the malware’s purpose, which is to:
- Steal different information from each device in the network.
- Steal network data.
- Obtain passwords and communication data.
- Obtain keystrokes and other data.
- Change parameters on the IoT device or change parameters on the end devices in the network in order to make them vulnerable for malware infections.
The devices that have so far been compromised can be found in the following list, which the Cisco Talos researchers have so far gathered to be among the 100% infected ones:
Besides these devices, the researchers have also reported TP-Link, Netgear, Linksys and other custom ISP routers and IoT devices to also be among the 500,000 infected as they believe that the malware may be more advanced than your average botnet in the wild. A dangerous characteristic of the VPNFilter malware is its ability to monitor Modbus SCADA protocols. This is one of the most popular serial communications protocols that is used in the industry for automated IoT devices. The protocol can be implemented using various connection types and remains one of the most versatile ways to control devices.

How to Remove the VPNFilter Malware and Protect Your Network from It
When we talk about malware on the level of VPNFilter, a simple cleanup and reset of your router won’t cut it for the removal, since the malware may be a complicated threat which can deeply embed objects in the firmware of your router as explained In the “Activity” paragraphs above. This is why, the first step is to check if your network has been compromised by this malware. Cisco researchers strongly advise to do that by following these steps:
Step 1: Create a new Host Group with the name “VPNFilter C2” and make it to be under the Outside Hosts via Java UI.
Step 2: Once done, validate that the group does not communicate at the moment by checking the “conversations” of the group itself on your device.
Step 3: If there is no active traffic, researchers advise network administators to create a trip wire type of alarm which notifies as soon as there is traffic in the host group via creating an event and selecting the host in the web user interface.
Besides this, in order to make sure that your network is safe as well as private, we do recommend that you choose a more secure router device, but keep in mind that a device is secure as it’s software, so you should make sure to also set up a VPN and in addition to this to talk to your ISP in order to make sure that the connection is secured along the way too. Below, you can find a list of the most secure routers and the best NAS devices among which you can choose the one that is appropriate for your network:
→Related:The Most Secure NAS Devices In 2017
→Related:Which Are the Most Secure Routers in 2017
And for end device security we would advise that you equip your organization with custom configured devices and keep the configuration information disclosed even to the employees of the company, since this minimalizes the risk of usage.
And as always, security researchers advise to secure the end-devices of your organization as well, since they often become the “patient zero” of such infections. Here are some tips you can follow to secure end devices from malware:
Step 1: Install an advanced anti-malware softwareon each device. It comes standard with active real-time protection and frequent updates.
Spy Hunter scanner will only detect the threat. If you want the threat to be automatically removed, you need to purchase the full version of the anti-malware tool.Find Out More About SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool / How to Uninstall SpyHunter
Step 2: Run programs in sandbox environment. It prevents any executed type of malware to run effectively on your computer by isolating it within an encrypted layer which acts like a wall of protection.
Step 3: Make sure that the users in your network are aware of different Router security risks which may become from weaknesses to a real cluster of headaches.
Step 4: Make sure to educate your employees on how to safely store your files to protect them from malware.
Preparation before removing VPNFilter.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
Step 1: Scan for VPNFilter with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by VPNFilter on your computer.
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by VPNFilter there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
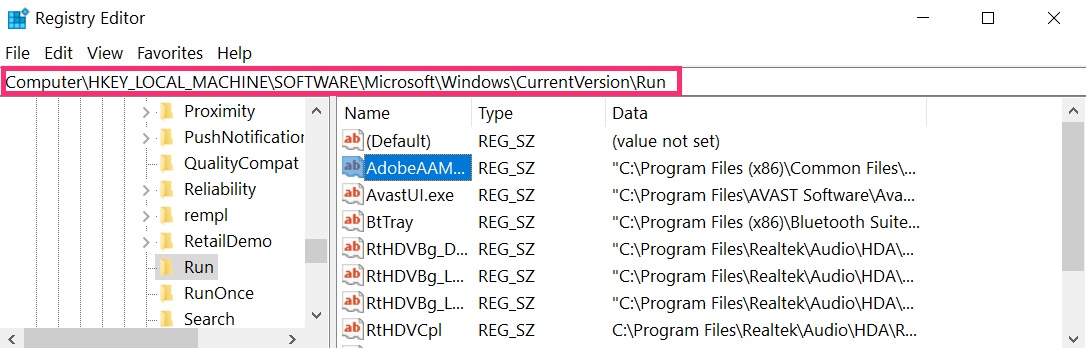
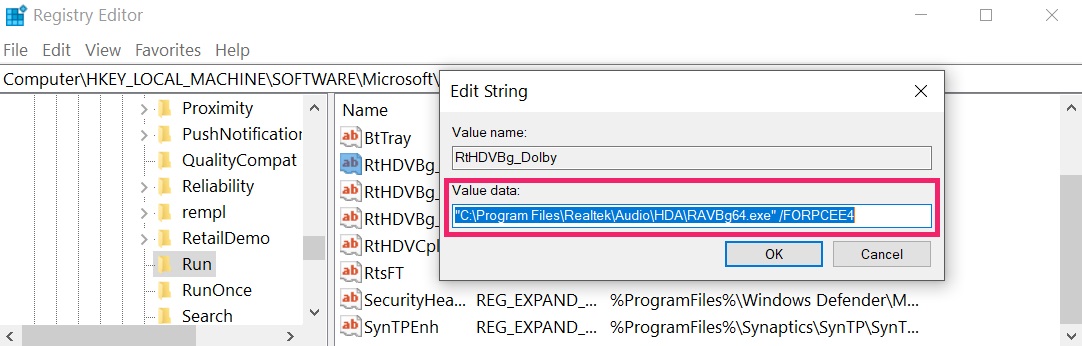 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by VPNFilter on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
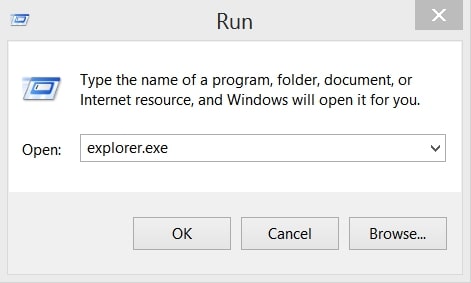
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
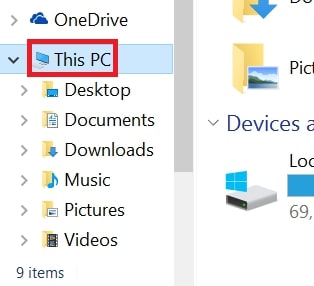
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
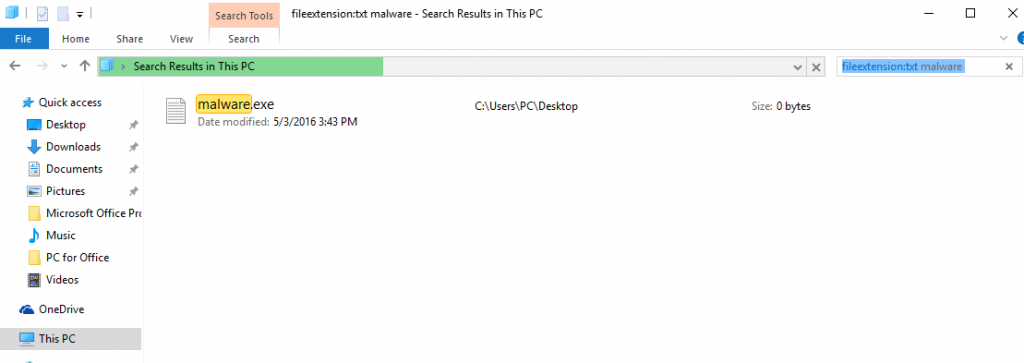
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
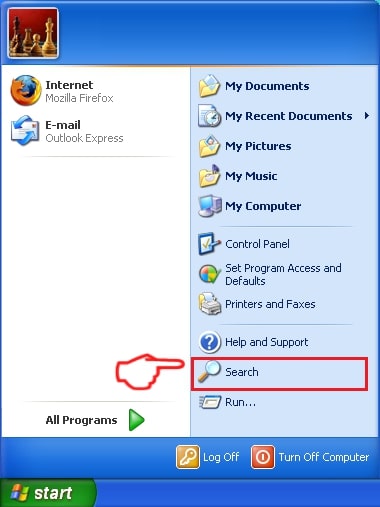
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
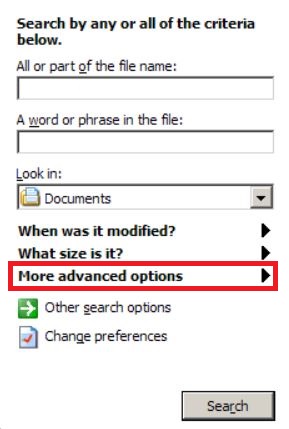
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
VPNFilter FAQ
What Does VPNFilter Trojan Do?
The VPNFilter Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like VPNFilter, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can VPNFilter Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can VPNFilter Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the VPNFilter Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this VPNFilter how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on VPNFilter?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the VPNFilter threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.




If I wanted to see if my network is affected could I run a Wireshark capture on my gateway and just look for the stage two public ip’s?