This article will help you understand which are the most used malicious files to infect Windows computers to date and will give you tips to increase your malware protection.
Antivirus institutes, like AV-TEST register approximately 400 000 new malware software per day. And these are new samples, but if we combine data from the already discovered malware, the situation becomes quite massive and makes for an extremely dangerous landscape. This is why, users should be aware of the methods used to infect their computers, without them noticing and how to protect themselves against such malicious practices.

These methods vary, but there is one particular bottleneck which is their weakness – they all use the same Windows-based file types for their infection to succeed. In this article, we will show you the most often used file types to infect computers with malware while remaining undetected.
Which Are the Most Popular File Extensions Used to Infect?
Or which type of files are vulnerable to computer viruses? There are many executable types of files, scripts, program files that can be manipulated, and even malicious shortcuts. The most chosen ones by the cyber-criminals however are the ones that are particularly easier to obfuscate from antivirus programs and load the payload of their malware while remaining undetected.
.EXE Executable Files

Are EXE files dangerous? Being the most often associated files with malware, the executable files are notorious for being spread as malicious e-mail attachments. However, since this method has become more and more outdated since most e-mail providers block these attachments, the executable files are often spread as fake setups, updates, or other types of seemingly legitimate programs with the malicious code built-in. They are also archived to further avoid antivirus detection. However, the executable files are crucial when it comes to configuring what activities the malware will do. This is because they have numerous functions that perform the actual malicious activities after the infection has been completed. This is why they are associated with the primary payload of different malware more often than being used as an actual infection file. But nonetheless, do not count that an .exe may not be malicious, just because of that.
.DOC, .DOCX, .DOCM and Other Microsoft Office Files

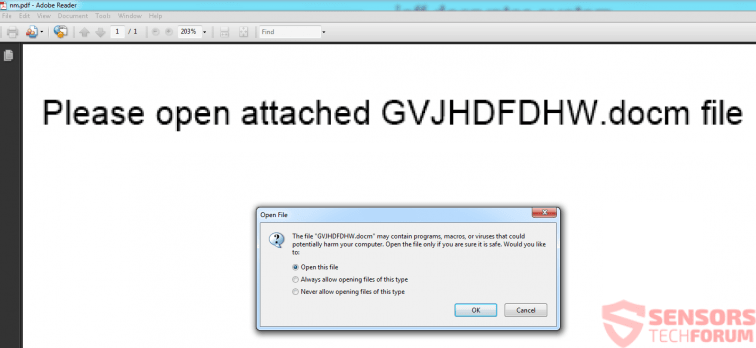
This particular type of files have lately become a very effective method to infect victims. The primary reason for that is the usage of malicious macros that are embedded within the documents themselves. This makes slipping past any antivirus software and e-mail attachment protection software like a walk in the park, if the right obfuscated code is used. However, the tricky part of infecting victims via these methods is to get them to click on the “Enable Content” button and the cyber-crooks, like the ones behind the ZeuS Trojan, usually use instructions within the document, like the image below:
.HTA, .HTML and .HTM Application Files

These particular types of files have lately become notorious to be associated with multiple ransomware variants. The most famous of them is called Cerber Ransomware and this virus has been classified as the most effective malware against the latest Windows 10 OS, primarily because of the exploit kit associated with the infection method via those files. The files themselves are HTML web applications that usually lead to a foreign host, from which the payload of the malware is downloaded onto the computer of the victim.
.JS and .JAR Files


These types of malicious files are notorious for containing malicious JavaScript code which causes the actual infection. Usually, JavaScript infections can also be caused by automatically downloading those files without knowing as a result of having clicked on a malicious URL. The .JS files are used for quite some time now, but gained popularity recently is associated with ransomware viruses, like Locky Ransomware, which so far remains as the cryptovirus that has inflicted the most damage on computer systems for all times.
.VBS and .VB Script Files

The Windows Visual Basic script files are particularly dangerous because they have not only been associated with one or two viruses, but most of the big malware names in the past few years. Starting with both Cerber and Locky ransomware using .vbs files in their e-mail spam campaign, the .vbs files also saw some action in relation to notorious Trojan infections. The primary choice of these particular files to infect with is the speed of infection and the skills of the hacker to create code in the Visual Basic environment. VBS is also a type of file that can be easily obfuscated and can pass as a legitimate e-mail message if it is in an archive.
.PDF Adobe Reader Files

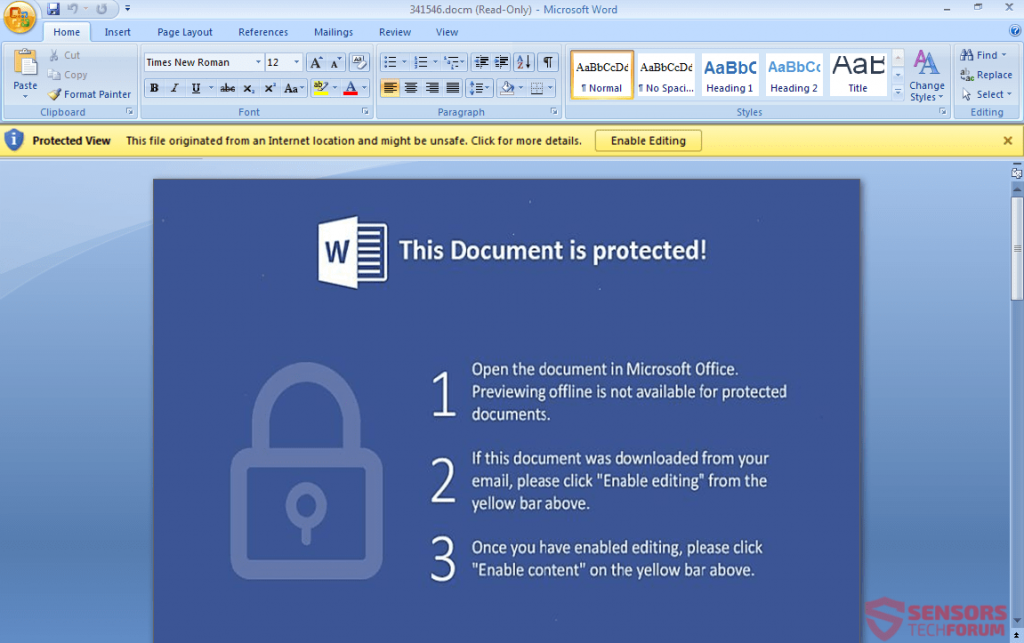
Cyber-criminals have the tendency to avoid associating .PDF files with scripts and codes, primarily because they crash very often. However, how there seems to be a method that has become very notorious and widespread. It includes sending .PDF files as spam message attachments and these .PDF files conceal in them the malicious documents that actually contain malicious macros. This “document inception” strategy so far has remained effective against inexperienced victims and is the main factor responsible for spreading a threat, known as Jaff Ransomware.
What actually happens is that the victim opens the malicious .PDF file and it has the Microsoft Word document embedded within it. However, like the pictures above show, the documents prompt the victim to extract the malicious .docm file, which in turn causes the infection. The very devious tactic, especially dangerous for the fast clickers.
.SFX Archive Files

When we discuss malicious files and malware infection, it important to mention the .SFX – the Self-Extracting archive types of files that were also used by major malware families to infect computers. The way they work is very similar to set up programs of Windows, primarily because these file types in the particular archive the malicious payload of the virus and when they are executed, they can be manipulated to extract the payload automatically and quietly in the background. The more sophisticated .SFX files are even programmed by their code or the payload files they have extracted to be self-deleted after the operation is complete.
.BAT Batch Files

Even though these command-containing files are not met so often, they are one of the most widespread ones ever to be used, primarily because of the Windows Command Prompt and its impact on the computer. If properly manipulated, the batch files may insert administrative commands that can do a variety of malicious activities, varying from deleting files on your computer to connecting to third-party hosts and downloading malware directly on your computer.
.DLL Files

The DLL files are basically known as Dynamic Link Library files and they are often system files of Microsoft, but malware finds ways to slither its own, compromised version with malicious functions in the DLL file itself. This ultimately results in the malware starting to perform various different types of malicious activities, like delete Windows files, execute files as an administrator on the compromised computer, and also perform different types of modifications in the Windows Registry Editor. This may result in DLL error messages appearing on your PC, but most viruses go through great extents to prevent those errors from being seen by the victim.
.TMP Temporary Files

TMP types of files are temporary files that hold data on your computer while you are using a program. In the malware world, the TMP files are basically used to hold information that is complementary to the infection itself. This information is related to the activities that the malware will perform and often used with the main purpose of allowing the malware to collect information which is then relayed to the cyber-criminals by the file itself being copied and sent without you even noticing. Removing the .TMP file may damage the activity of the malware, but most complicated viruses would not give the user permission to do that or create a backup copy that is used in a parallel way.
.PY Python Files

These types of files are most commonly used when ransomware viruses are in play, meaning that they are written in Python and their main goal may be to be modules that are used to encrypt the files on your computer(documents, videos, images) and make them unable to be opened again. The encrypted files of this ransomware virus are created with the aid of such python scrips which, provided the software, may use them for the file encryption. In addition to this, some malware detected to be coded entirely in the Python language, meaning that the virus uses it for every aspect of its activity.
Custom Types of Files
These types of files may be created exclusively for the virus at hand and are used for different purposes but their main goal is to help various program viruses that infect files with an extension for example to perform various different types of activities on the computer of the victim. The files may feature custom extensions which can be absolutely anything for example .virus .fun, etc.
Other vivid examples of virus extensions are all extensions used by data locker ransomware. The most popular ransomware at the moment dubbed Stop DJVU Ransomware release new such file extensions almost every week. Here is a ransomware extension list related to the nasty infection:
.shadow, .djvu, .djvur, .djvuu, .udjvu, .uudjvu, .djvuq, .djvus, .djvur, .djvut, .pdff, .tro, .tfude, .tfudet, .tfudeq, .rumba, .adobe, .adobee, .blower, .promos, .promoz, .promorad, .promock, .promok, .promorad2, .kroput, .kroput1, .pulsar1, .kropun1, .charck, .klope, .kropun, .charcl, .doples, .luces, .luceq, .chech, .proden, .drume, .tronas, .trosak, .grovas, .grovat, .roland, .refols, .raldug, .etols, .guvara, .browec, .norvas, .moresa, .vorasto, .hrosas, .kiratos, .todarius, .hofos, .roldat, .dutan, .sarut, .fedasot, .berost, .forasom, .fordan, .codnat, .codnat1, .bufas, .dotmap, .radman, .ferosas, .rectot, .skymap, .mogera, .rezuc, .stone, .redmat, .lanset, .davda, .poret, .pidom, .pidon, .heroset, .boston, .muslat, .gerosan, .vesad, .horon, .neras, .truke, .dalle, .lotep, .nusar, .litar, .besub, .cezor, .lokas, .godes, .budak, .vusad, .herad, .berosuce, .gehad, .gusau, .madek, .darus, .tocue, .lapoi, .todar, .dodoc, .bopador, .novasof, .ntuseg, .ndarod, .access, .format, .nelasod, .mogranos, .cosakos, .nvetud, .lotej, .kovasoh, .prandel, .zatrov, .masok, .brusaf, .londec, .krusop, .mtogas, .nasoh, .nacro, .pedro, .nuksus, .vesrato, .masodas, .cetori, .stare, .carote, .gero, .hese, .seto, .peta, .moka, .kvag, .karl, .nesa, .noos, .kuub, .reco, .bora, .reig, .tirp, .plam, .cosd, .ygkz, .cadq, .ribd, .qlkm, .coos, .wbxd, .pola
Other File Types Used by Viruses
Be advised that the viruses use a lot of different file types, otherwise considered to be legitimate in order for the malware to function properly. Some of these files may be legitimate at first, but contain malware component in them that is triggered upon execution. Such file kinds include the following:
- .INF, which is another format for text files.
- .LNK or Shortcuts that may lead to the virus.
- .SCF types of files, belonging to Windows Explorer.
- .MSI Files or MSI Installers.
- .MSP which are Patch Installers.
- .GADGET File Type or Windows Desktop Gadgets.
- .PS1, .PS1XML, .PS2, .PS2XML, .PSC1, .PSC2 also known as Shell Scripts.
What Other Malware Files You May Encounter
Despite the fact that these files are not so often encountered, they can still be manipulated into infecting your computer and still infect computers presently. These are the other potentially malicious objects, you should scan before opening:
Programs:
.MSI Files – installer types of files which are used to situate different programs on the computer. They are often used as Setups for different programs, and can also slither the malware also in the form of a setup of a program you are trying to install.
.MSP Files – files that are also the installer type, however, they are more oriented on patching currently installed software, meaning that the malware here may pose as a fake patch uploaded online.
.COM Files – similar to the .BAT files, these types of files are also used to insert commands. They were very popular back when Windows XP and older systems were widely used to spread old-school worms, viruses, and other malicious software. However, they may still be used for malicious activity and infection.
.GADGET Files – these particular malicious files are used primarily with the Windows Desktop Gadget. So if you are using a Windows version that has those floating Gadgets on your desktop, you should look out for those files. When Windows Vista firstly introduced gadgets, many exploits led to the infection of unpatched systems with Trojans and other viruses.
Script Files:
.CMD Files – also a Windows Command Prompt file that can insert malicious commands on your computer.
.VBE Files – Encrypted VBS files.
.JSE Files – Encrypted JavaScript files.
.PS1, .PS1XML, .PS2, .PS2XML, .PSC1, .PSC2 – The Windows PowerShell script files that when programmed can automatically run direct PowerShell commands on a Windows system, as long as they are ran with Administrative privileges. Particularly dangerous.
Malicious Shortcut Files:
.LNK Shortcuts – A shortcut used usually to link a program contained locally on the computer. However, with the right software and functions, it can perform multiple malicious activities on the infected computer, like delete important files.
.INF Files – These text files are usually not of a dangerous character, but they may also be utilized to launch an app. And if this app is malicious, this makes them dangerous as well.
.SCF Files – These types of files are used to interfere with Windows Explorer and can be modified to perform actions on Explorer that can ultimately lead to infection. But the actions can also be post-infection as well.
Conclusion, Prevention and Protection
It is one thing to know what types of files could ultimately lead to infection on your computer, but it is a whole different ball game to learn how to protect yourself. Since the malware scene is very dynamic and changes on a daily basis, there may be infections for which you still may be unprepared. This is why we have decided to create those general tips to help increase your protection and malware awareness significantly:
Tip 1: Make sure to install the appropriate protection software.
Tip 2: Learn how to safely store your important files and hence protect them from file encryptors or other malware.
Tip 3: Learn how to protect your computer from malicious e-mails.
Tip 4: Always make sure you scan a downloaded file. For archives, you can use the service Zip-e-Zip and for various file types and web links that you believe are malicious, you can use VirusTotal online scanner. Both services are completely free.
Tip 5: If you are ok with it, use Sandboxing, it is a very effective method to isolate malware within encrypted sandbox code, even if you do not have the proper protection. A good program to start with is Sandboxie.
Preparation before removing File.
Before starting the actual removal process, we recommend that you do the following preparation steps.
- Make sure you have these instructions always open and in front of your eyes.
- Do a backup of all of your files, even if they could be damaged. You should back up your data with a cloud backup solution and insure your files against any type of loss, even from the most severe threats.
- Be patient as this could take a while.
- Scan for Malware
- Fix Registries
- Remove Virus Files
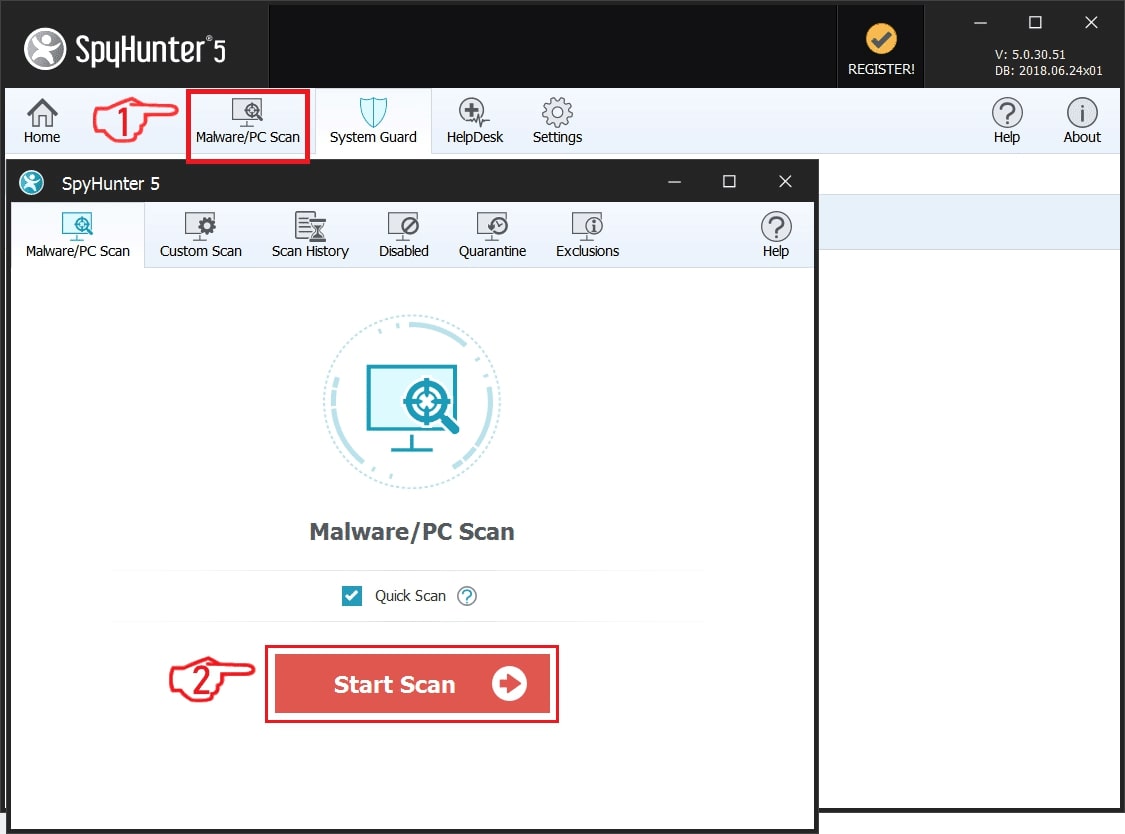
Step 1: Scan for File with SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
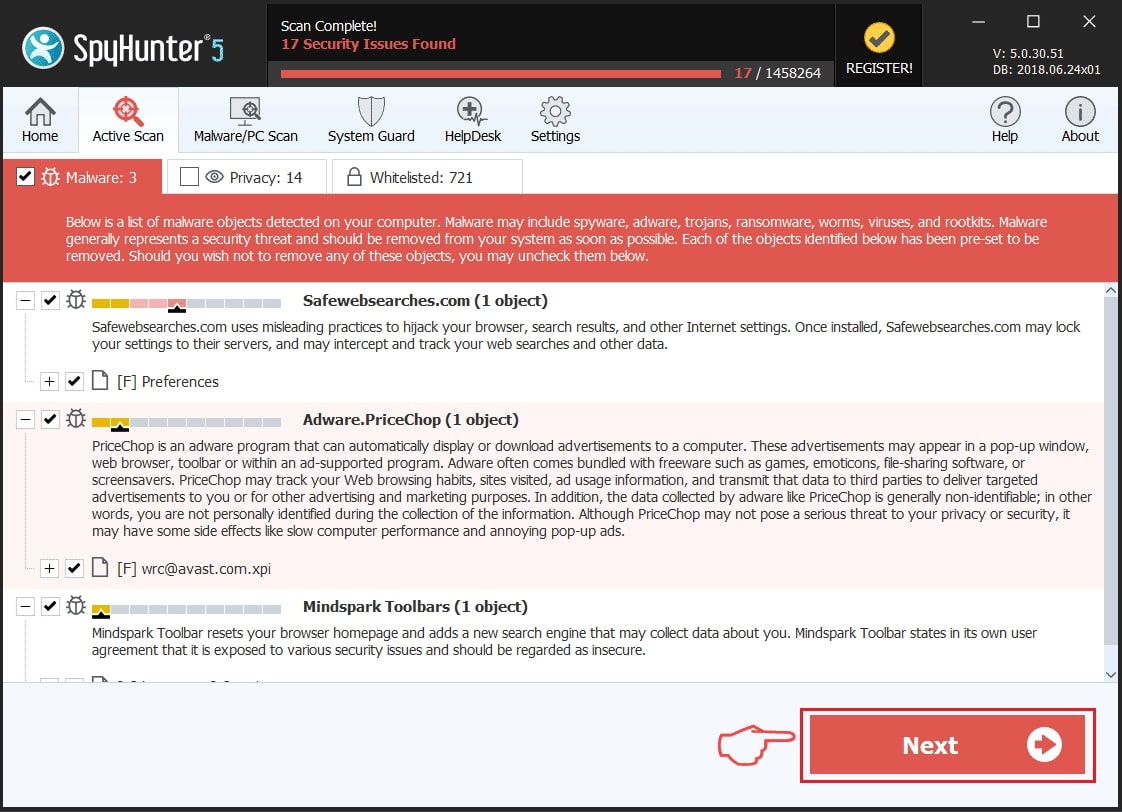
Step 2: Clean any registries, created by File on your computer.
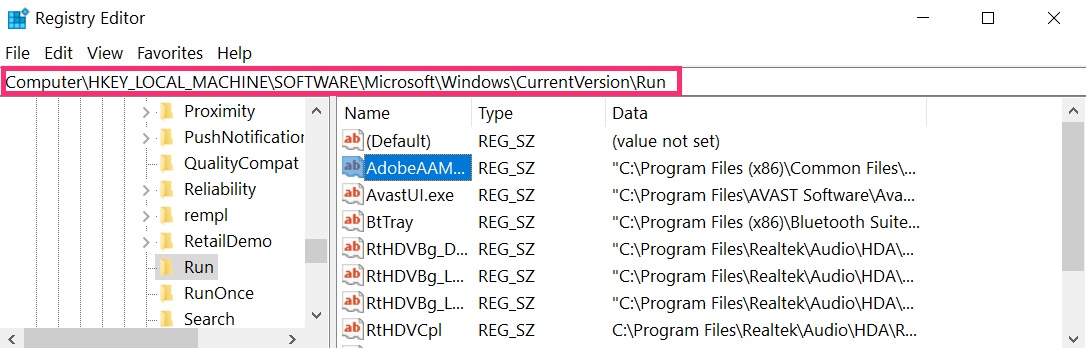
The usually targeted registries of Windows machines are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
You can access them by opening the Windows registry editor and deleting any values, created by File there. This can happen by following the steps underneath:
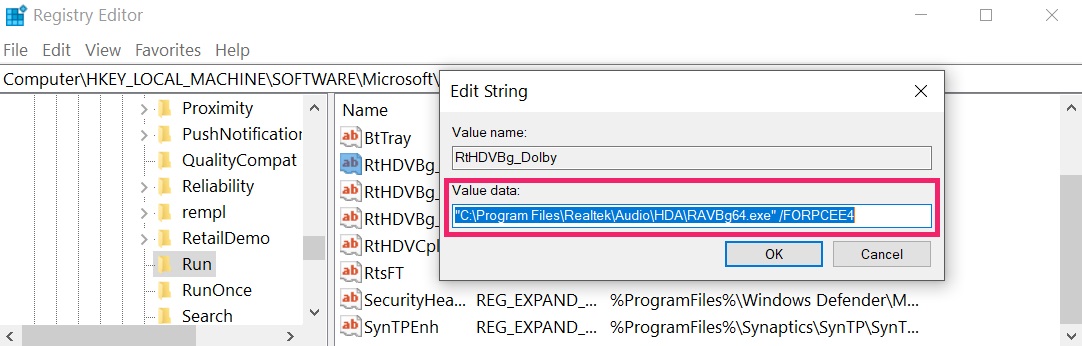 Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.
Tip: To find a virus-created value, you can right-click on it and click "Modify" to see which file it is set to run. If this is the virus file location, remove the value.Step 3: Find virus files created by File on your PC.
1.For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
For Newer Windows Operating Systems
1: On your keyboard press + R and write explorer.exe in the Run text box and then click on the Ok button.
2: Click on your PC from the quick access bar. This is usually an icon with a monitor and its name is either “My Computer”, “My PC” or “This PC” or whatever you have named it.
3: Navigate to the search box in the top-right of your PC's screen and type “fileextension:” and after which type the file extension. If you are looking for malicious executables, an example may be "fileextension:exe". After doing that, leave a space and type the file name you believe the malware has created. Here is how it may appear if your file has been found:
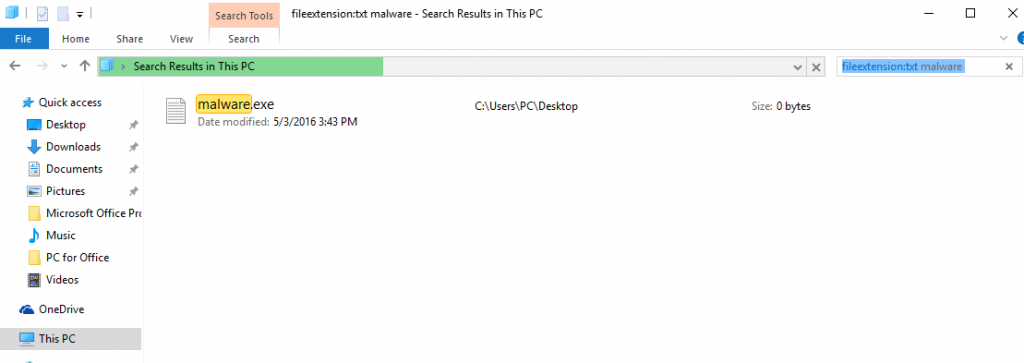
N.B. We recommend to wait for the green loading bar in the navigation box to fill up in case the PC is looking for the file and hasn't found it yet.
2.For Windows XP, Vista, and 7.
For Older Windows Operating Systems
In older Windows OS's the conventional approach should be the effective one:
1: Click on the Start Menu icon (usually on your bottom-left) and then choose the Search preference.
2: After the search window appears, choose More Advanced Options from the search assistant box. Another way is by clicking on All Files and Folders.
3: After that type the name of the file you are looking for and click on the Search button. This might take some time after which results will appear. If you have found the malicious file, you may copy or open its location by right-clicking on it.
Now you should be able to discover any file on Windows as long as it is on your hard drive and is not concealed via special software.
File FAQ
What Does File Trojan Do?
The File Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. It can be used to steal sensitive data, gain control over a system, or launch other malicious activities.
Can Trojans Steal Passwords?
Yes, Trojans, like File, can steal passwords. These malicious programs are designed to gain access to a user's computer, spy on victims and steal sensitive information such as banking details and passwords.
Can File Trojan Hide Itself?
Yes, it can. A Trojan can use various techniques to mask itself, including rootkits, encryption, and obfuscation, to hide from security scanners and evade detection.
Can a Trojan be Removed by Factory Reset?
Yes, a Trojan can be removed by factory resetting your device. This is because it will restore the device to its original state, eliminating any malicious software that may have been installed. Bear in mind that there are more sophisticated Trojans that leave backdoors and reinfect even after a factory reset.
Can File Trojan Infect WiFi?
Yes, it is possible for a Trojan to infect WiFi networks. When a user connects to the infected network, the Trojan can spread to other connected devices and can access sensitive information on the network.
Can Trojans Be Deleted?
Yes, Trojans can be deleted. This is typically done by running a powerful anti-virus or anti-malware program that is designed to detect and remove malicious files. In some cases, manual deletion of the Trojan may also be necessary.
Can Trojans Steal Files?
Yes, Trojans can steal files if they are installed on a computer. This is done by allowing the malware author or user to gain access to the computer and then steal the files stored on it.
Which Anti-Malware Can Remove Trojans?
Anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter are capable of scanning for and removing Trojans from your computer. It is important to keep your anti-malware up to date and regularly scan your system for any malicious software.
Can Trojans Infect USB?
Yes, Trojans can infect USB devices. USB Trojans typically spread through malicious files downloaded from the internet or shared via email, allowing the hacker to gain access to a user's confidential data.
About the File Research
The content we publish on SensorsTechForum.com, this File how-to removal guide included, is the outcome of extensive research, hard work and our team’s devotion to help you remove the specific trojan problem.
How did we conduct the research on File?
Please note that our research is based on an independent investigation. We are in contact with independent security researchers, thanks to which we receive daily updates on the latest malware definitions, including the various types of trojans (backdoor, downloader, infostealer, ransom, etc.)
Furthermore, the research behind the File threat is backed with VirusTotal.
To better understand the threat posed by trojans, please refer to the following articles which provide knowledgeable details.